逆波兰表达式在维基百科上的解释:
逆波兰表示法(Reverse Polish notation,RPN,或逆波兰记法),是一种是由波兰数学家扬·武卡谢维奇1920年引入的数学表达式方式,在逆波兰记法中,所有操作符置于操作数的后面,因此也被称为后缀表示法。逆波兰记法不需要括号来标识操作符的优先级。
我们中学学习的表达式叫中缀表达式例如:4+(2*5)-6
逆波兰表达式叫后缀表达式,操作符在操作数之后如:5 + ((1 + 2) * 4) − 3的逆波兰表达式 5 1 2 + 4 * + 3 −
我们人感觉中缀表达式比较好理解,但是计算机运行时调用的是堆栈,逆波兰表达式就是通过堆栈实现的,所以在计算机内部要把我们的中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式再进行运算。
我们来看看中缀表达式怎么样变成后缀表达式:
见到数字直接输出,见到符号按一定规则入栈出栈。
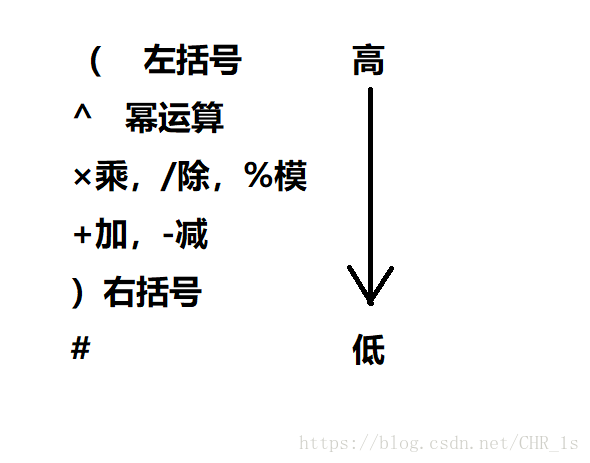
规则就是,用当前的符号与栈顶的符号比较优先级,如果当前符号优先级小于栈顶符号的优先级,则把栈里面的符号都弹出来。括号的操作除外,括号是左括号优先级最高,不管跟啥比,都是入栈;右括号是优先级最低,跟啥比都是弹出栈内符号,但只弹到跟它匹配的最近的那个左括号。
在这里我们需要知道符号运算优先级的问题:
这里我们要记住一句话:当前符号优先级大于栈顶符号优先级时,不弹出直接压入;小于等于时,弹出再压入。
下面我们来举个例子具体看看怎么使用栈将中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式。
5 + ((1 + 2) * 4) − 3
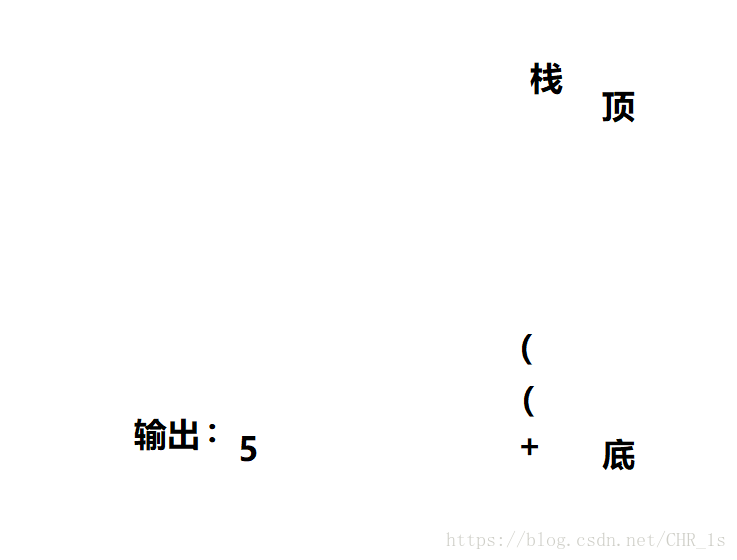
首先输出“5”,下一个运算符为+所以要压入栈中
紧接着有两个((,因为左括号优先级非常高,所以我们直接压入栈。
后面为一个1,所以直接输出。
1后面为一个+,虽然+比栈顶元素”( “低但是”( “只有遇到“ )”才会出栈,所以需要把+压栈。
后面的2直接输出。
2后面有“ )”这时我们就需要出栈了。
现在的栈顶为“( ”优先级比后面的“ * ”高所以我们需要压栈。紧接着输出4.
