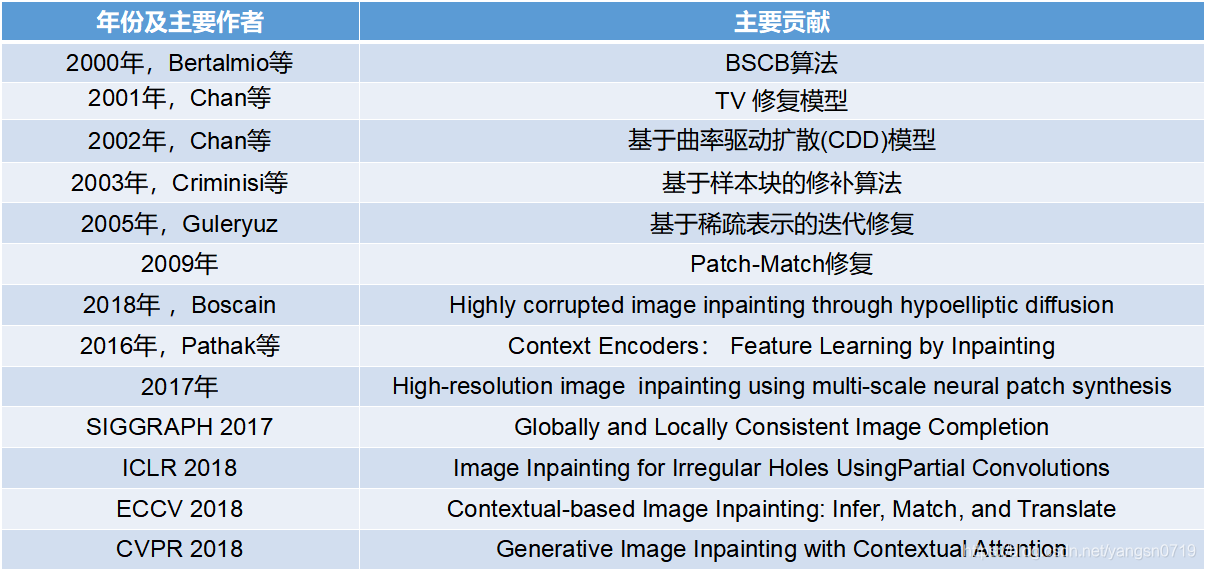
前言:
最近接触了一些 win32 方便的编程,由于不熟 可能会写一写这方便的基础东西 相当于
写日记了 提升一下
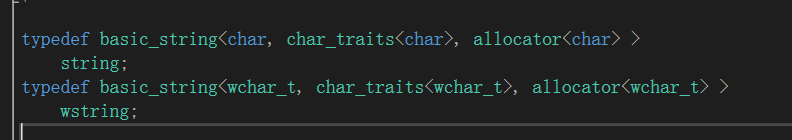
他们的声明
string 是 char
wstring 是wchar_t
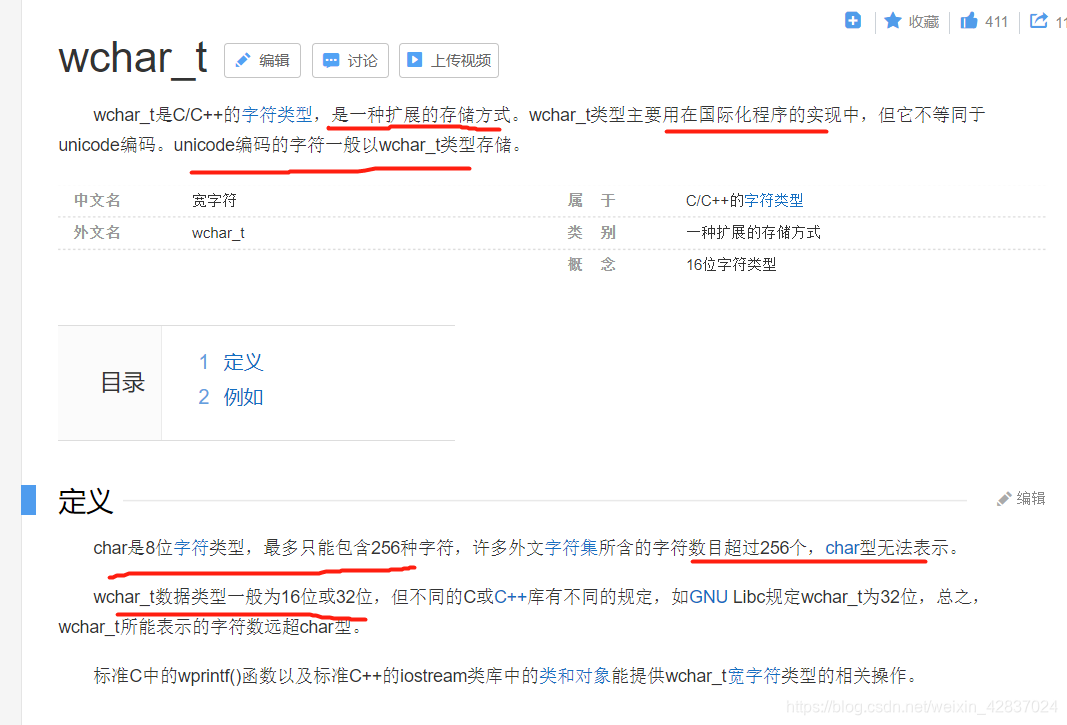
什么是wchar_t ?
string 转 wstring
inline
std::wstring StringToWString(const std::string& str)
{int len = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, str.c_str(), -1, NULL, 0);wchar_t* wide = new wchar_t[len + 1];memset(wide, '\0', sizeof(wchar_t) * (len + 1));MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, str.c_str(), -1, wide, len);std::wstring w_str(wide);delete[] wide;return w_str;
}wstring 转 string
inline
std::string WString2String(const std::wstring& wstr)
{int len = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, wstr.c_str(), wstr.size(), NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);char* buffer = new char[len + 1];memset(buffer, '\0', sizeof(char) * (len + 1));WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, wstr.c_str(), wstr.size(), buffer, len, NULL, NULL);std::string result(buffer);delete[] buffer;return result;
}
继续看两个接口 MultiByteToWideChar() 与 WideCharToMultiByte()

因为程序用的是 unicode 编码 所以 要用 wstring 用宽字符

std::wstring StringToWString(const std::string& str)int len = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, str.c_str(), -1, NULL, 0);
Codepage 我们是UTF-8
dwflag 否
将被转换的字符串 : str.c_str() 就是 const char *
指定-1 直到空字符串结束 就是末尾
被接受的缓存区 NULL
cchwide char 为0 返回 缓冲区所需要的宽字符数
len 就是 返回的 缓冲区所需要的宽字符数
这时 我们new wchar_t 长度就是 上面返回的+1 原因是‘\0’
然后 置空
wchar_t* wide = new wchar_t[len + 1];
memset(wide, '\0', sizeof(wchar_t) * (len + 1));
再次调用这个接口 把 str 的数据 放进 wide中 长度为len
MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, str.c_str(), -1, wide, len);
std::wstring w_str(wide);
delete[] wide;
然后把 wchar_t 转为 wstring delete 掉 wide 然后返回
wstring 转 string 也是类似 这里就不说了