javax.validation的一系列注解可以帮我们完成参数校验,免去繁琐的串行校验
1、首先就是在项目中引入依赖,在SpringBoot中spring-boot-starter-web(springbootweb启动器)依赖的时候中,内部已经依赖了 hibernate-validator 依赖包
<!-- jsr 303 --> <dependency><groupId>javax.validation</groupId><artifactId>validation-api</artifactId><version>2.0.1.Final</version> </dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate.validator/hibernate-validator --> <dependency><groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId><artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> </dependency>
2、常见注解说明
a、@NotNull:不能为null,但可以为empty(""," "," ")
b、@NotEmpty:不能为null,而且长度必须大于0 (" "," ")
c、@NotBlank:只能作用在String上,不能为null,而且调用trim()后,长度必须大于0("test")
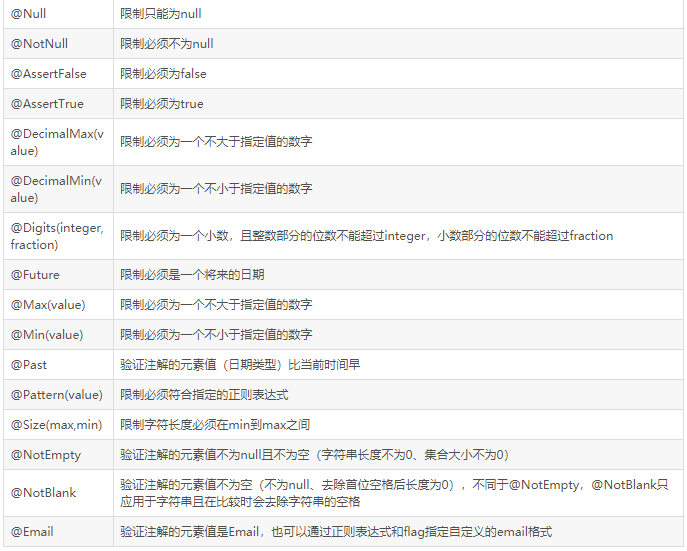
| 验证注解 | 验证的数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @AssertFalse | Boolean,boolean | 验证注解的元素值是false |
| @AssertTrue | Boolean,boolean | 验证注解的元素值是true |
| @NotNull | 任意类型 | 验证注解的元素值不是null |
| @Null | 任意类型 | 验证注解的元素值是null |
| @Min(value=值) | BigDecimal,BigInteger, byte,short, int, long,等任何Number或CharSequence(存储的是数字)子类型 | 验证注解的元素值大于等于@Min指定的value值 |
| @Max(value=值) | 和@Min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值小于等于@Max指定的value值 |
| @DecimalMin(value=值) | 和@Min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值大于等于@ DecimalMin指定的value值 |
