IO
java.io中最主要的五个类就是InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer、File。
从传输方式角度来说,可以将IO分类为:

一:File
File类的对象主要用来获取文件本身的一些信息,例如文件所在的目录、文件的长度或文件读写权限等,不涉及对文件的读写操作。
对文件属性的操作
public class TestFile {public static void main(String[] args) {File file=new File("E:\\Idea\\IOAndNIO\\src","TestFile.java");String fileName = file.getName();boolean canRead = file.canRead();boolean canWrite = file.canWrite();boolean isExists = file.exists();long length = file.length();String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath();String parent = file.getParent();boolean isDirectory = file.isDirectory();boolean isFile = file.isFile();file.lastModified();System.out.println("文件名为:"+fileName);System.out.println("文件是否可读:"+canRead);System.out.println("文件是否可写:"+canWrite);System.out.println("文件是否存在:"+isExists);System.out.println("文件长度:"+length);System.out.println("文件绝对路径:"+absolutePath);System.out.println("文件父目录:"+parent);System.out.println("是否是目录:"+isDirectory);System.out.println("是否是文件:"+isFile);}
}
目录
包含目录的创建和列出目录中的文件:
public class TestFile{public static void main(String[] args) {File file=new File("D:\\dir");//mkdir() 父文件夹存在的情况下创建一个新的子文件夹//mkdirs() 如果父文件夹不存在并最后一级子文件夹不存在,自动创建所有路径的文件夹boolean mkdir = file.mkdir();System.out.println(mkdir?"创建成功":"创建失败");FileAccept fileAccept = new FileAccept();fileAccept.setExtendName("dll");String[] list = file.list(fileAccept);File[] files = file.listFiles(fileAccept);for (String s : list) {System.out.println(s);}for (File file1 : files) {System.out.println(file1.getName());}}
}
/*
* 过滤器,过滤指定的文件
* */
class FileAccept implements FilenameFilter{private String extendName;public void setExtendName(String extendName) {this.extendName = "."+extendName;}@Overridepublic boolean accept(File dir, String name) {return name.endsWith(extendName);}
}
文件的创建和删除
文件的创建:当目录中没有名为"TestFile.java“的文件时,文件对象会调用createNewFile()方法来创建这个文件,但如果没有使用outputStream.write(),那么file作为一个普通的对象,存在于内存中,硬盘中看不到。
File file=new File("E:\\Idea\\IOAndNIO\\src","TestFile.java");
删除文件
file.delete();
运行可执行文件
当要执行一个本地机器上的可执行文件时,可以使用Runtime类, 调用exec(String command)可以打开本地机器的可执行文件或执行一个操作。
public class TestFile {public static void main(String[] args) {Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();File file=new File("E:\\sqlyog","SQLyog.exe");try {runtime.exec(file.getAbsolutePath());file=new File("C:\\Users\\abc\\AppData\\Local\\Google\\Chrome\\Application","chrome https://www.csdn.net/");runtime.exec(file.getAbsolutePath());} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
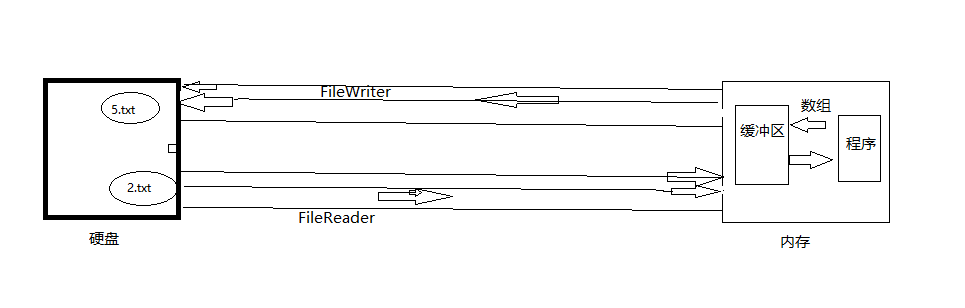
二:InputStream和OutputStream
二进制文件的读取和写入,以FileInputStream和FileOutputStream为例:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("C:\\Users\\abc\\Desktop", "index.docx");Test test = new Test();test.testOutputStream(file);test.testInputStream(file);}public void testInputStream(File file) throws IOException {FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];fileInputStream.read(bytes);System.out.println(new String(bytes));fileInputStream.close();}public void testOutputStream(File file) throws IOException {FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);byte[] bytes = "hello world".getBytes();fileOutputStream.write(bytes);}
}
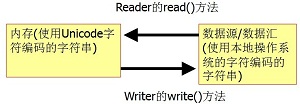
三:Writer和Reader
字符流,以FileWriter和FileReader、BufferedReader为例。
public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("C:\\Users\\abc\\Desktop", "index.docx");Test1 test1 = new Test1();test1.testWriter(file);test1.testReader(file);}public void testWriter(File file) throws IOException {//支持追加文件FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file,true);fileWriter.write("hello\nnice to meet you");fileWriter.flush();fileWriter.close();}public void testReader(File file) throws IOException{FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file);BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);String s=null;while ((s=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null && !"".equals(s)){System.out.println(s);}}
}
字节流和字符流的区别
- 字节流在操作的时候本身是不会用到缓冲区(内存)的,是与文件本身直接操作的,而字符流在操作的时候是使用到缓冲区的。
- 字节流在操作文件时,即使不关闭资源(close方法),文件也能输出,但是如果字符流不使用close方法的话,则不会输出任何内容,说明字符流用的是缓冲区,并且可以使用flush方法强制进行刷新缓冲区,这时才能在不close的情况下输出内容。
开发中,怎么选择使用哪种方式呢?
字符流只能处理字符类型(char,纯文本可以用字符流,比如汉字,传输de时候要查询编码表,得到汉字对应的字符),而字节流可以处理任何类型(比如图片,视频,是以二进制传输的),在所有的硬盘上保存文件或进行传输的时候都是以字节的方法进行的,包括图片也是按字节完成,而字符是只有在内存中才会形成的,所以使用字节的操作是最多的。