这两天,在学习JSP,正好找个小模块来练练手:
以下就是实现购物车模块的页面效果截图:

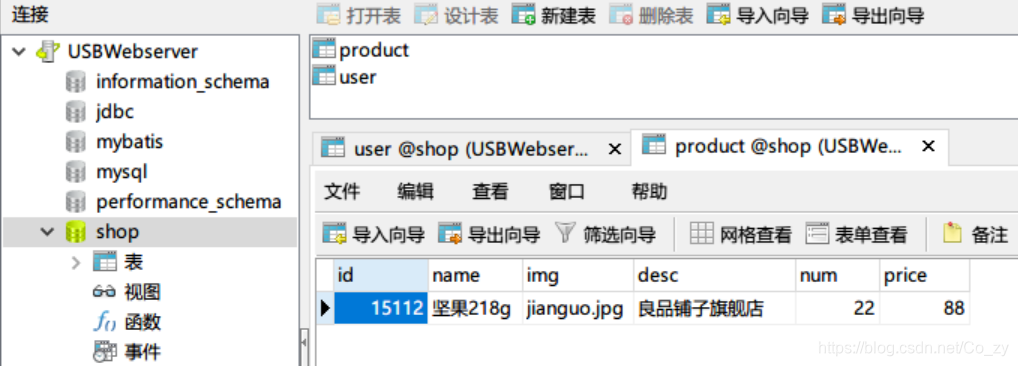
图1. 产品显示页面 通过此页面进行产品选择,加入到购物车

图2 .购物车页面

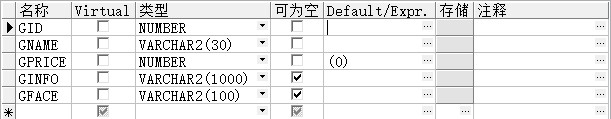
图3 . 商品数量设置
好了,先不贴图了,直接上代码;先看看项目的文档结构把(麻雀虽小,五脏俱全):

整个项目包含三个类,两个JSP页面,下面分别把他们的代码贴上:
Cart.java
package shopping.cart;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Cart {
List<CartItem> items = new ArrayList<CartItem>();
public List<CartItem> getItems() {
return items;
}
public void setItems(List<CartItem> items) {
this.items = items;
}
public void add(CartItem ci) {
for (Iterator<CartItem> iter = items.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
CartItem item = iter.next();
if(item.getProduct().getId() == ci.getProduct().getId()) {
item.setCount(item.getCount() + 1);
return;
}
}
items.add(ci);
}
public double getTotalPrice() {
double d = 0.0;
for(Iterator<CartItem> it = items.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
CartItem current = it.next();
d += current.getProduct().getPrice() * current.getCount();
}
return d;
}
public void deleteItemById(String productId) {
for (Iterator<CartItem> iter = items.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
CartItem item = iter.next();
if(item.getProduct().getId().equals(productId)) {
iter.remove();
return;
}
}
}
}
CartItem.java
package shopping.cart;
import shopping.cart.Product;
public class CartItem {
private Product product;
private int count;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public Product getProduct() {
return product;
}
public void setProduct(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
}
Product.java
package shopping.cart;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Product implements Serializable {
private String id;// 产品标识
private String name;// 产品名称
private String description;// 产品描述
private double price;// 产品价格
public Product() {
}
public Product(String id, String name, String description, double price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.price = price;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
}
下面是俩JSP页面源码:
ShowProducts.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GB18030"%>
<%@ page import="shopping.cart.*"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://"
+ request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()
+ path + "/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>My JSP 'ShowProductsJSP.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<%
Map products = new HashMap();
products.put("1", new Product("1", "mp3播放器",
"效果很不错的mp3播放器,存储空间达1GB", 100.00));
products.put("2", new Product("2", "数码相机", "象素500万,10倍光学变焦",
500.00));
products.put("3", new Product("3", "数码摄像机",
"120万象素,支持夜景拍摄,20倍光学变焦", 200.00));
products.put("4", new Product("4", "迷你mp4",
"市面所能见到的最好的mp4播放器,国产", 300.00));
products.put("5", new Product("5", "多功能手机",
"集mp3播放、100万象素数码相机,手机功能于一体", 400.00));
products.put("6", new Product("6", "多功能手机111",
"集mp3播放23、100万象素数码相机111,手机功能于一体111",600.00));
products.put("7", new Product("7", "11111111111",
"集mp3播放23、100万象素数码相机111,手机功能于一体111",700.00));
products.put("8", new Product("8", "2222222222",
"集mp3播放23、100万象素数码相机111,手机功能于一体111",800.00));
products.put("9", new Product("9", "33333333333333",
"集mp3播放23、100万象素数码相机111,手机功能于一体111",900.00));
session.setAttribute("products", products);
%>
<H1>
产品显示
</H1>
<form name="productForm"
action="http://localhost:8088/JSPlearning/ShopCartJSP.jsp"
method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="action" value="purchase">
<table border="1" cellspacing="0">
<tr bgcolor="#CCCCCC">
<tr bgcolor="#CCCCCC">
<td>
序号
</td>
<td>
产品名称
</td>
<td>
产品描述
</td>
<td>
产品单价(¥)
</td>
<td>
添加到购物车
</td>
</tr>
<%
Set productIdSet = products.keySet();
Iterator it = productIdSet.iterator();
int number = 1;
while (it.hasNext()) {
String id = (String) it.next();
Product product = (Product) products.get(id);
%><tr>
<td>
<%=number++%>
</td>
<td>
<%=product.getName()%>
</td>
<td><%=product.getDescription()%>
</td>
<td>
<%=product.getPrice()%></td>
<td>
<a href="Buy.jsp?id=<%=product.getId()%>&action=add" target="cart">我要购买</a>
</td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
<p>
</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Buy.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GB18030"%>
<%@ page import="shopping.cart.*" %>
<%
Cart c = (Cart)session.getAttribute("cart");
if(c == null) {
c = new Cart();
session.setAttribute("cart", c);
}
double totalPrice = c.getTotalPrice();
request.setCharacterEncoding("GBK");
String action = request.getParameter("action");
Map products = (HashMap)session.getAttribute("products");
if(action != null && action.trim().equals("add")) {
String id = request.getParameter("id");
Product p = (Product)products.get(id);
CartItem ci = new CartItem();
ci.setProduct(p);
ci.setCount(1);
c.add(ci);
}
if(action != null && action.trim().equals("delete")) {
String id = request.getParameter("id");
c.deleteItemById(id);
}
if(action != null && action.trim().equals("update")) {
for(int i=0; i<c.getItems().size(); i++) {
CartItem ci = c.getItems().get(i);
int count = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("p" + ci.getProduct().getId()));
ci.setCount(count);
}
}
%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<%
List<CartItem> items = c.getItems();
%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=GB18030">
<title>购物车</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- c的值是:<%=(c == null) %> items的值是:<%=(items == null) %> -->
<form action="Buy.jsp" method="get">
<input type="hidden" name="action" value="update"/>
<table align="center" border="1">
<tr>
<td>产品ID</td>
<td>产品名称</td>
<td>购买数量</td>
<td>单价</td>
<td>总价</td>
<td>处理</td>
</tr>
<%
for(Iterator<CartItem> it = items.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
CartItem ci = it.next();
%>
<tr>
<td><%=ci.getProduct().getId() %></td>
<td><%=ci.getProduct().getName() %></td>
<td>
<input type="text" size=3 name="<%="p" + ci.getProduct().getId() %>" value="<%=ci.getCount() %>"
οnkeypress="if (event.keyCode < 45 || event.keyCode > 57) event.returnValue = false;"
οnchange="document.forms[0].submit()">
</td>
<td><%=ci.getProduct().getPrice() %></td>
<td><%=ci.getProduct().getPrice()*ci.getCount() %></td>
<td>
<a href="Buy.jsp?action=delete&id=<%=ci.getProduct().getId() %>">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
<tr>
<td colspan=3 align="right">
所有商品总价格为:
</td>
<td colspan=3><%=c.getTotalPrice() %></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<!-- <td colspan=3>
<a href="javascript:document.forms[0].submit()">修改</a>
</td> -->
<td colspan=6 align="right">
<a href="">下单</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
配置好相关文件,在tomcat中发布后,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8088/shopCart/ShowProducts.jsp 即可进入产品展示页面,其它操作都可以在页面上完成!
注意:我使用的tomcat端口(8088)被自己改过,如果没改过tomcat端口的童鞋,默认端口为8080。