后面就到了第二个“ ) ”,优先级比较低,所以我们要出栈。
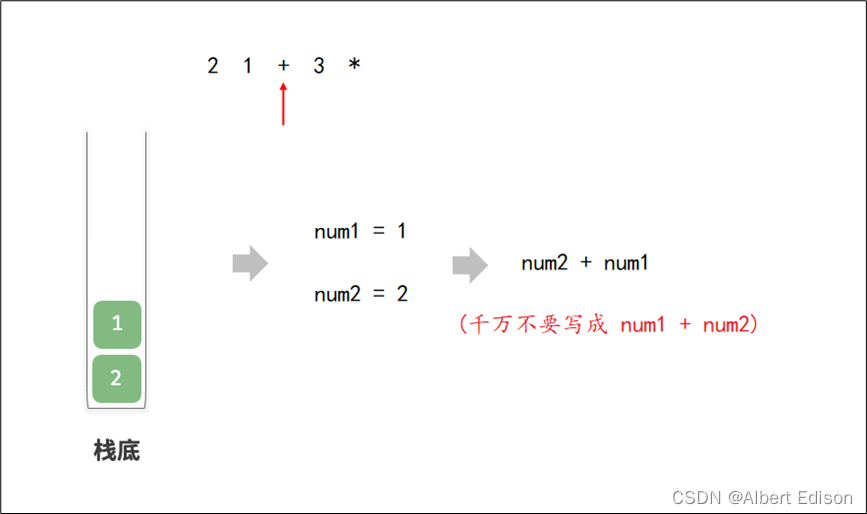
下面的“ - ”和“ + ”优先级相同所以要先压栈再出栈。
最后输出3,再将-出栈。所以换算成后缀表达式为
5 1 2 + 4 * + 3 -
维基百科C++程序实现:
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>// 操作符
// 优先级 符号 运算顺序
// 1 ! 从右至左
// 2 * / % 从左至右
// 3 + - 从左至右
// 4 = 从右至左
int op_preced(const char c)
{switch(c) {case '!':return 4;case '*': case '/': case '%':return 3;case '+': case '-':return 2;case '=':return 1;}return 0;
}unsigned int op_arg_count(const char c)
{switch(c) {case '*': case '/': case '%': case '+': case '-': case '=':return 2;case '!':return 1;default:return c - 'A';}return 0;
}#define op_left_assoc(c) (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '/' || c == '*' || c == '%')
#define is_operator(c) (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '/' || c == '*' || c == '!' || c == '%' || c == '=')
#define is_function(c) (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z')
#define is_ident(c) ((c >= '0' && c <= '9') || (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z'))bool shunting_yard(const char *input, char *output)
{const char *strpos = input, *strend = input + strlen(input);char c, stack[32], sc, *outpos = output;unsigned int sl = 0;while(strpos < strend) {c = *strpos;if(c != ' ') {// 如果输入为一个数字,则直接入输出队列if(is_ident(c)) {*outpos = c; ++outpos;}// 如果输入为一个函数记号,则压入堆栈else if(is_function(c)) {stack[sl] = c;++sl;}// 如果输入为函数分割符(如:逗号)else if(c == ',') {bool pe = false;while(sl > 0) {sc = stack[sl - 1];if(sc == '(') {pe = true;break;}else {// 直到栈顶元素是一个左括号// 从堆栈中弹出元素入输出队列*outpos = sc; ++outpos;sl--;}}// 如果没有遇到左括号,则有可能是符号放错或者不匹配if(!pe) {printf("Error: separator or parentheses mismatched\n");return false;}}// 如果输入符号为操作符,op1,然后:else if(is_operator(c)) {while(sl > 0) {sc = stack[sl - 1];// While there is an operator token, o2, at the top of the stack// op1 is left-associative and its precedence is less than or equal to that of op2,// or op1 is right-associative and its precedence is less than that of op2,if(is_operator(sc) &&((op_left_assoc(c) && (op_preced(c) <= op_preced(sc))) ||(!op_left_assoc(c) && (op_preced(c) < op_preced(sc))))) {// Pop o2 off the stack, onto the output queue;*outpos = sc; ++outpos;sl--;}else {break;}}// push op1 onto the stack.stack[sl] = c;++sl;}// If the token is a left parenthesis, then push it onto the stack.else if(c == '(') {stack[sl] = c;++sl;}// If the token is a right parenthesis:else if(c == ')') {bool pe = false;// Until the token at the top of the stack is a left parenthesis,// pop operators off the stack onto the output queuewhile(sl > 0) {sc = stack[sl - 1];if(sc == '(') {pe = true;break;}else {*outpos = sc; ++outpos;sl--;}}// If the stack runs out without finding a left parenthesis, then there