流处理 (Stream processing) 是一种计算机编程范式,其允许给定一个数据序列 (流处理数据源),一系列数据操作 (函数) 被应用到流中的每个元素。同时流处理工具可以显著提高程序员的开发效率,允许他们编写有效、干净和简洁的代码。
流数据处理在我们的日常工作中非常常见,举个例子,我们在业务开发中往往会记录许多业务日志,这些日志一般是先发送到 Kafka,然后再由 Job 消费 Kafaka 写到 elasticsearch,在进行日志流处理的过程中,往往还会对日志做一些处理,比如过滤无效的日志,做一些计算以及重新组合日志等等,示意图如下:
流处理工具 fx
go-zero是一个功能完备的微服务框架,框架中内置了很多非常实用的工具,其中就包含流数据处理工具fx,下面我们通过一个简单的例子来认识下该工具:
package mainimport ("fmt""os""os/signal""syscall""time""github.com/tal-tech/go-zero/core/fx"
)func main() {ch := make(chan int)go inputStream(ch)go outputStream(ch)c := make(chan os.Signal, 1)signal.Notify(c, syscall.SIGTERM, syscall.SIGINT)<-c
}func inputStream(ch chan int) {count := 0for {ch <- counttime.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500)count++}
}func outputStream(ch chan int) {fx.From(func(source chan<- interface{}) {for c := range ch {source <- c}}).Walk(func(item interface{}, pipe chan<- interface{}) {count := item.(int)pipe <- count}).Filter(func(item interface{}) bool {itemInt := item.(int)if itemInt%2 == 0 {return true}return false}).ForEach(func(item interface{}) {fmt.Println(item)})
}
inputStream 函数模拟了流数据的产生,outputStream 函数模拟了流数据的处理过程,其中 From 函数为流的输入,Walk 函数并发的作用在每一个 item 上,Filter 函数对 item 进行过滤为 true 保留为 false 不保留,ForEach 函数遍历输出每一个 item 元素。
流数据处理中间操作
一个流的数据处理可能存在许多的中间操作,每个中间操作都可以作用在流上。就像流水线上的工人一样,每个工人操作完零件后都会返回处理完成的新零件,同理流处理中间操作完成后也会返回一个新的流。
fx 的流处理中间操作:
| 操作函数 | 功能 | 输入 |
|---|---|---|
| Distinct | 去除重复的 item | KeyFunc,返回需要去重的 key |
| Filter | 过滤不满足条件的 item | FilterFunc,Option 控制并发量 |
| Group | 对 item 进行分组 | KeyFunc,以 key 进行分组 |
| Head | 取出前 n 个 item,返回新 stream | int64 保留数量 |
| Map | 对象转换 | MapFunc,Option 控制并发量 |
| Merge | 合并 item 到 slice 并生成新 stream | |
| Reverse | 反转 item | |
| Sort | 对 item 进行排序 | LessFunc 实现排序算法 |
| Tail | 与 Head 功能类似,取出后 n 个 item 组成新 stream | int64 保留数量 |
| Walk | 作用在每个 item 上 | WalkFunc,Option 控制并发量 |
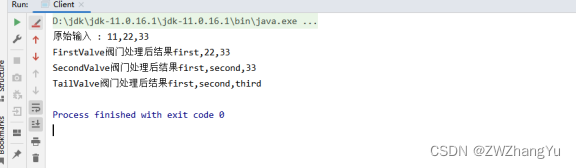
下图展示了每个步骤和每个步骤的结果:
用法与原理分析
From
通过 From 函数构建流并返回 Stream,流数据通过 channel 进行存储:
// 例子
s := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
fx.From(func(source chan<- interface{}) {for _, v := range s {source <- v}
})// 源码
func From(generate GenerateFunc) Stream {source := make(chan interface{})go func() {defer close(source)// 构造流数据写入channelgenerate(source)}()return Range(source)
}
Filter
Filter 函数提供过滤 item 的功能,FilterFunc 定义过滤逻辑 true 保留 item,false 则不保留:
// 例子 保留偶数
s := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
fx.From(func(source chan<- interface{}) {for _, v := range s {source <- v}
}).Filter(func(item interface{}) bool {if item.(int)%2 == 0 {return true}return false
})// 源码
func (p Stream) Filter(fn FilterFunc, opts ...Option) Stream {return p.Walk(func(item interface{}, pipe chan<- interface{}) {// 执行过滤函数true保留,false丢弃if fn(item) {pipe <- item}}, opts...)
