问题提出:
无奈别人的电脑没有装python编译环境,无法运行py文件。
本教程为在window环境下,使用PyInstaller3.4将Python脚本打包成exe可执行程序。
使用命令:
pip install pyinstaller

上图为成功安装效果图,由红色框框看出:pyinstaller需要有altgraph-0.16.1 future-0.17.1 macholib-1.11 pefile-2019.4.18 pyinstaller-3.4 pywin32-ctypes-0.2.0支持。
用法:
usage: pyinstaller [-h] [-v] [-D] [-F] [--specpath DIR] [-n NAME][--add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>][--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST>] [-p DIR][--hidden-import MODULENAME][--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH][--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS] [--exclude-module EXCLUDES][--key KEY] [-d [{all,imports,bootloader,noarchive}]] [-s][--noupx] [-c] [-w][-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns>][--version-file FILE] [-m <FILE or XML>] [-r RESOURCE][--uac-admin] [--uac-uiaccess] [--win-private-assemblies][--win-no-prefer-redirects][--osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER][--runtime-tmpdir PATH] [--bootloader-ignore-signals][--distpath DIR] [--workpath WORKPATH] [-y][--upx-dir UPX_DIR] [-a] [--clean] [--log-level LEVEL]scriptname [scriptname ...]
下文底部有详解。
常用的参数:
• -F 表示生成单个可执行文件。
• -D –onedir 创建一个目录,包含exe文件,但会依赖很多文件(默认选项)。
• -w 表示去掉控制台窗口,这在GUI界面时非常有用。不过如果是命令行程序的话那就把这个。选项删除吧
• -c –console, –nowindowed 使用控制台,无界面(默认)。
• -p 表示你自己自定义需要加载的类路径,一般情况下用不到。
• -i 表示可执行文件的图标。
打包前:

进入python需要打包的脚本所在目录,然后执行简单打包命令即可:
pyinstaller -F *.py

会直接生成一个exe可执行文件。
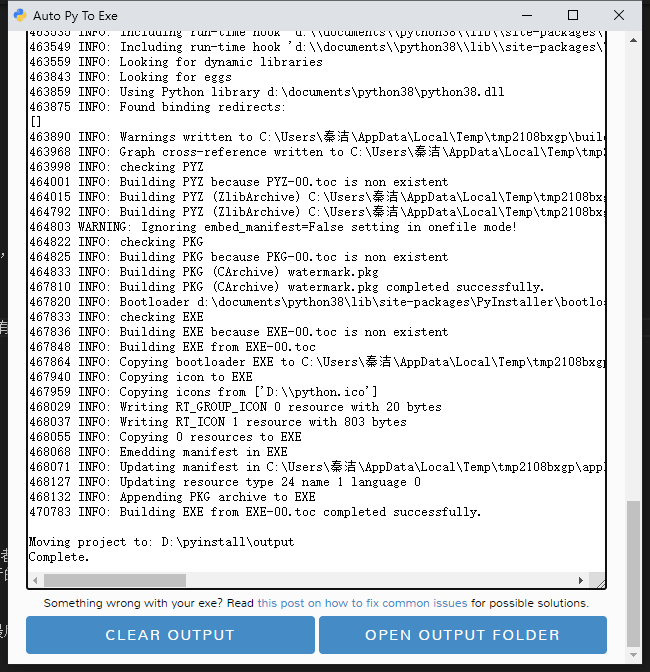
运行结果:

