一,fetch概述

二,fetch基本用法

第一个then是fetch的一部分,返回一个promise对象,于是可以继续用then来处理返回的结果ret。
这段代码是服务器的代码:
//这是在创建服务器,通过express,创建名为app的服务器
const express=require('express')
const app=express()
//为获取post参数
const bodyParser=require('body-parser')
//拦截所有的请求,对post请求做出处理,把参数存在req.body中
//extended:false 方法内部使用querysyring模块处理请求参数的格式
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended:false}))
//静态资源的获取
const path=require('path')
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname,'public')))//拼接路径,然后static返回一个函数//设置允许跨域访问该网址
app.all('*',function(req,res,next){res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin","*")res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods",'PUT,GET,POST,DELETE,OPTIONS')res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers",'X-Requested-With')res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers",'Content-Type')next()
})app.get('/fdata',(req,res)=>{res.send("hello")
})//post请求参数的获取
app.post('/add',(req,res)=>{//接收post请求参数,res.send(req.body)
})//get请求参数的获取
app.get('/index',(req,res)=>{res.send(req.query)
})
//路由从上到下匹配,如果都没匹配上,程序运行到这里
//那么就说明没找到页面
app.use((req,res,next)=>{res.status(404).send('当前访问的页面是不存在的')
})
//监听端口
app.listen(3000)
console.log('网站服务器启动成功')
这段代码是客户端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title></head><body><script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata').then(function(data){return data.text()//需要注意的是data.text()是fetch的方法,返回的是一个promise对象}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})//运行这段代码,他就会以get请求向http://localhost:3000/fdata发送请求//服务器res.send()返回的信息存在ert中,客户端爱咋用咋用。</script></body>
</html>三,fetch请求的参数传递get和delete
可以注意到的是,上文中fetch传递的参数有限,比如请求方式?默认以get方式,但若要以post方式呢?

这里只演示传统的问号传参的方式:
<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata?id=123&name=zhangsan',{method:'get'}).then(function(data){return data.text()//需要注意的是data.text()是fetch的方法,返回的是一个promise对象}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})//运行这段代码,他就会以get请求向http://localhost:3000/fdata发送请求//服务器res.send()返回的信息存在ert中,客户端爱咋用咋用。</script>
对应的路由:
app.get('/fdata',(req,res)=>{res.send(req.query.id+'---'+req.query.name)
})
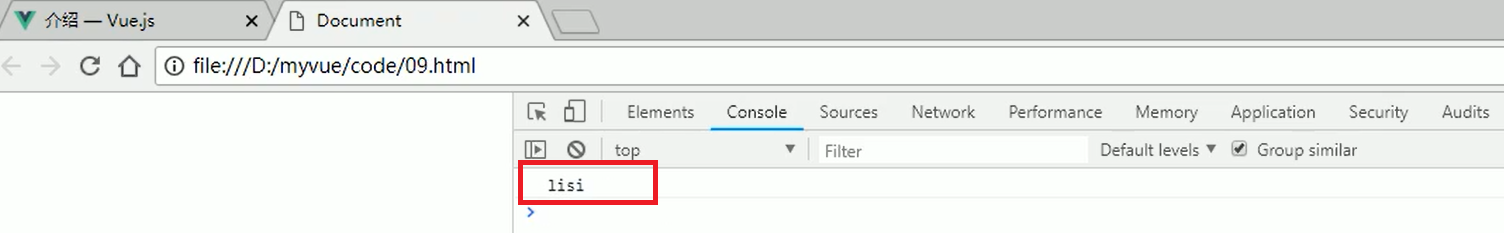
效果:

至于delete请求传参,和get类似:
<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata/id/123',{method:'delete'}).then(function(data){return data.text()//需要注意的是data.text()是fetch的方法,返回的是一个promise对象}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})//运行这段代码,他就会以get请求向http://localhost:3000/fdata发送请求//服务器res.send()返回的信息存在ert中,客户端爱咋用咋用。</script>
app.delete('/fdata/:id',(req,res)=>{res.send('restful形式传参'+req.params.id)
})
三,fetch请求的参数传递post

<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata',{method:'post',body:'id=123&name=zhangsan',headers:{'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}}).then(function(data){return data.text()//需要注意的是data.text()是fetch的方法,返回的是一个promise对象}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})//运行这段代码,他就会以get请求向http://localhost:3000/fdata发送请求//服务器res.send()返回的信息存在ert中,客户端爱咋用咋用。</script>
对应的路由:
app.post('/fdata',(req,res)=>{res.send(req.body.id+"-----"+req.body.name)
})
另外,还有json格式:

<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata',{method:'post',body:JSON.stringify({id:12,name:'zhangsan'}),headers:{'Content-Type':'application/json'}}).then(function(data){return data.text()//需要注意的是data.text()是fetch的方法,返回的是一个promise对象}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})//运行这段代码,他就会以get请求向http://localhost:3000/fdata发送请求//服务器res.send()返回的信息存在ert中,客户端爱咋用咋用。</script>
路由无变化,但是需要多加一句代码:
// 处理json格式的post请求
app.use(bodyParser.json())
四,put请求方式的参数传递
一般用于修改数据

五,fetch的响应结果

第一种,客户端接收到的就是常见的字符串形式。
第二种,客户端接受的到的就是json对象形式,使用起来很方便:
<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata',{method:'post',body:'name=zhangsan&age=12',headers:{'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}}).then(function(data){// return data.text()return data.json()//返回json数据}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})</script>
对应的路由可以这样写:
app.post('/fdata',(req,res)=>{// res.send(req.body)//也可以传json对象去服务端res.json({name:'猪八戒',age:'18',hobby:'调戏嫦娥'})
})
客户端接收到的数据:

而第一种传过来的字符串:
<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata',{method:'post',body:'name=zhangsan&age=12',headers:{'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}}).then(function(data){return data.text()// return data.json()//返回json数据}).then(function(ert){console.log(ert)})</script>

也可以在客户端把字符串转化为json格式:
<script type="text/javascript">fetch('http://localhost:3000/fdata',{method:'post',body:'name=zhangsan&age=12',headers:{'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}}).then(function(data){return data.text()// return data.json()//返回json数据}).then(function(ert){var obj=JSON.parse(ert) //把字符串转化为jsonconsole.log(obj)})</script>

也就是说,实际上,.json()也就比.text(),多了一步转化为json对象的步骤,实际上是一样的。