}
Group
Group 对流数据进行分组,需定义分组的 key,数据分组后以 slice 存入 channel:
// 例子 按照首字符"g"或者"p"分组,没有则分到另一组
ss := []string{"golang", "google", "php", "python", "java", "c++"}
fx.From(func(source chan<- interface{}) {for _, s := range ss {source <- s}
}).Group(func(item interface{}) interface{} {if strings.HasPrefix(item.(string), "g") {return "g"} else if strings.HasPrefix(item.(string), "p") {return "p"}return ""
}).ForEach(func(item interface{}) {fmt.Println(item)
})// 源码
func (p Stream) Group(fn KeyFunc) Stream {// 定义分组存储mapgroups := make(map[interface{}][]interface{})for item := range p.source {// 用户自定义分组keykey := fn(item)// key相同分到一组groups[key] = append(groups[key], item)}source := make(chan interface{})go func() {for _, group := range groups {// 相同key的一组数据写入到channelsource <- group}close(source)}()return Range(source)
}
Reverse
reverse 可以对流中元素进行反转处理:
// 例子
fx.Just(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).Reverse().ForEach(func(item interface{}) {fmt.Println(item)
})// 源码
func (p Stream) Reverse() Stream {var items []interface{}// 获取流中数据for item := range p.source {items = append(items, item)}// 反转算法for i := len(items)/2 - 1; i >= 0; i-- {opp := len(items) - 1 - iitems[i], items[opp] = items[opp], items[i]}// 写入流return Just(items...)
}
Distinct
distinct 对流中元素进行去重,去重在业务开发中比较常用,经常需要对用户 id 等做去重操作:
// 例子
fx.Just(1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6).Distinct(func(item interface{}) interface{} {return item
}).ForEach(func(item interface{}) {fmt.Println(item)
})
// 结果为 1,2,3,4,5,6// 源码
func (p Stream) Distinct(fn KeyFunc) Stream {source := make(chan interface{})threading.GoSafe(func() {defer close(source)// 通过key进行去重,相同key只保留一个keys := make(map[interface{}]lang.PlaceholderType)for item := range p.source {key := fn(item)// key存在则不保留if _, ok := keys[key]; !ok {source <- itemkeys[key] = lang.Placeholder}}})return Range(source)
}
Walk
Walk 函数并发的作用在流中每一个 item 上,可以通过 WithWorkers 设置并发数,默认并发数为 16,最小并发数为 1,如设置 unlimitedWorkers 为 true 则并发数无限制,但并发写入流中的数据由 defaultWorkers 限制,WalkFunc 中用户可以自定义后续写入流中的元素,可以不写入也可以写入多个元素:
// 例子
fx.Just("aaa", "bbb", "ccc").Walk(func(item interface{}, pipe chan<- interface{}) {newItem := strings.ToUpper(item.(string))pipe <- newItem
}).ForEach(func(item interface{}) {fmt.Println(item)
})// 源码
func (p Stream) walkLimited(fn WalkFunc, option *rxOptions) Stream {pipe := make(chan interface{}, option.workers)go func() {var wg sync.WaitGrouppool := make(chan lang.PlaceholderType, option.workers)for {// 控制并发数量pool <- lang.Placeholderitem, ok := <-p.sourceif !ok {<-poolbreak}wg.Add(1)go func() {defer func() {wg.Done()<-pool}()// 作用在每个元素上fn(item, pipe)}()}// 等待处理完成wg.Wait()close(pipe)}()return Range(pipe)
}
并发处理
fx 工具除了进行流数据处理以外还提供了函数并发功能,在微服务中实现某个功能往往需要依赖多个服务,并发的处理依赖可以有效的降低依赖耗时,提升服务的性能。
fx.Parallel(func() {userRPC() // 依赖1
}, func() {accountRPC() // 依赖2
}, func() {orderRPC() // 依赖3
})
注意 fx.Parallel 进行依赖并行处理的时候不会有 error 返回,如需有 error 返回或者有一个依赖报错需要立马结束依赖请求请使用MapReduce工具进行处理。
总结
本篇文章介绍了流处理的基本概念和 go-zero 中的流处理工具 fx,在实际的生产中流处理场景应用也非常多,希望本篇文章能给大家带来一定的启发,更好的应对工作中的流处理场景。
项目地址
https://github.com/tal-tech/go-zero
组件地址
https://github.com/tal-tech/go-zero/tree/master/core/fx
Example
https://github.com/tal-tech/go-zero/tree/master/example/fx