如果过程中出现某些问题,请自行google或者bing解决。
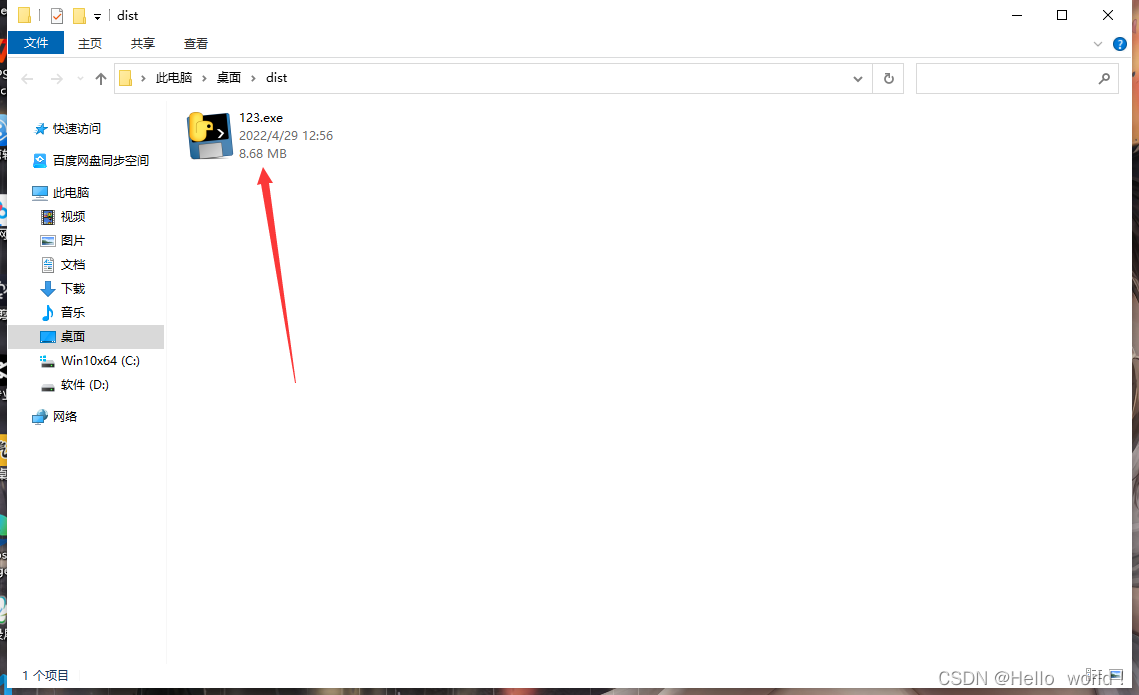
打包结果:
打包完成后,进入到当前目录下,会发现多了build、dist、*.spec这四个文件夹或者文件,其中打包好的exe应用在dist目录下面,进入即可看到,可以把他拷贝到其他地方直接使用,如下图所示,是打包完成后的目录。

