绘制Saleh-Valenzuela信道模型
% plot_SV_model_ct.m%MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communications with MATLAB㈢ Yong Soo Cho, Jaekwon Kim, Won Young Yang and Chung G. Kang
%?2010 John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltdclear, close all
b002=1; % Power of 1st ray of 1st cluster
N=1000 ; % Number of channels
Lam=0.0233; lambda=2.5;
Gam=7.4; gamma=4.3;
sigma_x=3; % Standard deviation of log-normal shadowing
subplot(221)
t1=0:300; p_cluster=Lam*exp(-Lam*t1); % ideal exponential pdf
h_cluster=exprnd(1/Lam,1,N); % # of random number are generated
[n_cluster x_cluster]=hist(h_cluster,25); % gets distribution
plot(t1,p_cluster,'k'), hold on
plot(x_cluster,n_cluster*p_cluster(1)/n_cluster(1),'k:');%plotting
legend('Ideal','Simulation')
title(['Distribution of Cluster Arrival Time, \Lambda=', num2str(Lam)])
xlabel('T_m-T_{m-1} [ns]'), ylabel('p(T_m|T_{m-1})')
subplot(222)
t2=0:0.01:5; p_ray=lambda*exp(-lambda*t2); % ideal exponential pdf
h_ray=exprnd(1/lambda,1,1000); % # of random number are generated
[n_ray,x_ray]=hist(h_ray,25); % gets distribution
plot(t2,p_ray,'k'), hold on
plot(x_ray,n_ray*p_ray(1)/n_ray(1),'k:'); % plotting graph
legend('Ideal','Simulation')
title(['Distribution of Ray Arrival Time, \lambda=', num2str(lambda)])
xlabel('\tau_{r,m}-\tau_{(r-1),m} [ns]')
ylabel('p(\tau_{r,m}|\tau_{(r-1),m})')
subplot(223)
[h,t,t0,np]= SV_model_ct(Lam,lambda,Gam,gamma,N,b002,sigma_x);
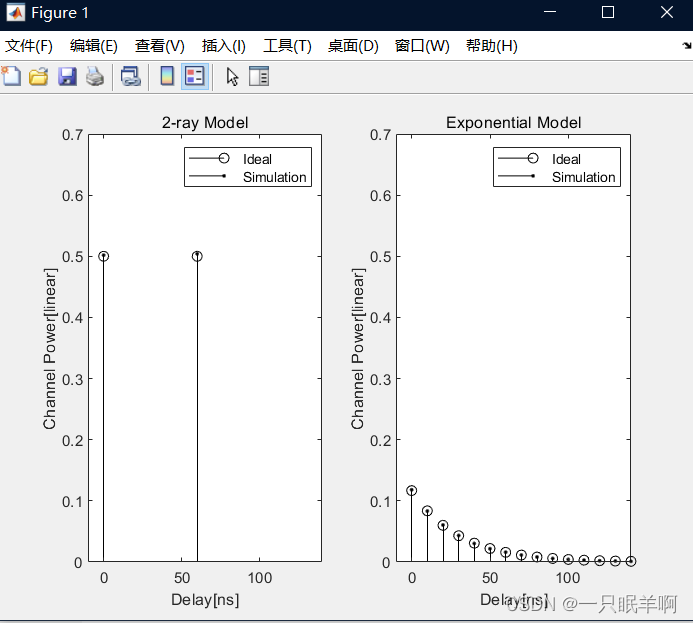
stem(t(1:np(1),1),abs(h(1:np(1),1)),'ko');
title('Generated Channel Impulse Response')
xlabel('delay[ns]'), ylabel('Magnitude')
subplot(224)
X=10.^(sigma_x*randn(1,N)./20);
[temp,x]=hist(20*log10(X),25);
plot(x,temp,'k-'), axis([-10 10 0 120])
title(['Log-normal Distribution, \sigma_X=',num2str(sigma_x),'dB'])
xlabel('20*log10(X)[dB]'), ylabel('Occasion')
function [h,t,t0,np]=SV_model_ct(Lam,lam,Gam,gam,num_ch,b002,sdi,nlos)
% S-V channel model
% Input
% Lam : Cluster arrival rate in GHz (avg # of clusters per nsec)
% lam : Ray arrival rate in GHz (avg # of rays per nsec)
% Gam : Cluster decay factor (time constant, nsec)
% gam : Ray decay factor (time constant, nsec)
% num_ch : number of random realizations to generate
% b002 : power of first ray of first cluster
% sdi : Standard deviation of log-normal shadowing
% of entire impulse response [dB]
% nlos : Flag to specify generation of Non Line Of Sight channels
% Output
% h: a matrix with num_ch columns, each column
% having a random realization of channel model (impulse response)
% t: organized as h, but holds the time instances (in nsec) of the
% paths whose signed amplitudes are stored in h
% t0: the arrival time of the first cluster for each realization
% np: the number of paths for each realization.
% Thus, the k'th realization of the channel impulse response is the
% sequence of (time,value) pairs given by(t(1:np(k),k),h(1:np(k),k))%MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communications with MATLAB㈢ Yong Soo Cho, Jaekwon Kim, Won Young Yang and Chung G. Kang
%?2010 John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltdif nargin<8, nlos=0; end % LOS environment
if nargin<7, sdi=0; end % 0dB
if nargin<6, b002=1; end % power of first ray of first cluster
h_len=1000; %There must be a better estimate of # of paths than???
for k=1:num_ch % loop over number of channelstmp_h = zeros(h_len,1); tmp_t = zeros(h_len,1);if nlos, Tc = exprnd(1/Lam); % First cluster random arrival ???else Tc = 0; % First cluster arrival occurs at time 0endt0(k) = Tc;path_ix = 0;while (Tc<10*Gam) % cluster loop % Determine Ray arrivals for each clusterTr=0; %1st ray arrival defined to be time 0 relative to clusterwhile (Tr<10*gam) % ray loopbrm2 = b002*exp(-Tc/Gam)*exp(-Tr/gam); % ray power (2.20)r = sqrt(randn^2+randn^2)*sqrt(brm2/2); % rayleigh distributed mean power pow_bklh_val=exp(j*2*pi*rand)*r; % uniform phase path_ix = path_ix+1; % row index of this raytmp_h(path_ix) = h_val; tmp_t(path_ix) = Tc+Tr; % time of arrival of this rayTr = Tr + exprnd(1/Lam); % (2.16) ???endTc = Tc + exprnd(1/lam); % (2.17) ???endnp(k)=path_ix; % number of rays (or paths) for this realization[sort_tmp_t,sort_ix] = sort(tmp_t(1:np(k))); %in ascending ordert(1:np(k),k) = sort_tmp_t;h(1:np(k),k) = tmp_h(sort_ix(1:np(k))); % now impose a log-normal shadowing on this realizationfac = 10^(sdi*randn/20)/sqrt(h(1:np(k),k)'*h(1:np(k),k));h(1:np(k),k) = h(1:np(k),k)*fac; % (2.21)
end