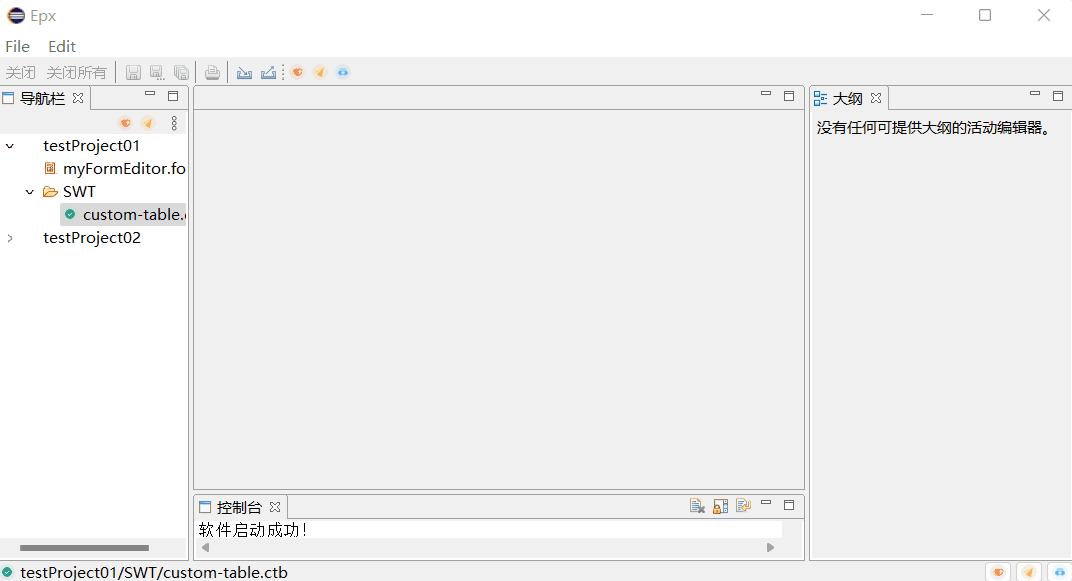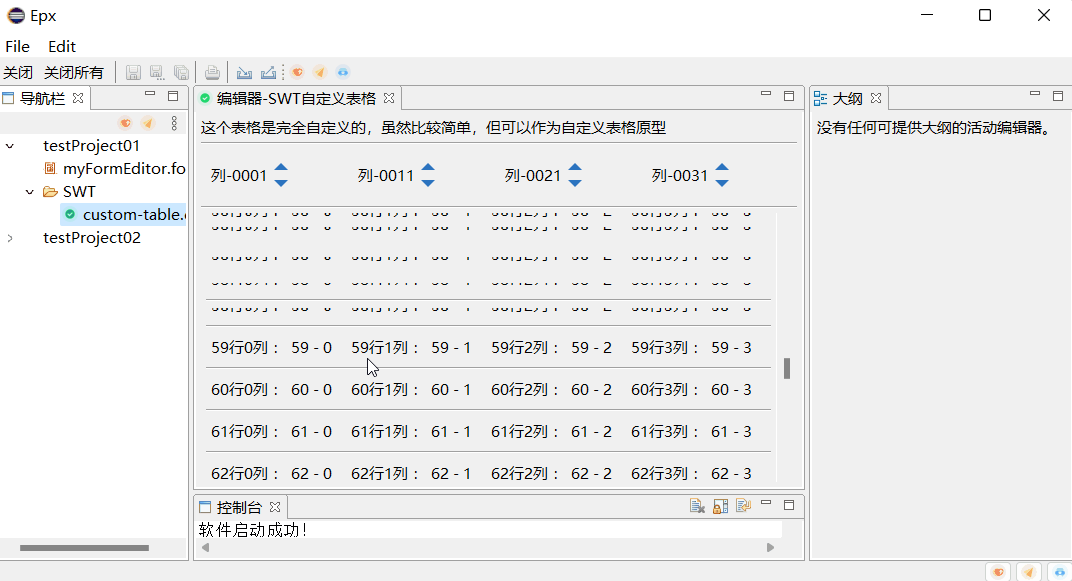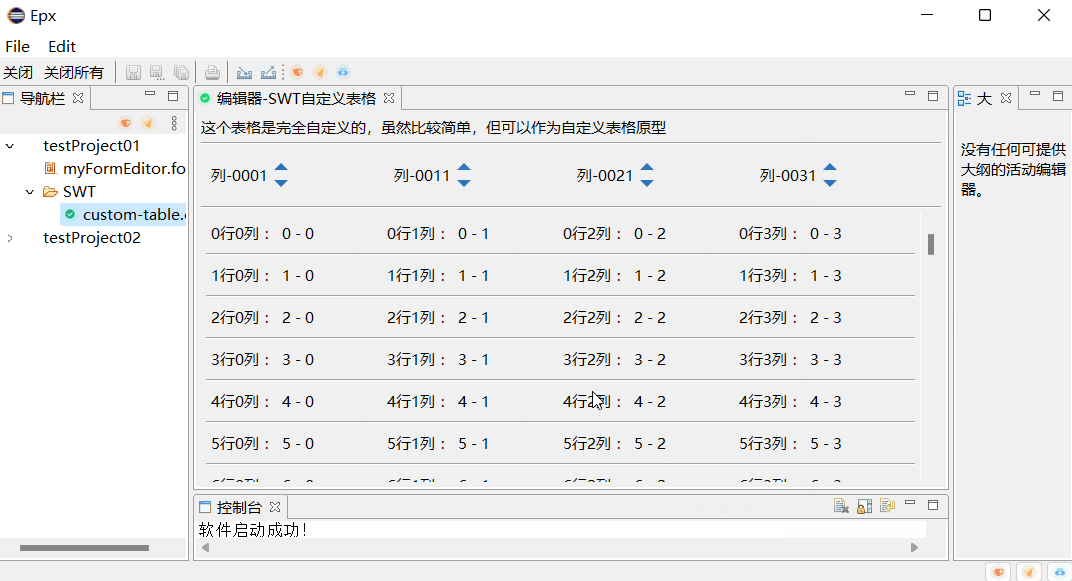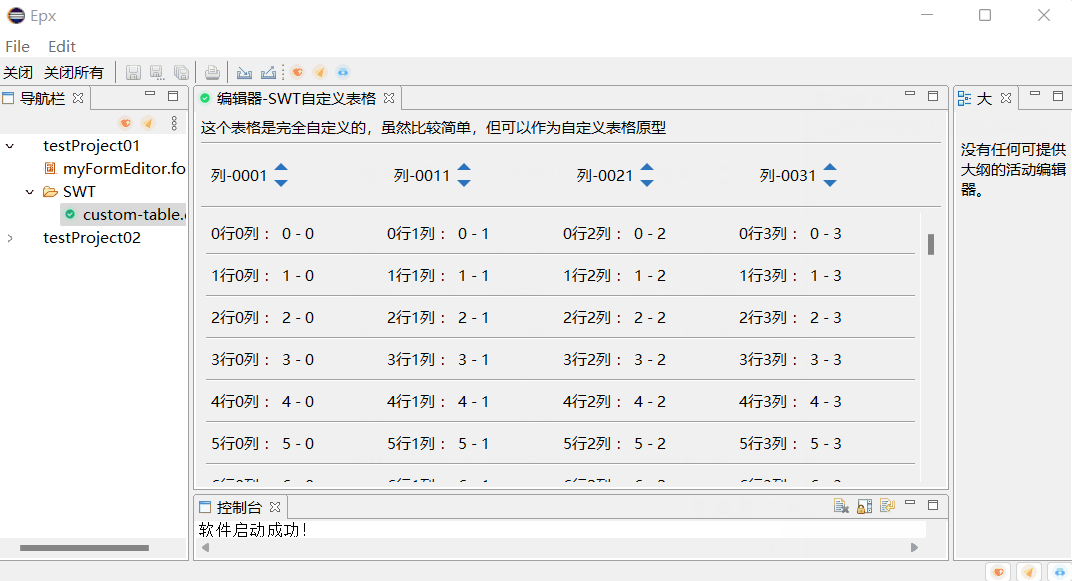
一个表格就类似于一张二维表。第一行为关系模型,就是每一列的列名。从第二行开始就是表的数据,简称元组。下面实现对其Table的封装。
首先显示一个窗口。创建一个Table。将在showTableInfos()方法对Table表格进行封装。
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = Display.getDefault();Shell shell = new Shell();shell.setSize(900, 700);Table table = new Table(shell,SWT.BORDER | SWT.FULL_SELECTION);table.setBounds(189, 59, 500, 530);showTableInfos(table);shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {display.sleep();}}display.dispose();}public static void showTableInfos(Table table) {table.setHeaderVisible(true);table.setLinesVisible(true);}
}
效果为:

1.显示列。
Table中的列用到的是TableColumn类用来实现。用setText()设置每一列的列名。
在上述代码只需添加一个提供列名的字符串数组传入到showTableInfos()方法里面即可。
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;public class Test {public static String[] sclnames = { "姓名", "编号", "年龄" };public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = Display.getDefault();Shell shell = new Shell();shell.setSize(900, 700);Table table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER | SWT.FULL_SELECTION);table.setBounds(139, 59, 600, 530);showTableInfos(table, sclnames);shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {display.sleep();}}display.dispose();}public static void showTableInfos(Table table, String[] clnames) {table.setHeaderVisible(true);table.setLinesVisible(true);TableColumn column = null;for (int i = 0; i < clnames.length; i++) {column = new TableColumn(table, SWT.NONE);column.setWidth(200);column.setText(clnames[i]);}}
}
显示效果:

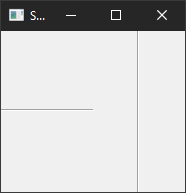
2.显示行。
为了方便Table显示的数组能够呈现动态,我们对其从数据库读取出来的数组封装成ArrayList<HashMap<String,Object>>类型。 List用于存储多行,每一行数组为一个Map,Map里面每一个数值的对应是数据库的属性名为Key ,数值为 Value。 Value可以是任意类型,所以用到了Object类型。
这个时候我们发现Map的存储的顺序会与每列对应的列名不一致,我们不能直接遍历,我们需要传一个数据库属性名的字符串数组,用于规范显示的数据能够与每一列的列名一致。
在对其模拟读取的数据。在Table显示每一行的数组用到的是TableItem类。 用该类的setText(new String[]{ })来设置文本的值。
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = Display.getDefault();Shell shell = new Shell();shell.setSize(900, 700);Table table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER | SWT.FULL_SELECTION);table.setBounds(139, 59, 600, 530);String[] clnames = { "姓名", "编号", "年龄" };String[] dbnames = { "cid","cname","cage"};HashMap<String,Object> student1 = new HashMap<String,Object>();student1.put("cid", "A001");student1.put("cname", "张三");student1.put("cage",20);List<HashMap<String,Object>> students = new ArrayList<HashMap<String,Object>>();students.add(student1);showTableInfos(table,clnames,dbnames,students);shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {display.sleep();}}display.dispose();}public static void showTableInfos(Table table, String[] clnames,String [] dbname, List<HashMap<String,Object>> lists) {table.setHeaderVisible(true);table.setLinesVisible(true);TableColumn column = null;TableItem item = null;for (int i = 0; i < clnames.length; i++) {column = new TableColumn(table, SWT.NONE);column.setWidth(200);column.setText(clnames[i]);}for(HashMap<String,Object> maps:lists) {item = new TableItem(table,SWT.NONE);ArrayList<String> rowstr = new ArrayList<String>();for(int i =0 ;i<dbname.length;i++) {rowstr.add( String.valueOf(maps.get(dbname[i]) ));}item.setText((String[])rowstr.toArray(new String[] {}));}}
}
这个时候我们就可以动态的在Table里面显示数组了。
运行效果:






![[转]实时股票数据接口大全](http://image.sinajs.cn/newchart/monthly/n/sh000001.gif)