一,ArrayList的缺陷
1.空间浪费
在之前的博客中,我利用源码详细的讲解了ArrayList这个集合类(尤其是扩容机制),可以知道ArrayList的底层主要是一个动态的可变数组,容量满的时候需要进行1.5倍扩容。但是我们现在考虑这样一个问题,假设ArrayList底层数组的容量是100,我们需要存放101个元素时,当存放第101个元素时需要1.5倍扩容(扩容之后的容量是150),此时势必会造成49个存储空间的浪费!
2.时间开销大
ArrayList底层是一个数组,当我们对顺序表进行插入和删除时,需要移动大量的元素,大大提高了时间复杂度,所以可以看出ArrayList并不适用于进行大量插入和删除的操作。
针对上述ArrayList的两大缺陷,Java是否提供了其他的集合类或者数据结构来解决呢?
1.进行元素扩容时能否根据需求来进行扩容,需要多少空间就去申请多少空间;
2.在进行插入和删除的时候,可不可以不需要移动大量元素。
今天所要介绍的LinkedList集合类和链表的数据结构将很好的解决这两个问题!!!
二,链表
2.1 链表的概念
相对于顺序表,链表是一种在逻辑上连续,在存储上不一定连续的数据结构。其中链表每个元素之间的逻辑关系是通过引用来实现的。
链表中的每一个元素称为一个节点,每一个节点至少包含两类数据:
1.数据域(存放该节点的数据信息)
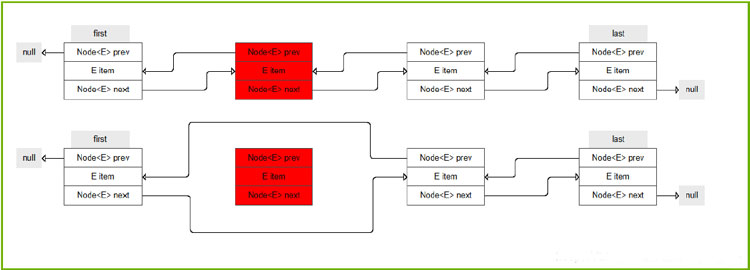
2.节点域(实现链表节点与节点之间的逻辑关系,对于单链表来说只需要存储一个next即可(存储下一个节点的地址),对于双链表来说则需要存储next和prev(分别存储下一个节点和前一个节点的地址))
2.2 链表的分类
1.单向或者双向
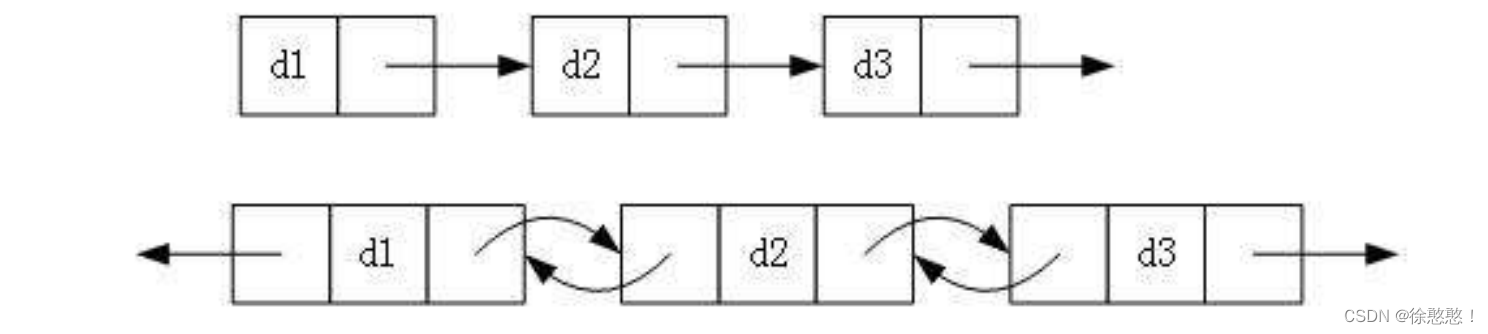
2.带头或者不带头
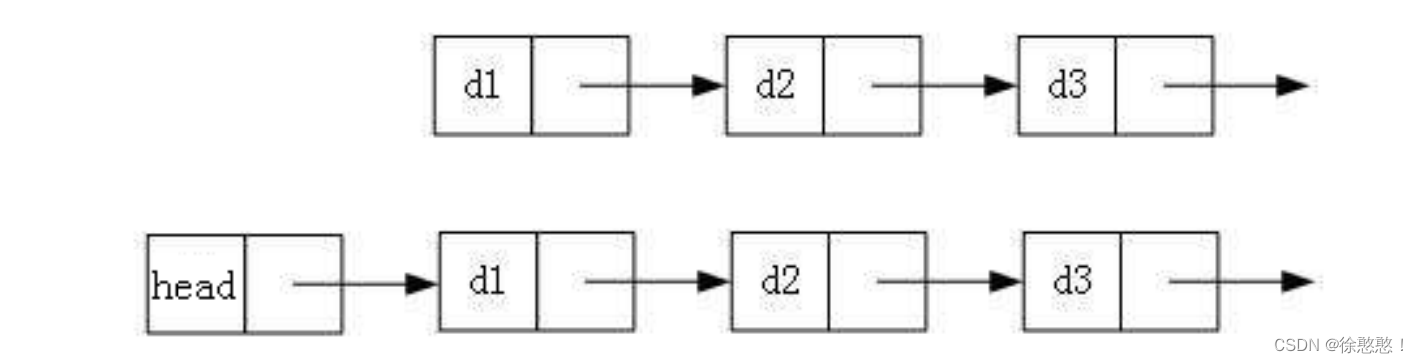
3.循环或者非循环
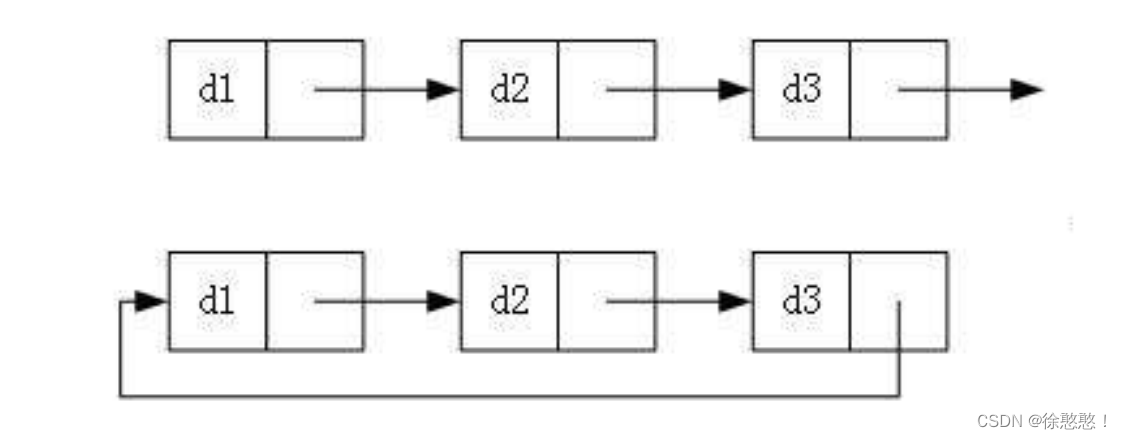
我们只需要重点掌握两种即可:
1.无头单向非循环链表(因为笔试的OJ题中经常会考);
2.无头双向链表(因为LinkedList的底层就是不带头的双链表)。
三,顺序表和链表的区别
| 不同点 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持: O(1) | 不支持: O(N) |
| 头插 | 需要搬移元素,效率低 O(N) | 只需修改引用的指向,时间复杂度为 O(1) |
| 插入 | 空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储 + 频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |
四,无头单向非循环链表的实现
定义一个MySingleList类来实现单链表的方法,用TestMySingleList类来测试MySingleList类的方法
