1.为什么需要线程和协程:
(1)使程序中的任务可以并发执行,让程序同时处理多个任务,提高程序的运行效率和响应速度
(2)线程和协程可以共享同一个进程的资源,避免多个进程之间的资源浪费
(3)可以动态调整程序的并发度,从而提高程序的可伸缩性,以便适应不同的负载情况
(4)将程序拆分为多个任务,使程序的结构更清晰,更易维护
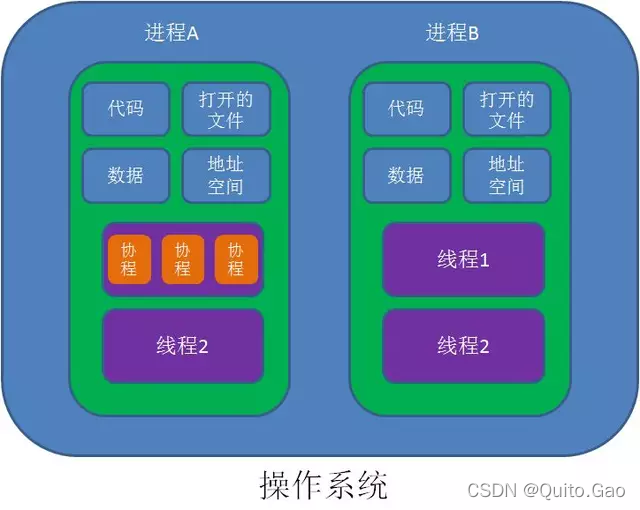
2.线程和协程的区别:线程是由操作系统调度的,而协程则是由程序自身控制的。
线程的应用:
(1) 可以将一些耗时的操作放在子线程中进行,避免阻塞主线程,提高用户体验。
(2) 线程可以用来处理一些实时性要求比较高的任务,如网络通信、I/O操作等。
协程的应用:
(1)可以用来实现游戏中的动画效果,如角色的移动、攻击等。(2)可以用来实现服务器中的异步请求处理,如异步读取数据库、异步处理请求等。
一、线程
1..Thread类的一些属性
using System;
using System.Threading;namespace ThreadTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ThreadStart childRef = new ThreadStart(ChildMethod);Thread th=new Thread(ChildMethod);th.Start();//Thread类的一些属性,属性表示的意思,可参考:https://www.runoob.com/csharp/csharp-multithreading.htmlConsole.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentContext);Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentPrincipal);Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread);//获取当前正在运行的线程Console.WriteLine(th.CurrentCulture);Console.WriteLine(th.CurrentUICulture);Console.WriteLine(th.ExecutionContext);Console.WriteLine(th.IsAlive);//获取表示当前线程执行状态的一个值Console.WriteLine(th.IsBackground);是否为后台线程Console.WriteLine(th.IsThreadPoolThread);Console.WriteLine(th.ManagedThreadId);Console.WriteLine(th.Name);//获取或设置线程的名称Console.WriteLine(th.Priority);//获取或设置线程的调度优先级Console.WriteLine(th.ThreadState);}static void ChildMethod(){Thread.Sleep(2000);//线程休眠,让线程暂停一段时间Console.WriteLine("Child");}}
} 2.创建线程
2.创建线程
using System;
using System.Threading;namespace ThreadTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//第一种方式,通过ThreadStart线程入口创建,它是一个无参无返回值的委托Thread th1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ThreadTest));//第二种方式,直接传递方法,这方式本质是与第一种方式是一样的,直接传递方法后,Thread内部会自动转成ThreadStart,因此一般情况不用担心因为重载问题而使它报错,因为TreadStart是无参无返回值的,它会自动匹配对应的方法类型,如果没有找到对应的类型就会提示报错Thread th2 = new Thread(ThreadTest1);//第三种方式,通过ParameterizedThreadStart创建,它是一个有参无返回值的委托,且只有一个参数Thread th3=new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(ThreadTest2));//第四种方式,使用Lambda表达式创建线程,可以自己定义参数的传递//至于为什么可以这样写,可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/eve612/p/14342087.htmlThread th4 = new Thread(() => ThreadTest3("Lambda","很好用"));th1.Start();//开启线程th2.Start();th3.Start();th4.Start();}static void ThreadTest(){Console.WriteLine("Thread");}static void ThreadTest1(){Console.WriteLine("Thread1");}static void ThreadTest2(object obj){Console.WriteLine("ParameterizedThreadStart");}static void ThreadTest3(string str,string info){Console.WriteLine(str+info);}}
}更多内容:https://www.cnblogs.com/eve612/p/14342087.html
3.终止线程
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ThreadTest
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("主线程开始");Thread th = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Test));th.Start();Thread.Sleep(1000);//线程休眠,阻止当前线程1s//终止进程,会引发ThreadAbortException异常//th.Abort();th.Abort("我们要终止子线程");//重载方法,终止进程的同时传递终止的异常信息Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");}static void Test(){try{Console.WriteLine("子线程开始");for(int i=0;i<10;i++){Thread.Sleep(400);Console.WriteLine(i);}}catch(ThreadAbortException e){//Console.WriteLine(e.Message);Console.WriteLine(e.ExceptionState);//打印终止的异常信息}finally{Console.WriteLine("捕获不到异常");}Console.WriteLine("子线程结束");}}
