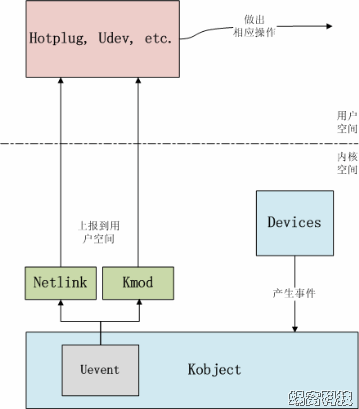
查找linux的uevent节点(find /sys -name uevent),大概有1000多个,那这些节点是怎么实现的呢。

drivers/base/core.c
有如下代码,每创建一个device,都会创建一个event节点
static ssize_t uevent_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,char *buf)
{...retval = kset->uevent_ops->uevent(kset, &dev->kobj, env);...
}static ssize_t uevent_store(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count)
{}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RW(uevent);int device_add(struct device *dev)
{...device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);...
}来个demo看下
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>static struct class *demo_class;
static struct cdev demo_cdev;
dev_t demo_number = 0;
int demo_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{return 0;
}static struct file_operations demo_nod_fops =
{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = demo_open,
};int demo_uevent(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env)
{int ret = 0;char *p="aaa";char *q="bbb";ret = add_uevent_var(env, "demo_NAME=%s",p);ret = add_uevent_var(env, "demo_NAME=%s",q);return ret;
}static int __init example_init(void)
{int ret;demo_number=MKDEV(0,0);ret=alloc_chrdev_region(&demo_number,0,1,"6");if(ret<0){printk("alloc chardev region err\n");return ret;}cdev_init(&demo_cdev,&demo_nod_fops);demo_cdev.owner=THIS_MODULE;ret=cdev_add(&demo_cdev,demo_number,1);if(ret<0){printk("add demo cdev err!\n");return ret;}demo_class=class_create(THIS_MODULE,"demo");if(IS_ERR(demo_class)){printk("create demo class err!\n");return -1;}device_create(demo_class,NULL,demo_number,NULL,"66"); demo_class->dev_uevent = demo_uevent;return 0;
}static void __exit example_exit(void)
{cdev_del(&demo_cdev);device_destroy(demo_class,demo_number);unregister_chrdev_region(demo_number, 1);class_destroy(demo_class);
}module_init(example_init);
module_exit(example_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Greg Kroah-Hartman <greg@kroah.com>");
在代码中,还会看到通过uevent给上层发信息,如
电量变化,插拔充电器
static void power_supply_changed_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
...
kobject_uevent(&psy->dev.kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE);
...
}int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action)
{return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL);
}int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action,char *envp_ext[])
{
...
#if defined(CONFIG_NET)/* send netlink message */list_for_each_entry(ue_sk, &uevent_sock_list, list) {struct sock *uevent_sock = ue_sk->sk;struct sk_buff *skb;size_t len;if (!netlink_has_listeners(uevent_sock, 1))continue;/* allocate message with the maximum possible size */len = strlen(action_string) + strlen(devpath) + 2;skb = alloc_skb(len + env->buflen, GFP_KERNEL);if (skb) {char *scratch;/* add header */scratch = skb_put(skb, len);sprintf(scratch, "%s@%s", action_string, devpath);/* copy keys to our continuous event payload buffer */for (i = 0; i < env->envp_idx; i++) {len = strlen(env->envp[i]) + 1;scratch = skb_put(skb, len);strcpy(scratch, env->envp[i]);}NETLINK_CB(skb).dst_group = 1;retval = netlink_broadcast_filtered(uevent_sock, skb,0, 1, GFP_KERNEL,kobj_bcast_filter,kobj);/* ENOBUFS should be handled in userspace */if (retval == -ENOBUFS || retval == -ESRCH)retval = 0;} elseretval = -ENOMEM;}
#endif
...
}来个demo看下
/** Sample kset and ktype implementation** Copyright (C) 2004-2007 Greg Kroah-Hartman <greg@kroah.com>* Copyright (C) 2007 Novell Inc.** Released under the GPL version 2 only.**/
#include <linux/kobject.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>/** This module shows how to create a kset in sysfs called* /sys/kernel/kset-example* Then tree kobjects are created and assigned to this kset, "foo", "baz",* and "bar". In those kobjects, attributes of the same name are also* created and if an integer is written to these files, it can be later* read out of it.*//** This is our "object" that we will create a few of and register them with* sysfs.*/
struct foo_obj {struct kobject kobj;int bar;int baz;
};
#define to_foo_obj(x) container_of(x, struct foo_obj, kobj)/* a custom attribute that works just for a struct foo_obj. */
struct foo_attribute {struct attribute attr;ssize_t (*show)(struct foo_obj *foo, struct foo_attribute *attr, char *buf);ssize_t (*store)(struct foo_obj *foo, struct foo_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count);
};
#define to_foo_attr(x) container_of(x, struct foo_attribute, attr)/** The default show function that must be passed to sysfs. This will be* called by sysfs for whenever a show function is called by the user on a* sysfs file associated with the kobjects we have registered. We need to* transpose back from a "default" kobject to our custom struct foo_obj and* then call the show function for that specific object.*/
static ssize_t attr_show(struct kobject *kobj,struct attribute *attr,char *buf)
{struct foo_attribute *attribute;struct foo_obj *foo;attribute = to_foo_attr(attr);foo = to_foo_obj(kobj);if (!attribute->show)return -EIO;return attribute->show(foo, attribute, buf);
}/** Just like the default show function above, but this one is for when the* sysfs "store" is requested (when a value is written to a file.)*/
static ssize_t attr_store(struct kobject *kobj,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t len)
{struct foo_attribute *attribute;struct foo_obj *foo;attribute = to_foo_attr(attr);foo = to_foo_obj(kobj);if (!attribute->store)return -EIO;return attribute->store(foo, attribute, buf, len);
}/* Our custom sysfs_ops that we will associate with our ktype later on */
static const struct sysfs_ops sysfs_ops = {.show = attr_show,.store = attr_store,
};/** The release function for our object. This is REQUIRED by the kernel to* have. We free the memory held in our object here.** NEVER try to get away with just a "blank" release function to try to be* smarter than the kernel. Turns out, no one ever is...*/
static void release(struct kobject *kobj)
{struct foo_obj *foo;foo = to_foo_obj(kobj);kfree(foo);
}static ssize_t bar_show(struct foo_obj *foo_obj, struct foo_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{return sprintf(buf, "%d\n", foo_obj->bar);
}static ssize_t bar_store(struct foo_obj *foo_obj, struct foo_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count)
{int ret;ret = kstrtoint(buf, 10, &foo_obj->bar);if (ret < 0)return ret;return count;
}static ssize_t baz_show(struct foo_obj *foo_obj, struct foo_attribute *attr,char *buf)
{return sprintf(buf, "%d\n", foo_obj->baz);
}static ssize_t baz_store(struct foo_obj *foo_obj, struct foo_attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count)
{int ret;ret = kstrtoint(buf, 10, &foo_obj->baz);if (ret < 0)return ret;return count;
}static struct foo_attribute bar_attribute =__ATTR(bar, 0664, bar_show, bar_store);
static struct foo_attribute baz_attribute =__ATTR(baz, 0664, baz_show, baz_store);/** Create a group of attributes so that we can create and destroy them all* at once.*/
static struct attribute *default_attrs[] = {&bar_attribute.attr,&baz_attribute.attr,NULL, /* need to NULL terminate the list of attributes */
};/** Our own ktype for our kobjects. Here we specify our sysfs ops, the* release function, and the set of default attributes we want created* whenever a kobject of this type is registered with the kernel.*/
static struct kobj_type ktype = {.sysfs_ops = &sysfs_ops,.release = release,.default_attrs = default_attrs,
};static struct kset *example_kset;
static struct foo_obj *bar_obj;
static struct foo_obj *baz_obj;static struct foo_obj *create_foo_obj(const char *name)
{struct foo_obj *foo;int retval;/* allocate the memory for the whole object */foo = kzalloc(sizeof(*foo), GFP_KERNEL);if (!foo)return NULL;/** As we have a kset for this kobject, we need to set it before calling* the kobject core.*/foo->kobj.kset = example_kset;/** Initialize and add the kobject to the kernel. All the default files* will be created here. As we have already specified a kset for this* kobject, we don't have to set a parent for the kobject, the kobject* will be placed beneath that kset automatically.*/retval = kobject_init_and_add(&foo->kobj, &ktype, NULL, "%s", name);if (retval) {kobject_put(&foo->kobj);return NULL;}/** We are always responsible for sending the uevent that the kobject* was added to the system.*/kobject_uevent(&foo->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);return foo;
}static void destroy_foo_obj(struct foo_obj *foo)
{kobject_put(&foo->kobj);
}static int __init example_init(void)
{/** Create a kset with the name of "kset_example",* located under /sys/kernel/*/example_kset = kset_create_and_add("kset_example", NULL, kernel_kobj);if (!example_kset)return -ENOMEM;bar_obj = create_foo_obj("bar");if (!bar_obj)goto bar_error;baz_obj = create_foo_obj("baz");if (!baz_obj)goto baz_error;return 0;baz_error:destroy_foo_obj(bar_obj);
bar_error:kset_unregister(example_kset);return -EINVAL;
}static void __exit example_exit(void)
{destroy_foo_obj(baz_obj);destroy_foo_obj(bar_obj);kset_unregister(example_kset);
}module_init(example_init);
module_exit(example_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Greg Kroah-Hartman <greg@kroah.com>");应用层监听
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <asm/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/netlink.h>void MonitorNetlinkUevent()
{int sockfd;struct sockaddr_nl sa;int len;char buf[4096];struct iovec iov;struct msghdr msg;int i;memset(&sa, 0, sizeof(sa));sa.nl_family = AF_NETLINK;sa.nl_groups = NETLINK_KOBJECT_UEVENT;sa.nl_pid = 0; //getpid(); both is okmemset(&msg, 0, sizeof(msg));iov.iov_base = (void *)buf;iov.iov_len = sizeof(buf);msg.msg_name = (void *)&sa;msg.msg_namelen = sizeof(sa);msg.msg_iov = &iov;msg.msg_iovlen = 1;sockfd = socket(AF_NETLINK, SOCK_RAW, NETLINK_KOBJECT_UEVENT);if (sockfd == -1)printf("socket creating failed:%s\n", strerror(errno));if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&sa, sizeof(sa)) == -1)printf("bind error:%s\n", strerror(errno));len = recvmsg(sockfd, &msg, 0);if (len < 0)printf("receive error\n");else if (len < 32 || len > sizeof(buf))printf("invalid message");for (i = 0; i < len; i++)if (*(buf + i) == '\0')buf[i] = '\n';printf("received %d bytes\n%s\n", len, buf);close(sockfd);
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{printf("***********************start***********************\n");MonitorNetlinkUevent();printf("***********************ends************************\n");return 0;
}运行结果