问题分析:
读者优先:
- 读者进程执行:
- 无其他读者写者, 直接执行
- 有写者等, 但其他读者在读, 直接读
- 有写者写, 等待
- 写者进程执行:
- 无其他读写者, 直接执行
- 有其他读写者, 等待
写者优先:
- 读者进程执行:
- 如果此时没有写者等待, 直接执行
- 如果有写者等待, 那么等待
- 写者进程执行:
- 如果没有其他写者, 那么执行
- 如果有其他读写者, 那么等待
伪代码:
读者优先:
读者R:
Wait(rmutex);
rcount++;
if(rcount == 1)
Wait(wmutex);
Signal(rmutex);
Read_Action();
Wait(rmutex);
rcount--;
if(rcount == 0)
Signal(wmutex);
Signal(rmutex);写者W:
Wait(wmutex);
Write_Action();
Signal(wmutex);
写者优先:
int wcount=0,rcount=0;
semaphore w=1,r=1,x=1;读者R:
reader(){P(r);P(x);rcount++;if(rcount==1)P(w);V(x);V(r);//Read()P(x);rcount--;if(rcount==0)V(w);V(x);
}写者W:
writer(){P(x);wcount++;if(wcount==1)P(r);V(x);P(w);//Write()V(w);P(x);wcount--;if(wcount==0)V(r);V(x);
}源码C++实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#define MAX_THREAD_NUM 64 //最大线程数
#define INTE_PER_SEC 1000 //每秒时钟中断的数目
#define MAX_FILE_NUM 32 //最大文件数目数
#define MAX_STR_LEN 32 //字符串的长度
using namespace std;
int readcount = 0; //读者数目
int writecount = 0; //写者数目
CRITICAL_SECTION RP_Write; //临界资源
CRITICAL_SECTION cs_Write;
CRITICAL_SECTION cs_Read;
struct ThreadInfo
{int serial; //线程序号 char entity; //线程类别(判断是读者还是写者线程) double delay; //线程延迟时间 double persist; //线程读写操作时间
};
//读者优先<--->读者线程//
void RP_ReaderThread(void *p) //P:读者线程信息
{//互斥变量 HANDLE h_Mutex;h_Mutex = OpenMutex(MUTEX_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, "mutex_for_readcount");DWORD wait_for_mutex; //等待互斥变量所有权 DWORD m_delay; //延迟时间 DWORD m_persist; //读文件持续时间 int m_serial; //线程序号 // 从参数中获得信息 m_serial = ((ThreadInfo*)(p))->serial;m_delay = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->delay *INTE_PER_SEC);m_persist = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->persist *INTE_PER_SEC);Sleep(m_delay); //延迟等待cout << "Reader thread " << m_serial << " sents the reading require !" << endl;//等待互斥信号,保证对 ReadCount 的访问,修改互斥 wait_for_mutex = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex, -1);//读者数目增加 readcount++;if (readcount == 1){//第一个读者,等待资源 EnterCriticalSection(&RP_Write);}ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex); //释放互斥信//读文件 cout << "Reader thread " << m_serial << " begins to read file !" << endl;Sleep(m_persist);//退出线程 cout << "Reader thread " << m_serial << " finished reading file !" << endl;//等待互斥信号,保证对 ReadCount 的访问,修改互斥 wait_for_mutex = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex, -1);//读者数目减少 readcount--;if (readcount == 0){//如果所有的读者读完,唤醒写者 LeaveCriticalSection(&RP_Write);}ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex); //释放互斥信号
}
//P:写者线程信息
void RP_WriterThread(void *p)
{DWORD m_delay; //延迟时间 DWORD m_persist; //写文件持续时间 int m_serial; //线程序号 // 从参数中获得信息 m_serial = ((ThreadInfo*)(p))->serial;m_delay = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->delay *INTE_PER_SEC);m_persist = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->persist *INTE_PER_SEC);Sleep(m_delay);cout << "Writer thread " << m_serial << " sents the writing require !" << endl;//等待资源 EnterCriticalSection(&RP_Write);//写文件 cout << "Writer thread " << m_serial << " begins to write file !" << endl;Sleep(m_persist);//退出线程cout << "Writer thread " << m_serial << " finished writing file !" << endl;//释放资源 LeaveCriticalSection(&RP_Write);
}
//读者优先处理函数
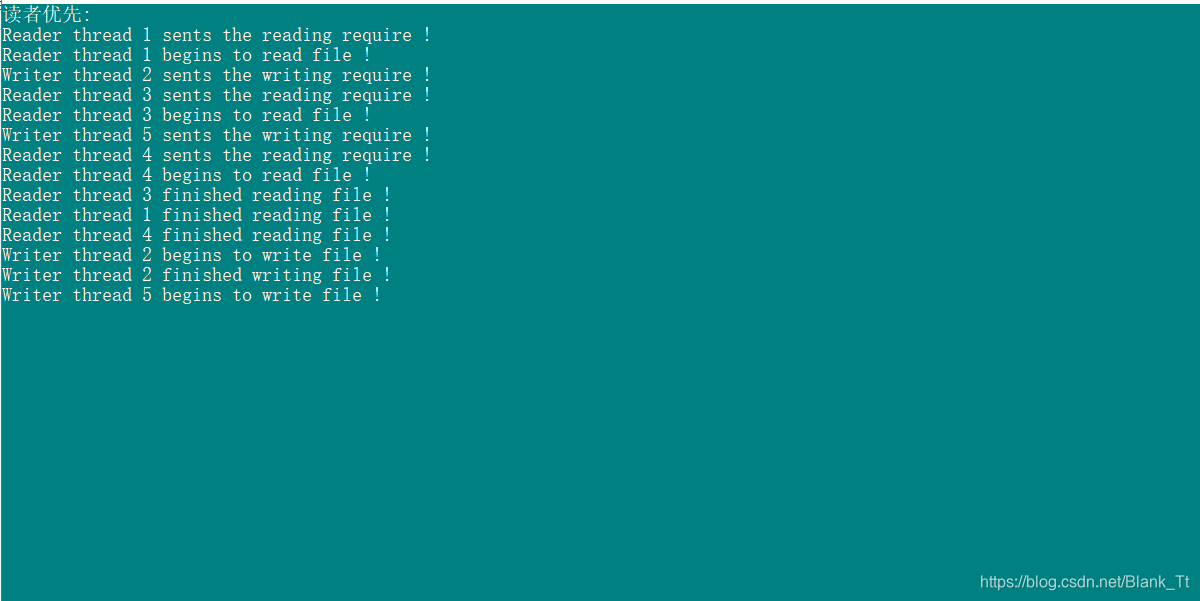
void ReaderPriority(const char *fileName)
