目录
- 简介
- 列表基本方法
- 访问列表元素(即索引)
- index方法
- enumerate()函数
- 在列表中添加元素
- append方法
- insert方法
- 修改列表元素
- 删除列表元素
- del语句
- pop()函数
- remove方法
- 列表排序
- sort方法
- sorted()函数
- reverse方法
- 列表长度 len()函数
- 列表转换
- 列表高阶
- 操作数字列表
- min()函数
- max()函数
- sum()函数
- 列表推导式
- 切片
- 参考书目
简介
今天博主为大家整理了Python操作列表的常用函数和方法,建议收藏!
注意:这篇博文中所有的代码均在Python交互式环境(IDLE)中进行。
打开方法见附录。
列表基本方法
访问列表元素(即索引)
**** 列表中元素的索引从 0 开始,不是 1 !!****
索引负数表示从列表结尾数索引的绝对值个的元素。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','c','d']
>>> list_a[0]
'a'
>>> list_a[-1]
'd'
注意:如果索引超过列表长度,会引发IndexError:
>>> list_a = ['a','b','c','d']
>>> list_a[4]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<pyshell#3>", line 1, in <module>list_a[4]
IndexError: list index out of range
index方法
index方法接受一个列表中的元素,返回该元素在列表中的索引。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','c','d']
>>> list_a.index('b')
1
如果该元素在列表中多次出现,返回第一次出现的索引。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','b','c','c','d']
>>> list_a.index('b')
1
>>> list_a.index('c')
3
如果该元素不在该列表内,会引发ValueError:
>>> list_a = ['a','b','b','c','c','d']
>>> list_a.index('e')
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<pyshell#3>", line 1, in <module>list_a.index('e')
ValueError: 'e' is not in list
enumerate()函数
enumerate函数将索引和值连接在一起,通常用于for循环。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','c','d','e']
>>> for index,letter in enumerate(list_a):
... print(f'列表的第{index}项是{letter}。')
...
列表的第0项是a。
列表的第1项是b。
列表的第2项是c。
列表的第3项是d。
列表的第4项是e。
在列表中添加元素
append方法
append方法在列表的末尾添加元素。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','b','c','c','d']
>>> list_a.append('e')
>>> list_a
['a', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'd', 'e']
insert方法
insert方法可以在列表的指定位置添加元素。
所需的两个参数是列表索引和所添元素。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','b','c','c','d']
>>> list_a.insert(1,'e')
>>> list_a
['a', 'e', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'd']
修改列表元素
直接通过索引修改。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','b','c','c','d']
>>> list_a[0] = 'e'
>>> list_a
['e', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'd']
删除列表元素
del语句
格式:del list_name[index]
>>> list_a = ['a','b','b','c','c','d']
>>> del list_a[0]
>>> list_a
['b','b','c','c','d']
pop()函数
pop()函数可以将列表中的一项删除,并赋给一个变量。
pop()函数需要一个参数:弹出元素的索引(默认为-1)
>>> list_a = ['one','two','three','four']
>>> number = list_a.pop()
>>> number
'four'
>>> list_a
['one', 'two', 'three']
>>> number_2 = list_a.pop(0)
>>> number_2
'one'
>>> list_a
['two', 'three']
remove方法
remove 方法直接通过值来删除元素。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','a','c','d','e','f']
>>> list_a.remove('b')
>>> list_a
['a', 'a', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
注意,如果删除的元素在列表中出现多次,remove 方法会删除最早出现的那个元素。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','a','c','d','e','f']
>>> list_a.remove('a')
>>> list_a
['b', 'a', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
如果要删除的值不存在,会引发ValueError:
>>> list_a = ['a','b','c','d','e','f']
>>> list_a.remove(1)
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<pyshell#6>", line 1, in <module>list_a.remove(1)
ValueError: list.remove(x): x not in list
列表排序
sort方法
sort 方法对列表永久排序。
>>> list_a = ['Ab','ABB','ab','AA','aB','aa','AB']
>>> list_a.sort()
>>> list_a
['AA', 'AB', 'ABB', 'Ab', 'aB', 'aa', 'ab']
可以提供关键字参数 reverse 来反向排序。
>>> list_a = ['Ab','ABB','ab','AA','aB','aa','AB']
>>> list_a.sort(reverse=True)
>>> list_a
['ab', 'aa', 'aB', 'Ab', 'ABB', 'AB', 'AA']
sorted()函数
sorted()函数可以保证原列表不变。
>>> list_a = ['Ab','ABB','ab','AA','aB','aa','AB']
>>> new_list = sorted(list_a)
>>> new_list #新列表
['AA', 'AB', 'ABB', 'Ab', 'aB', 'aa', 'ab']
>>> list_a #原列表
['Ab', 'ABB', 'ab', 'AA', 'aB', 'aa', 'AB']
同理,也可以用 关键字参数 reverse 来反向排列。
>>> list_a = ['Ab','ABB','ab','AA','aB','aa','AB']
>>> new_list = sorted(list_a,reverse=True)
>>> new_list #新列表
['ab', 'aa', 'aB', 'Ab', 'ABB', 'AB', 'AA']
>>> list_a #原列表
['Ab', 'ABB', 'ab', 'AA', 'aB', 'aa', 'AB']
reverse方法
reverse 方法将指定列表倒序排列。
>>> list_a = ['Ab','ABB','ab','AA','aB','aa','AB']
>>> list_a.reverse()
>>> list_a
['AB', 'aa', 'aB', 'AA', 'ab', 'ABB', 'Ab']
列表长度 len()函数
使用len()函数。
>>> list_a = ['Ab','ABB','ab','AA','aB','aa','AB']
>>> len(list_a)
7
列表转换
使用 list() 函数将字符串、元组转换为列表。
>>> string = 'Hello,world!'
>>> list_a = list(string)
>>> list_a
['H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ',', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!']
>>> tuple_1 = ('a','b','c')
>>> list_b = list(tuple_1)
>>> list_b
['a', 'b', 'c']
列表高阶
操作数字列表
min()函数
min() 函数返回数字列表中最小的数。
>>> number_list = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
>>> min(number_list)
1
max()函数
max() 函数正好相反,返回数字列表中最大的数。
>>> list_a = [10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100]
>>> max(list_a)
100
sum()函数
sum() 函数返回数字列表之和。
>>> list_a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]
>>> sum(list_a)
210
列表推导式
列表推导式是一种简洁的代码。
格式:list_name = [ 表达式 for 变量名 in 可迭代对象 条件表达式(可有可无) ]
例一
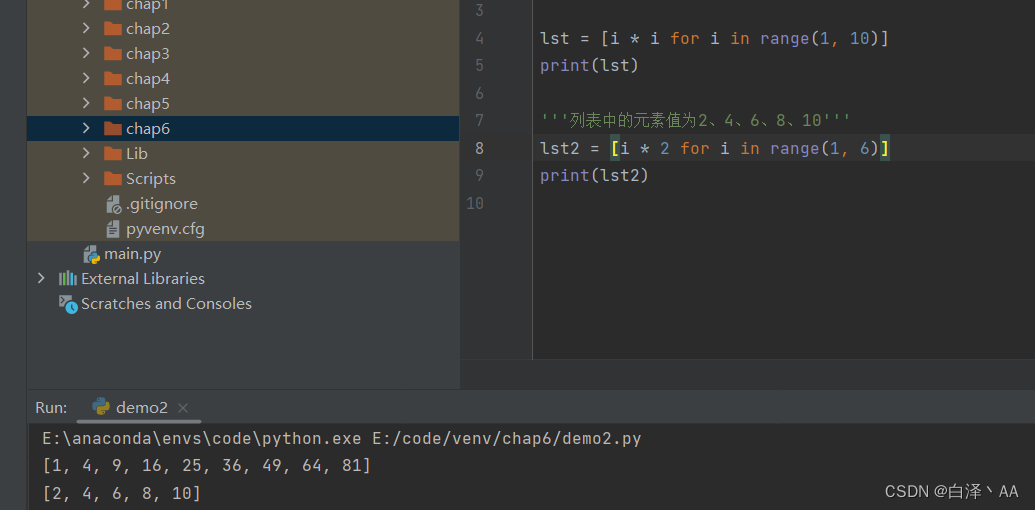
>>> even_number = [i for i in range(1,21) if i % 2 == 0]
>>> even_number
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20]
例二
>>> number_1 = [i for i in range(1,101) if '1' in str(i)]
>>> number_1
[1, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 31, 41, 51, 61, 71, 81, 91, 100]
切片
切片可以获得列表的一部分。
格式:list_name[start_index : end_index]
start_index 默认为0,end_index 默认为-1。
返回列表包括开始索引,不包括结束索引。
>>> list_a = ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k']
>>> list_a[2:5] #'c' 到 'e'
['c', 'd', 'e']
>>> list_a[:4] #从开头到 'd'
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
>>> list_a[4:] #从'e'到结尾
['e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k']
>>> list_a[:] #全部
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k']
参考书目
Python编程:从入门到实践(第二版)
[美]埃里克·马瑟斯(EricMatthes)著 袁国忠译
附录:打开Python交互式环境的方法
1.按下 win键+R,打开运行窗口。

2.输入 cmd,点击确定。

3.在打开的窗口中输入python,再点击enter键。

4.打开完成,即可使用。