import java.util.List;public class MySingleList {static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}ListNode head;//第一节点的引用,默认为null//打印链表public void display() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}//获取链表长度public int size() {ListNode cur = this.head;int count = 0;while (cur != null) {count++;cur = cur.next;}return count;}//头插法public void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = this.head;this.head = node;}//尾插法public void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);ListNode cur = this.head;if (this.head == null) {this.head = node;} else {while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}//此时已经处于尾节点cur.next = node;}}//任意index位置插入(假设第一个节点的下表为0)public void add(int index, int data) {//判断index位置的合法性if (index < 0 || index > size()) {System.out.println("index位置不合法!");//也可以抛异常} else if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);} else if (index == size()) {addLast(data);} else {//1.找到所需插入index位置的前驱ListNode cur = findIndexPrev(index);//2.修改引用的指向ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}}private ListNode findIndexPrev(int index) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}//删除第一次出现的关键字keypublic void remove(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("链表为空!");return;}if (this.head.val == key) {this.head = this.head.next;return;}ListNode cur = findPrev(key);//找到所需删除关键字key的前驱if (cur == null) {System.out.println("没有关键字key!");} else {cur.next = cur.next.next;}}private ListNode findPrev(int key) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}//删除所有出现的关键字keypublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("链表为空!");return;}ListNode prev = this.head;ListNode cur = this.head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;} else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (this.head.val == key) {this.head = this.head.next;}}//清空链表public void clear() {this.head = null;//单链表只需要将指向第一个节点的引用指向null即可}
}
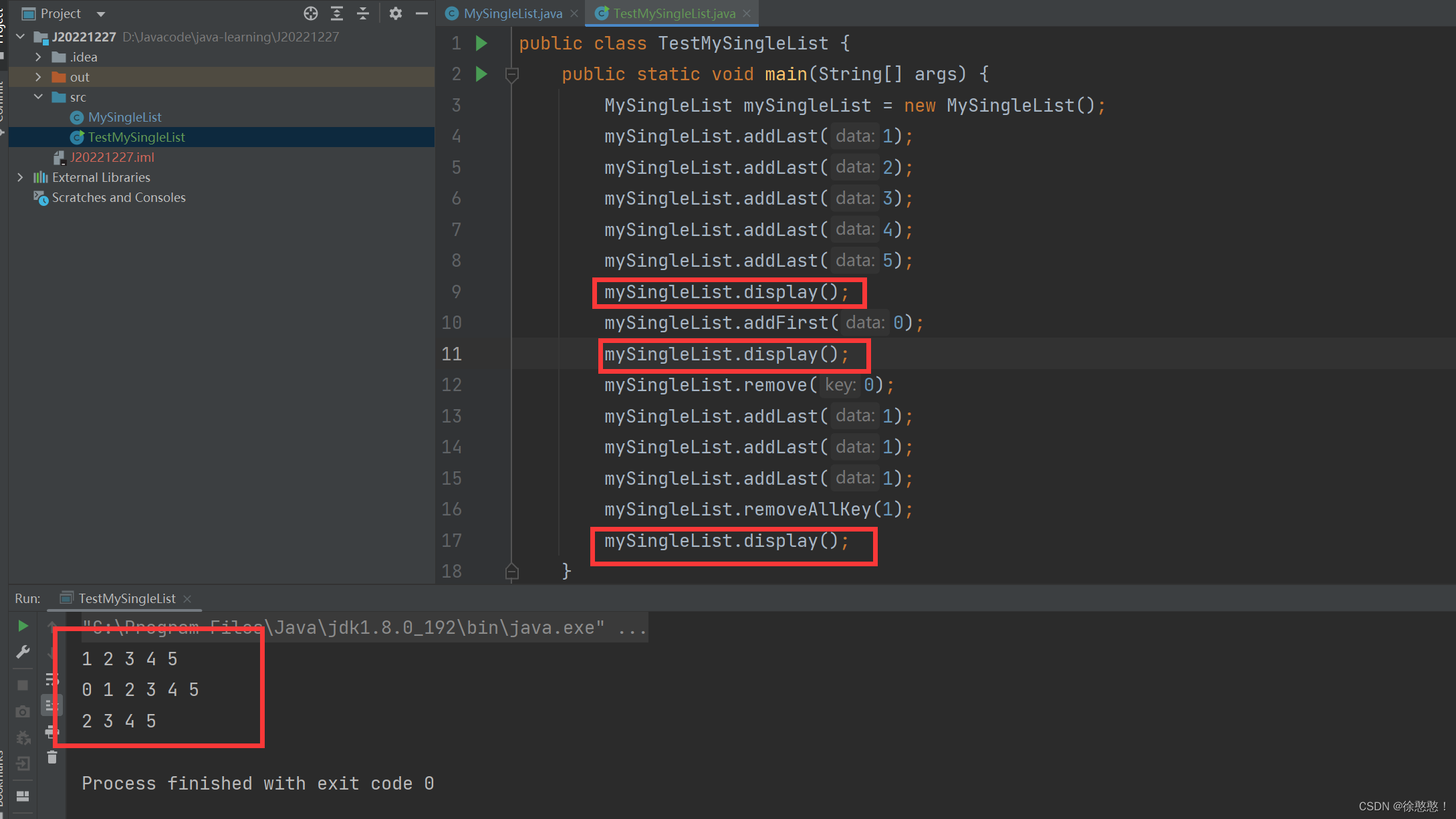
public class TestMySingleList {public static void main(String[] args) {MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList();mySingleList.addLast(1);mySingleList.addLast(2);mySingleList.addLast(3);mySingleList.addLast(4);mySingleList.addLast(5);mySingleList.display();mySingleList.addFirst(0);mySingleList.display();mySingleList.remove(0);mySingleList.addLast(1);mySingleList.addLast(1);mySingleList.addLast(1);mySingleList.removeAllKey(1);mySingleList.display();}
}
五,无头双向非循环链表的实现
定义一个MyLinkedList类来实现单链表的方法,用TestMyLinkedList类来测试MyLinkedList类的方法