are mismatched parentheses.if(!pe) {printf("Error: parentheses mismatched\n");return false;}// Pop the left parenthesis from the stack, but not onto the output queue.sl--;// If the token at the top of the stack is a function token, pop it onto the output queue.if(sl > 0) {sc = stack[sl - 1];if(is_function(sc)) {*outpos = sc; ++outpos;sl--;}}}else {printf("Unknown token %c\n", c);return false; // Unknown token}}++strpos;}// When there are no more tokens to read:// While there are still operator tokens in the stack:while(sl > 0) {sc = stack[sl - 1];if(sc == '(' || sc == ')') {printf("Error: parentheses mismatched\n");return false;}*outpos = sc; ++outpos;--sl;}*outpos = 0; // Null terminatorreturn true;
}bool execution_order(const char *input) {printf("order: (arguments in reverse order)\n");const char *strpos = input, *strend = input + strlen(input);char c, res[4];unsigned int sl = 0, sc, stack[32], rn = 0;// While there are input tokens leftwhile(strpos < strend) {// Read the next token from input.c = *strpos;// If the token is a value or identifierif(is_ident(c)) {// Push it onto the stack.stack[sl] = c;++sl;}// Otherwise, the token is an operator (operator here includes both operators, and functions).else if(is_operator(c) || is_function(c)) {sprintf(res, "_%02d", rn);printf("%s = ", res);++rn;// It is known a priori that the operator takes n arguments.unsigned int nargs = op_arg_count(c);// If there are fewer than n values on the stackif(sl < nargs) {// (Error) The user has not input sufficient values in the expression.return false;}// Else, Pop the top n values from the stack.// Evaluate the operator, with the values as arguments.if(is_function(c)) {printf("%c(", c);while(nargs > 0) {sc = stack[sl - 1];sl--;if(nargs > 1) {printf("%s, ", &sc);}else {printf("%s)\n", &sc);}--nargs;}}else {if(nargs == 1) {sc = stack[sl - 1];sl--;printf("%c %s;\n", c, &sc);}else {sc = stack[sl - 1];sl--;printf("%s %c ", &sc, c);sc = stack[sl - 1];sl--;printf("%s;\n",&sc);}}// Push the returned results, if any, back onto the stack.stack[sl] = *(unsigned int*)res;++sl;}++strpos;}// If there is only one value in the stack// That value is the result of the calculation.if(sl == 1) {sc = stack[sl - 1];sl--;printf("%s is a result\n", &sc);return true;}// If there are more values in the stack// (Error) The user input has too many values.return false;
}int main() {// functions: A() B(a) C(a, b), D(a, b, c) ...// identifiers: 0 1 2 3 ... and a b c d e ...// operators: = - + / * % !const char *input = "a = D(f - b * c + d, !e, g)";char output[128];printf("input: %s\n", input);if(shunting_yard(input, output)) {printf("output: %s\n", output);if(!execution_order(output))printf("\nInvalid input\n");}return 0;
}