}4.线程优先级:每个线程都有一个默认优先级,优先级高的线程相对于低级别的线程更有机会被优先调度,但并非绝对的。(优先级值从高到低:Highest,AboveNormal,Normal,BelowNormal,Lowest)
using System;
using System.Threading;namespace ThreadTest
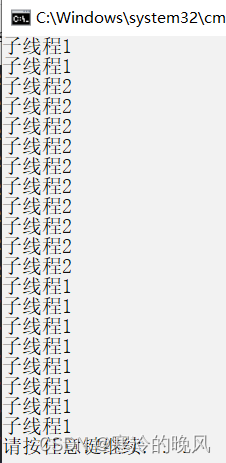
{internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Thread th1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Test));Thread th2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Test2));th2.Priority=ThreadPriority.Highest;th1.Priority=ThreadPriority.Lowest;th1.Start();th2.Start();}static void Test(){for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.WriteLine("子线程1");}}static void Test2(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.WriteLine("子线程2");}}}
}5.Lock:实现线程同步
线程同步:一个线程要等待上一个线程执行完之后才能开始执行当前线程
线程异步:线程各走各的,不需要相对等待就开始执行
using System;
using System.Threading;namespace ThreadTest
{internal class Program{static LockTest kt=new LockTest();static void Main(string[] args){Thread th1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(kt.Test));Thread th2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(kt.Test2));th1.Start();th2.Start();}}public class LockTest{public void Test(){lock (this)//给线程加锁,确保代码块能完整运行,而不会被其它线程打断,this不能在静态方法中使用{for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.WriteLine("子线程1");}}}public void Test2(){lock(this){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.WriteLine("子线程2");}}}}
}参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhan520g/p/11388591.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u012395622/article/details/46581359
https://www.runoob.com/csharp/csharp-multithreading.html
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67296957/article/details/126910726
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.thread?view=net-7.0
二、协程:在主程序运行的同时,开启另外一段逻辑处理,来协助主程序的执行。在Unity中使用协程,大多数情况是为了延时调用某个功能方法、模块
注:如果开启的协程比较多,多个高开销的协程在同一帧执行会导致卡顿,因此常用于并行性要求不高的并行操作或延时执行等控制时间轴的操作(对于延时调用,Unity还有一个Invoke函数,但是Invoke所要调用的函数必须是在当前类里面的方法)
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;public class IEnumeratorTest : MonoBehaviour
{Coroutine mCoroutine=null;//定义协程WaitForSeconds waitS = new WaitForSeconds(5.0f);// Start is called before the first frame updatevoid Start(){//调用和暂停协程//方式一//StartCoroutine(Test());//StopCoroutine(Test());这种方式无法停止协程//方式二//StartCoroutine("Test");//StopCoroutine("Test");//可以暂停协程//方式三mCoroutine = StartCoroutine(Test());//StopCoroutine(mCoroutine);//可以暂停协程}//协程函数IEnumerator Test(){Debug.Log("开始");//yield的多用方法://yield return new WaitForEndOfFrame();//每帧结束后再执行//yield return new WaitForFixedUpdate();//等待FixEdUpdate结束后再执行//yield return new WaitForSeconds(5.0f);//等待5s后执行//用全局中断指令来控制//yield return waitS;//等待5s后执行yield return StartCoroutine(Test2());//在协程中开启协程,协程一旦开启,就会立即执行Show();Debug.Log("等待了5s");} IEnumerator Test2(){//yield return new WaitForSeconds(2.0f);//程序等待N秒后从当前位置继续执行//yield return null;//程序在下一帧中从当前位置继续执行//yield return 0;//程序在下一帧中从当前位置继续执行yield break;//直接终止协程Debug.Log("第二个协程");}void Show(){Debug.Log("Show");}
}参考:Unity C# 协程:(开始一个协程、停止一个协程、优化协程、协程中yield的用法)_c#停止协程_Iamzls的博客-CSDN博客
结语:合抱之木,生于毫末;九层之台,起于累土;千里之行,始于足下。