public class MyLinkedList {static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode prev;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}ListNode head;//定义一个头引用,默认为nullListNode tail;//定义一个尾引用,默认为null//打印链表public void display() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}//获取链表长度public int size() {ListNode cur = this.head;int count = 0;while (cur != null) {count++;cur = cur.next;}return count;}//判断链表是否包含某个元素keypublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}//头插法public void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if (this.head == null) {this.head = node;this.tail = node;} else {node.next = this.head;this.head.prev = node;this.head = node;}}//尾插法public void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if (this.head == null) {this.head = node;this.tail = node;} else {this.tail.next = node;node.prev = this.tail;this.tail = node;}}//任意index位置插入(假设第一个节点的下标为0)public void add(int index, int data) {//判断index位置的合法性if (index < 0 || index > size()) {System.out.println("index位置不合法!");//也可以抛异常} else if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);} else if (index == size()) {addLast(data);} else {//1.找到index位置的节点ListNode cur = findIndexPrev(index);//2.修改指向的引用ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = cur;node.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev.next = node;cur.prev = node;}}private ListNode findIndexPrev(int index) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (index != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}//删除第一次出现的关键字keypublic void remove(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("链表为空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;} else {this.tail = null;}} else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;if (cur.next != null) {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;} else {this.tail = cur.prev;this.tail.next = null;}}return;}cur = cur.next;}}//删除所有出现的关键字keypublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("链表为空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;} else {this.tail = null;}} else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;if (cur.next != null) {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;} else {this.tail = cur.prev;this.tail.next = null;}}}cur = cur.next;}}//清空链表public void clear() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.prev = null;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}this.head = null;this.tail = null;}
}
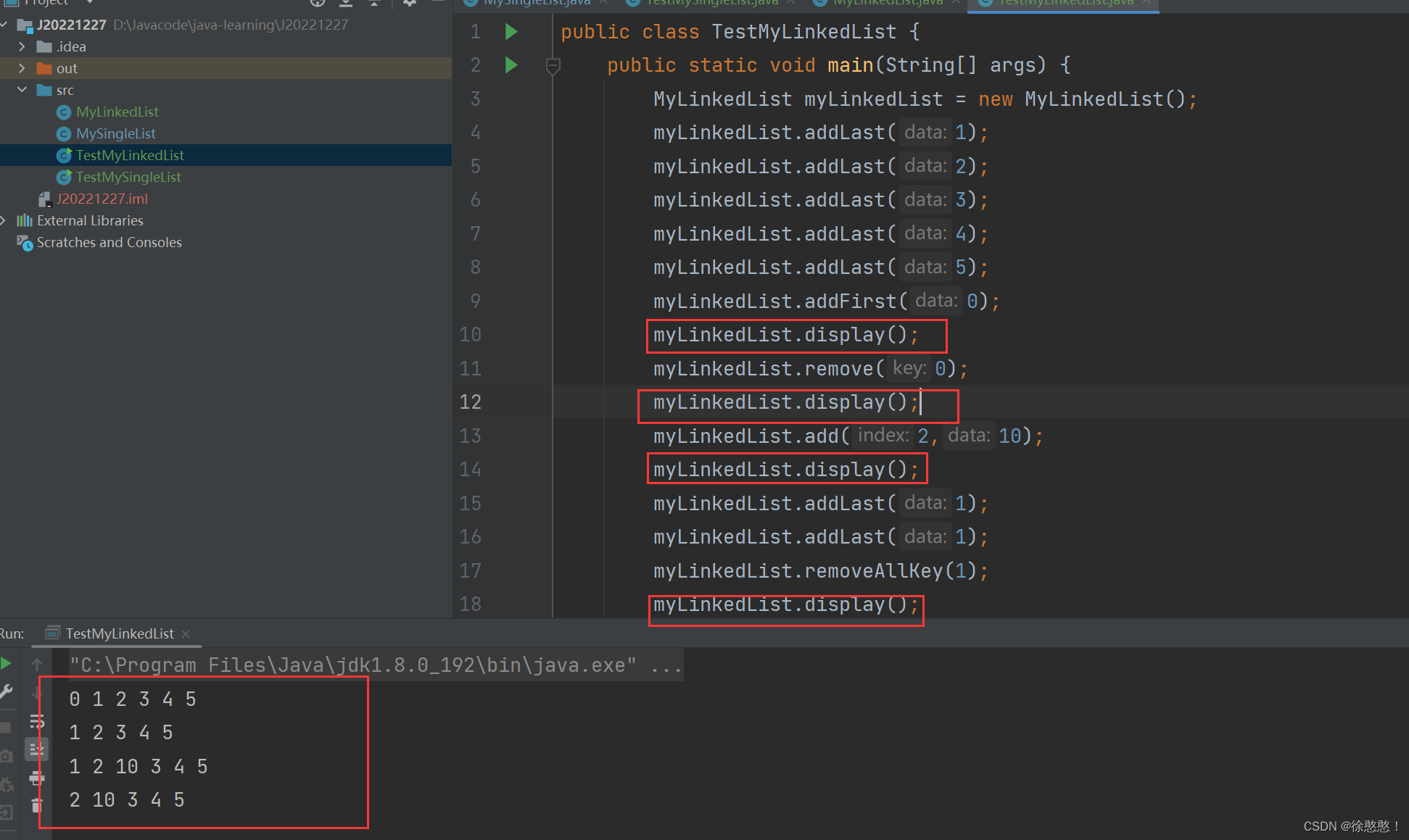
public class TestMyLinkedList {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(3);myLinkedList.addLast(4);myLinkedList.addLast(5);myLinkedList.addFirst(0);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.remove(0);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.add(2,10);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.removeAllKey(1);myLinkedList.display();}
}