执行exe应用:
因为是exe应用,是可执行文件了,所以直接双击运行即可。
进阶:
还有其它你想要的功能可通过pyinstaller --help查看其他参数。
| 参数 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|
| optional arguments | -h | show this help message and exit |
-v | show this help message and exit | |
--distpath DIR | Where to put the bundled app (default: .\dist) | |
--workpath WORKPATH | Where to put all the temporary work files, .log, .pyzand etc. (default: .\build) | |
-y, --noconfirm | Replace output directory (default: SPECPATH\dist\SPECNAME) without asking for confirmation | |
--upx-dir UPX_DIR | Path to UPX utility (default: search the execution path) | |
-a, --ascii | Do not include unicode encoding support (default: included if available) | |
--clean | Clean PyInstaller cache and remove temporary files before building. | |
--log-level LEVEL | Amount of detail in build-time console messages. LEVEL,may be one of TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, CRITICAL (default: INFO). | |
| What to generate: | -D, --onedir | Create a one-folder bundle containing an executable(default) |
-F, --onefile | Create a one-file bundled executable. | |
--specpath DIR | Folder to store the generated spec file (default:current directory) | |
-n NAME, --name NAME | Name to assign to the bundled app and spec file(default: first script’s basename) | |
| What to bundle, where to search: | --add-data <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST> | Additional non-binary files or folders to be added to the executable. The path separator is platform specific, os.pathsep (which is ; on Windows and : on most unix systems) is used. This option can be used multiple times. |
--add-binary <SRC;DEST or SRC:DEST> | Additional binary files to be added to the executable. See the --add-data option for more details. This option can be used multiple times. | |
-p DIR, --paths DIR | A path to search for imports (like using PYTHONPATH). Multiple paths are allowed, separated by ‘;’, or use this option multiple times | |
--hidden-import MODULENAME, --hiddenimport MODULENAME | Name an import not visible in the code of the.script(s). This option can be used multiple times. | |
--additional-hooks-dir HOOKSPATH | An additional path to search for hooks. This option can be used multiple times. | |
--runtime-hook RUNTIME_HOOKS | Path to a custom runtime hook file. A runtime hook is code that is bundled with the executable and is executed before any other code or module to set up special features of the runtime environment. This option can be used multiple times. | |
--exclude-module EXCLUDES | Optional module or package (the Python name, not the path name) that will be ignored (as though it was not found). This option can be used multiple times. | |
--key KEY | The key used to encrypt Python bytecode. | |
| How to generate: | -d [{all,imports,bootloader,noarchive}], --debug [{all,imports,bootloader,noarchive}] | Provide assistance with debugging a frozen application, by specifying one or more of the following choices.- all: All three of the below options; this is the default choice, unless one of the choices below is specified.- imports: specify the -v option to the underlying Python interpreter, causing it to print a message each time a module is initialized, showing the place (filename or built-in module) from which it is loaded. See https://docs.python.org/3/using/cmdline.html#id4. - bootloader: tell the bootloader to issue progress messages while initializing and starting the bundled app. Used to diagnose problems with missing imports.- noarchive: instead of storing all frozen Python source files as an archive inside the resulting executable, store them as files in the resulting output directory. |
-s, --strip | Apply a symbol-table strip to the executable and shared libs (not recommended for Windows) | |
--noupx | Do not use UPX even if it is available (works differently between Windows and *nix) | |
| Windows and Mac OS X specific options: | -c, --console, --nowindowed | Open a console window for standard i/o (default) |
-w, --windowed, --noconsole | Windows and Mac OS X: do not provide a console window for standard i/o. On Mac OS X this also triggers building an OS X .app bundle. This option is ignored in *NIX systems. | |
-i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns>, --icon <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns> | FILE.ico: apply that icon to a Windows executable. FILE.exe,ID, extract the icon with ID from an exe. FILE.icns: apply the icon to the .app bundle on Mac OS X | |
| Windows specific options: | --version-file FILE | add a version resource from FILE to the exe |
-m <FILE or XML>, --manifest <FILE or XML> | add manifest FILE or XML to the exe | |
-r RESOURCE, --resource RESOURCE | Add or update a resource to a Windows executable. The RESOURCE is one to four items, FILE[,TYPE[,NAME[,LANGUAGE]]]. FILE can be a data file or an exe/dll. For data files, at least TYPE and NAME must be specified. LANGUAGE defaults to 0 or may be specified as wildcard * to update all resources of the given TYPE and NAME. For exe/dll files, all resources from FILE will be added/updated to the final executable if TYPE, NAME and LANGUAGE are omitted or specified as wildcard *.This option can be used multiple times. | |
--uac-admin | Using this option creates a Manifest which will request elevation upon application restart. | |
--uac-uiaccess | Using this option allows an elevated application to work with Remote Desktop. | |
| Windows Side-by-side Assembly searching options (advanced): | --win-private-assemblies | Any Shared Assemblies bundled into the application will be changed into Private Assemblies. This means the exact versions of these assemblies will always be used, and any newer versions installed on user machines at the system level will be ignored. |
--win-no-prefer-redirects | While searching for Shared or Private Assemblies to bundle into the application, PyInstaller will prefer not to follow policies that redirect to newer versions, and will try to bundle the exact versions of the assembly. | |
| Mac OS X specific options: | --osx-bundle-identifier BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER | Mac OS X .app bundle identifier is used as the default unique program name for code signing purposes. The usual form is a hierarchical name in reverse DNS notation. For example: com.mycompany.department.appname (default: first script’s basename) |
| Rarely used special options: | --runtime-tmpdir PATH | Where to extract libraries and support files in ‘onefile’-mode. If this option is given, the bootloader will ignore any temp-folder location defined by the run-time OS. The `_MEIxxxxxx’-folder will be created here. Please use this option only if you know what you are doing. |
--bootloader-ignore-signals | Tell the bootloader to ignore signals rather than forwarding them to the child process. Useful in situations where e.g. a supervisor process signals both the bootloader and child (e.g. via a process group) to avoid signalling the child twice. |
看我码这么多文字的份上点个赞再走啊~(❤ ω ❤)