{DWORD n_thread = 0; //线程数目 DWORD thread_ID; //线程 ID DWORD wait_for_all; //等待所有线程结束 //互斥对象 HANDLE h_Mutex;h_Mutex = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, "mutex_for_readcount");//线程对象的数组 HANDLE h_Thread[MAX_THREAD_NUM];ThreadInfo thread_info[MAX_THREAD_NUM];readcount = 0; //初始化 readcount InitializeCriticalSection(&RP_Write); //初始化临界区 ifstream inFile;inFile.open(fileName);if (!inFile){cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;}cout << "读者优先:" << endl;while (inFile){//读入每一个读者,写者的信息 inFile >> thread_info[n_thread].serial;inFile >> thread_info[n_thread].entity;inFile >> thread_info[n_thread].delay;inFile >> thread_info[n_thread++].persist;inFile.get();}for (int i = 0; i < (int)(n_thread); i++){if (thread_info[i].entity == 'R'){//创建读者进程 h_Thread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)(RP_ReaderThread),&thread_info[i], 0, &thread_ID);}else{//创建写线程 h_Thread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)(RP_WriterThread), &thread_info[i], 0, &thread_ID);}}//等待所有的线程结束 wait_for_all = WaitForMultipleObjects(n_thread, h_Thread, TRUE, -1);cout << "All reader and writer have finished operating !" << endl;
}//写者优先---读者线程
//P:读者线程信息
void WP_ReaderThread(void *p)
{HANDLE print;print = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, LPCTSTR("mutex_for_print"));//互斥变量 HANDLE h_Mutex1;h_Mutex1 = OpenMutex(MUTEX_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, "mutex1");HANDLE h_Mutex2;h_Mutex2 = OpenMutex(MUTEX_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, "mutex2");DWORD wait_for_mutex1; //等待互斥变量所有权 DWORD wait_for_mutex2;DWORD m_delay; //延迟时间 DWORD m_persist; //读文件持续时间 int m_serial; //线程的序号 //从参数中得到信息 m_serial = ((ThreadInfo*)(p))->serial;m_delay = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->delay *INTE_PER_SEC);m_persist = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->persist *INTE_PER_SEC);Sleep(m_delay); //延迟等待DWORD wait_to_print = WaitForSingleObject(print, -1);cout << "Reader thread " << m_serial << " sents the reading require !" << endl;ReleaseMutex(print);wait_for_mutex1 = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex1, -1);//读者进去临界区EnterCriticalSection(&cs_Read);//阻塞互斥对象 Mutex2,保证对 readCount 的访问和修改互斥 wait_for_mutex2 = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex2, -1);//修改读者的数目 readcount++;if (readcount == 1){// 如果是第 1 个读者,等待写者写完 EnterCriticalSection(&cs_Write);}ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex2);// 释放互斥信号 Mutex2 //让其他读者进去临界区 LeaveCriticalSection(&cs_Read);ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex1);//读文件 wait_to_print = WaitForSingleObject(print, -1);cout << "Reader thread " << m_serial << " begins to read file !" << endl;ReleaseMutex(print);Sleep(m_persist);//退出线程wait_to_print = WaitForSingleObject(print, -1);cout << "Reader thread " << m_serial << " finished reading file !" << endl;ReleaseMutex(print);//阻塞互斥对象 Mutex2,保证对 readcount 的访问,修改互斥wait_for_mutex1 = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex2, -1);readcount--;if (readcount == 0){//最后一个读者,唤醒写者 LeaveCriticalSection(&cs_Write);}ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex2); //释放互斥信号
}///
//写者优先---写者线程
//P:写者线程信息
void WP_WriterThread(void *p)
