List集合:
1 ArrayList集合:
优点:查找快
缺点: 元素增删慢
注:日常开发使用最多的功能就是查询数据,遍历数据,所以该集合是最常用的集合。
常用方法:

方法测试:
新建一个集合添加数据:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();int start = list.size();System.out.println("初始长度:"+start);list.add("张三");list.add("李四");list.add("王五");int end = list.size();System.out.println("添加数据后的长度:"+end);遍历集合:
将指定元素添加到指定元素上:
list.add(1,"牛六");
添加后的集合:

返回指定位置的元素:
System.out.println("返回的元素:"+list.get(1));返回结果:
![]()
删除元素 方法:
list.remove("张三");Object s = list.remove(0);int size = list.size();System.out.println("删除后的集合长度"+size);remove里面的参数可以填下标也可以填元素,两者都有返回值,填元素的时候返回值是Boolean型,填下标的时候返回的就是删除的具体元素。
删除结果:

修改元素:
list.set(0,"李中正");System.out.println("修改后的遍历:");for (int i = 0; i <list.size() ; i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}返回指定元素:
![]()
LinkdeList集合:
常用方法:

大部分方法与Array里面的方法差不多,这里只说明两个,pop方法和push方法:
这个方法的源代码如下:
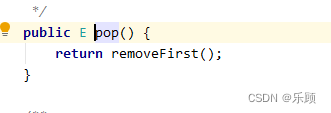
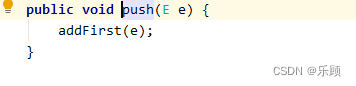
这两个方法从实现层次上来说,就是removeFirst()和addfirst()两个方法的调用,上述所以方法的使用案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();int start=linkedList.size();System.out.println("集合初始长度为:"+start);linkedList.add("张三");linkedList.add("张三");linkedList.add("李四");linkedList.add("王五");linkedList.add("牛六");int size=linkedList.size();System.out.println("加入数据后的长度:"+size);System.out.println("初始遍历:");for (int i = 0; i <linkedList.size() ; i++) {System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));}/*添加元素至首位*/linkedList.addFirst("六六");System.out.println(linkedList.get(0));/*添加元素至末尾*/linkedList.addLast("默默");System.out.println("添加末尾元素后的遍历:");for (int i = 0; i <linkedList.size() ; i++) {System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));}Object shouwei=linkedList.getFirst();System.out.println("返回的首位元素:"+shouwei);Object mowei=linkedList.getLast();System.out.println("返回的末尾元素:"+mowei);Object removefirst=linkedList.removeFirst();System.out.println("删除的首位元素:"+removefirst);Object removeend=linkedList.removeLast();System.out.println("删除的末尾元素:"+removeend);Object l=linkedList.pop();//弹出,把第一个元素删除并返回,无参数System.out.println("弹出返回的元素:"+l);System.out.println("用完pop方法后的集合遍历:");for (int i = 0; i <linkedList.size() ; i++) {System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));}linkedList.push("推入元素");//没有返回值,同时也是添加到第一位,括号内无参数System.out.println("推入后的元素遍历:");for (int i = 0; i <linkedList.size() ; i++) {System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));}boolean b=linkedList.isEmpty();//集合是否为空System.out.println(b);}打印结果:

Set接口:
java.util.Set接口和java.util.List接口一样,同样继承自Collection接口,它与Collection接口中的方法基本一致,并没有对Collection接口进行功能上的扩充,只是比Collection接口更加严格了。与List接口不同的是,Set接口都会以某种规则保证存入的元素不出现重复。
HashSet集合:
为set接口的一个实现类,存储元素不重复,且没有顺序。
HashSet是根据对象的哈希值来确定元素在集合中的存储位置,因此具有良好的存储和查找性能。保证元素唯一性的方式依赖于:hashCode与equals方法。
eg:
public class HashSetDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建 Set集合HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>();//添加元素set.add(new String("cba"));set.add("abc");set.add("bac"); set.add("cba"); //遍历for (String name : set) {System.out.println(name);}}
}存储结果:
cba
abc
bac
可以看到数据并没有重复。
当关于集合里面存储的是对象的时候,我们为了仍旧保持数据的唯一性,需要重写hascode和equals方法。
eg:
Student类:
public class Student {private String name;private int age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age &&Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}
}测试类:
public class TestMyType {public static void main(String[] args) {HashSet<Object> set = new HashSet<>();Student student = new Student("张三",20);Student student1 = new Student("李四", 21);Student student2 = new Student("王五", 22);Student student3 = new Student("张三", 20);Student student4= new Student("张三", 26);set.add(student);set.add(student1);set.add(student2);set.add(student3);set.add(student4);for (Object o : set) {System.out.println(o);}}存储结果:
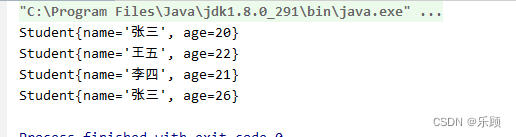
这里有一个疑问,为什么要同时重写两个方法?能不能只重写一个方法呢?
经过查阅资料,发现如果不同时重写两个方法的话,会有隐藏的bug存在,这里推荐大家看一下下面这位大佬的博客,解释的很详细。作者id:leeeeJay,博客文章名叫从一道面试题那个。