在 Linux 系统下对常见的错误做了一个编号,每一个编号都代表着每一种不同的错误类型,当函数执行发生错误的时候,操作系统会将这个错误所对应的编号赋值给 errno 变量,每一个进程(程序)都维护了自己的 errno 变量,它是程序中的全局变量,该变量用于存储就近发生的函数执行错误编号。
描述:该函数可以将对应的 errno 转换成适合我们查看的字符串信息。
#include <string.h>
char *strerror(int errnum);errnum:错误编号 errno。
返回值:对应错误编号的字符串描述信息。
示例代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>/*
#include <string.h>char *strerror(int errnum);errnum:错误编号 errno。
返回值:对应错误编号的字符串描述信息。描述 :该函数可以将对应的 errno 转换成适合我们查看的字符串信息
*/int main(void)
{int fd;/* 打开文件 */fd = open("./test_file", O_RDONLY);if (-1 == fd){printf("Error: %s\n", strerror(errno));return -1;}close(fd);return 0;
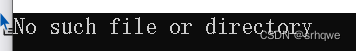
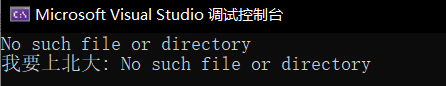
}编译测试结果:
从打印信息可以知道,strerror 返回的字符串是"No such file or directory",所以从打印信息可知,我们就 可以很直观的知道 open 函数执行的错误原因是文件不存在!