{DWORD wait_for_mutex3; //互斥变量 DWORD m_delay; //延迟时间 DWORD m_persist; //读文件持续时间 int m_serial; //线程序号 HANDLE h_Mutex3;h_Mutex3 = OpenMutex(MUTEX_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, "mutex3");//从参数中获得信息 m_serial = ((ThreadInfo*)(p))->serial;m_delay = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->delay *INTE_PER_SEC);m_persist = (DWORD)(((ThreadInfo*)(p))->persist *INTE_PER_SEC);Sleep(m_delay); //延迟等待 cout << "Writer thread " << m_serial << " sents the writing require !" << endl;wait_for_mutex3 = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex3, -1);writecount++; //修改写者数目 if (writecount == 1){EnterCriticalSection(&cs_Read);}ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex3);EnterCriticalSection(&cs_Write);cout << "Writer thread " << m_serial << " begins to write file !" << endl;Sleep(m_persist);cout << "Writer thread " << m_serial << " finished writing file !" << endl;LeaveCriticalSection(&cs_Write);wait_for_mutex3 = WaitForSingleObject(h_Mutex3, -1);writecount--;if (writecount == 0){LeaveCriticalSection(&cs_Read);}ReleaseMutex(h_Mutex3);
}/
//写者优先处理函数
// fileName:文件名
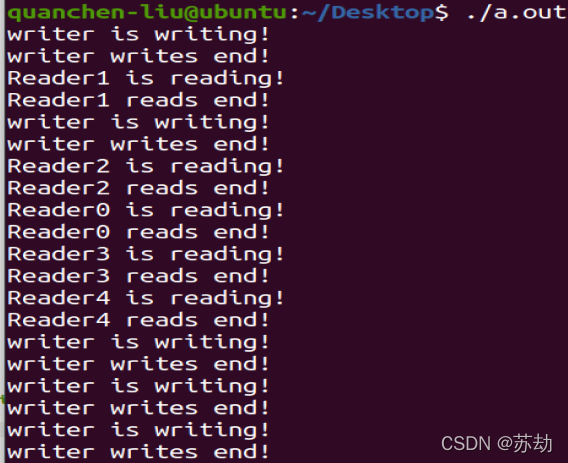
void WriterPriority(const char * fileName)
{DWORD n_thread = 0;DWORD thread_ID;DWORD wait_for_all;HANDLE h_Mutex1;h_Mutex1 = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, "mutex1");HANDLE h_Mutex2;h_Mutex2 = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, "mutex2");HANDLE h_Mutex3;h_Mutex3 = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, "mutex3");HANDLE h_Thread[MAX_THREAD_NUM];ThreadInfo thread_info[MAX_THREAD_NUM];readcount = 0;writecount = 0;InitializeCriticalSection(&cs_Write);InitializeCriticalSection(&cs_Read);ifstream inFile;inFile.open(fileName);cout << "Writer Priority:" << endl;while (inFile){inFile >> thread_info[n_thread].serial;inFile >> thread_info[n_thread].entity;inFile >> thread_info[n_thread].delay;inFile >> thread_info[n_thread++].persist;inFile.get();}for (int i = 0; i < (int)(n_thread); i++){if (thread_info[i].entity == 'R'){//创建读者进程h_Thread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)(WP_ReaderThread), &thread_info[i], 0, &thread_ID);}else if (thread_info[i].entity == 'W'){//创建写线程 h_Thread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)(WP_WriterThread), &thread_info[i], 0, &thread_ID);}}//等待所有的线程结束 wait_for_all = WaitForMultipleObjects(n_thread, h_Thread, TRUE, -1);cout << "All reader and writer have finished operating !" << endl;
}
/
//主函数
int main(void)
{system("color 3f"); //改变颜色const char * file = "test1.txt";char ch;while (1){cout << "--------------------------------读者与写者问题---------------------------------" << endl;cout << "*******************************************************************************" << endl;cout << "* 1、读者优先 *" << endl;cout << "* 2、写者优先 *" << endl;cout << "* 3、退出... *" << endl;cout << "*******************************************************************************" << endl;printf("请选择(1,2,3): ");do {ch = (char)getchar();} while (ch != '1'&&ch != '2'&&ch != '3');system("cls"); //执行清屏幕命令switch (ch){case '1':ReaderPriority(file);break;case '2':WriterPriority(file);break;case '3':return 0;}cout << endl << "按任意键继续..." << endl;getchar();system("cls");}return 0;
}
test1.txt内容:
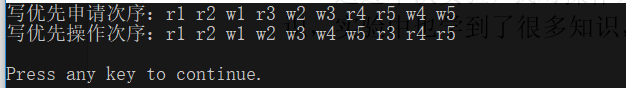
1 R 3 5
2 W 4 5
3 R 5 2
4 R 6 5
5 W 5.1 3
结果: