一般无需java来处理byte字节的数据转成 int , C语言更适合干这事. 但是无奈遇到了这种需求.
网上百度了一小部分代码, 发现好多错误代码… 干脆自己手写了一遍…
byte[]数据的格式协议文档如下:
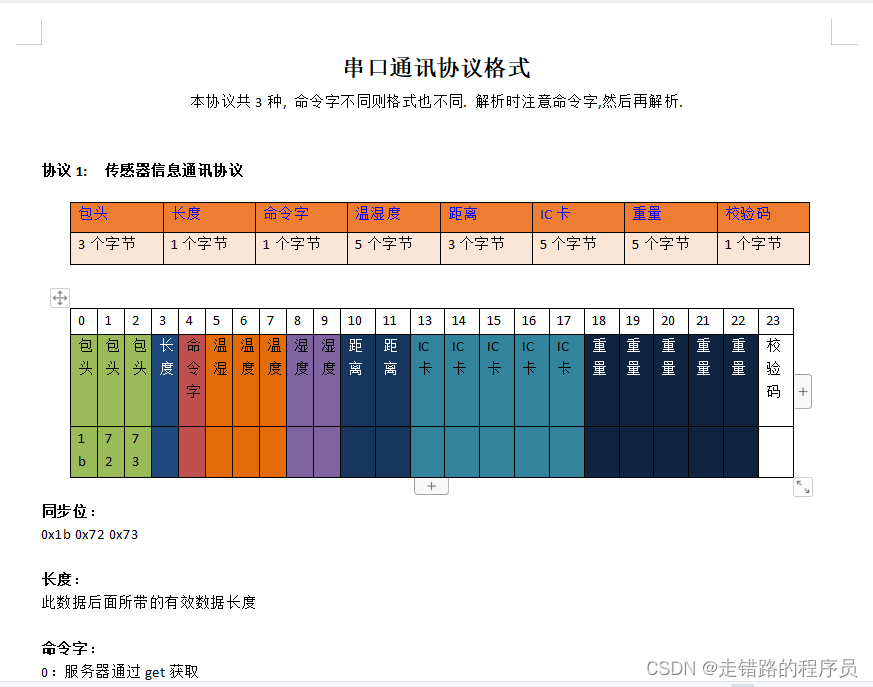
先上使用代码
byte[] hex = Base64.getDecoder().decode(data);
int head = Read3Bytes(hex, 0) ;// 3个字节 1b7273if(head != 1798771) // 十进制 1798771 ==== 16进制 0x1b7273{throw new Exception("不可识别的数据包");}
// 数据长度是
int datalength = Read1Bytes(hex, 3); //1字节 此数据后面所带的有效数据长度
// 命令字
int cmd = Read1Bytes(hex, 4); ; // 命令字 0:服务器通过get获取 1:开门 2:关门
//温度
int wendu = Read3Bytes(hex, 5) ;// 3个字节 0x01+2字节温度数据
//湿度
int shidu = Read2Bytes(hex, 8);// 2个字节 2字节湿度数据
//距离: 0x02+2字节距离数据
int juli = Read3Bytes(hex, 10);java中数字是依照补码的形式存储的.
正数的补码是不变的.
负数的补码表示为 原码 取反 之后再加1
以-127为例:①127的原码:0111 1111②127的反码:1000 0000③127的反码加1:1000 0001 ④答案就出来了 :-127的补码就是,1000 0001
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/moshiyaofei/article/details/88353435
下面是主要代码, 此代码适合高位在前,低位在后的byte顺序, 如需反着的可以试着自己修改代码.
另外此代码对负数没有处理. 后面抽空补上.
//循环累加、或运算都可以public static int Read1Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] ; }public static int Read2Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 8 | (bytes[startindex + 1] << 0) ; }public static int Read3Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 16 | (bytes[startindex + 1] <<8) | (bytes[startindex + 2] <<0); }public static int Read4Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 24 | (bytes[startindex + 1] << 16) | (bytes[startindex + 2] << 8)| (bytes[startindex + 3] << 0); }public static double Read5Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 32 | (bytes[startindex + 1] << 24) | (bytes[startindex + 2] << 16)| (bytes[startindex + 3] << 8) | (bytes[startindex + 4] << 0); }public static double Read6Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 40 | (bytes[startindex + 1] << 32) | (bytes[startindex + 2] << 24)| (bytes[startindex + 3] << 16) | (bytes[startindex + 4] << 8)| (bytes[startindex + 5] << 0); }public static double Read7Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 48| (bytes[startindex + 1] << 40) | (bytes[startindex + 2] << 32) | (bytes[startindex + 3] << 24)| (bytes[startindex + 4] << 16) | (bytes[startindex + 5] << 8)| (bytes[startindex + 6] << 0); }public static double Read8Bytes(byte[] bytes,int startindex){return bytes[startindex] << 56 | (bytes[startindex + 1] << 48) | (bytes[startindex + 2] << 40) | (bytes[startindex + 3] << 32) | (bytes[startindex + 4] << 24)| (bytes[startindex + 5] << 16) | (bytes[startindex + 6] << 8)| (bytes[startindex + 7] << 0); }