| @DecimalMax(value=值) | 和@Min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值小于等于@ DecimalMax指定的value值 |
| @Digits(integer=整数位数, fraction=小数位数) | 和@Min要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值的整数位数和小数位数上限 |
| @Size(min=下限, max=上限) | 字符串、Collection、Map、数组等 | 验证注解的元素值的在min和max(包含)指定区间之内,如字符长度、集合大小 |
| @Past | java.util.Date,java.util.Calendar;Joda Time类库的日期类型 | 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间早 |
| @Future | 与@Past要求一样 | 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间晚 |
| @NotBlank | CharSequence子类型 | 验证注解的元素值不为空(不为null、去除首位空格后长度为0),不同于@NotEmpty,@NotBlank只应用于字符串且在比较时会去除字符串的首位空格 |
| @Length(min=下限, max=上限) | CharSequence子类型 | 验证注解的元素值长度在min和max区间内 |
| @NotEmpty | CharSequence子类型、Collection、Map、数组 | 验证注解的元素值不为null且不为空(字符串长度不为0、集合大小不为0) |
| @Range(min=最小值, max=最大值) | BigDecimal,BigInteger,CharSequence, byte, short, int, long等原子类型和包装类型 | 验证注解的元素值在最小值和最大值之间 |
| @Email(regexp=正则表达式,flag=标志的模式) | CharSequence子类型(如String) | 验证注解的元素值是Email,也可以通过regexp和flag指定自定义的email格式 |
| @Pattern(regexp=正则表达式,flag=标志的模式) | String,任何CharSequence的子类型 | 验证注解的元素值与指定的正则表达式匹配 |
| @Valid | 任何非原子类型 | 指定递归验证关联的对象如用户对象中有个地址对象属性,如果想在验证用户对象时一起验证地址对象的话,在地址对象上加@Valid注解即可级联验证 |
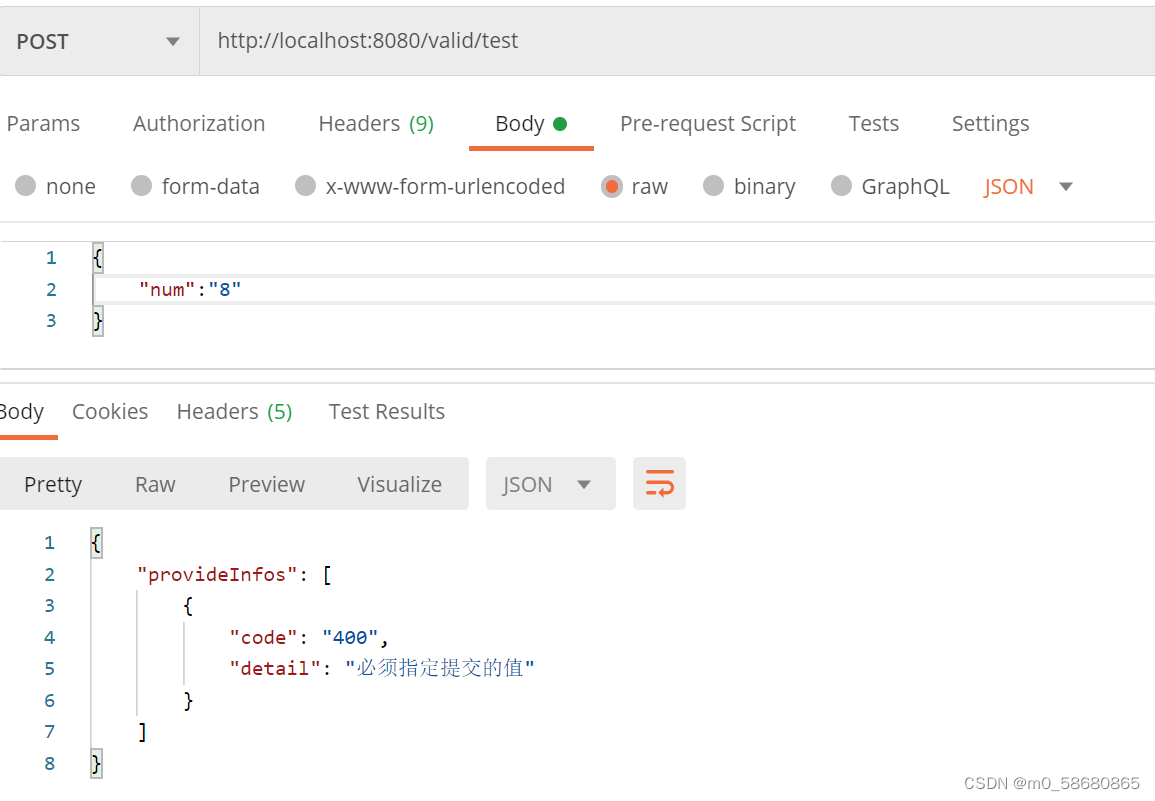
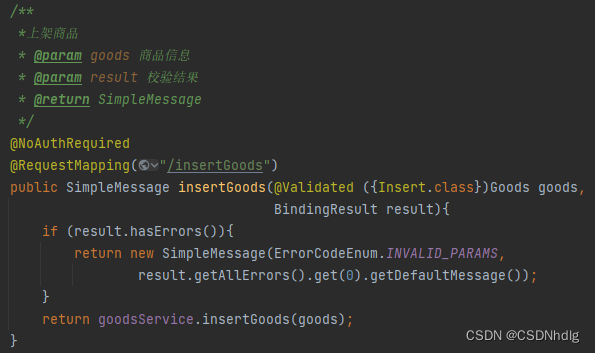
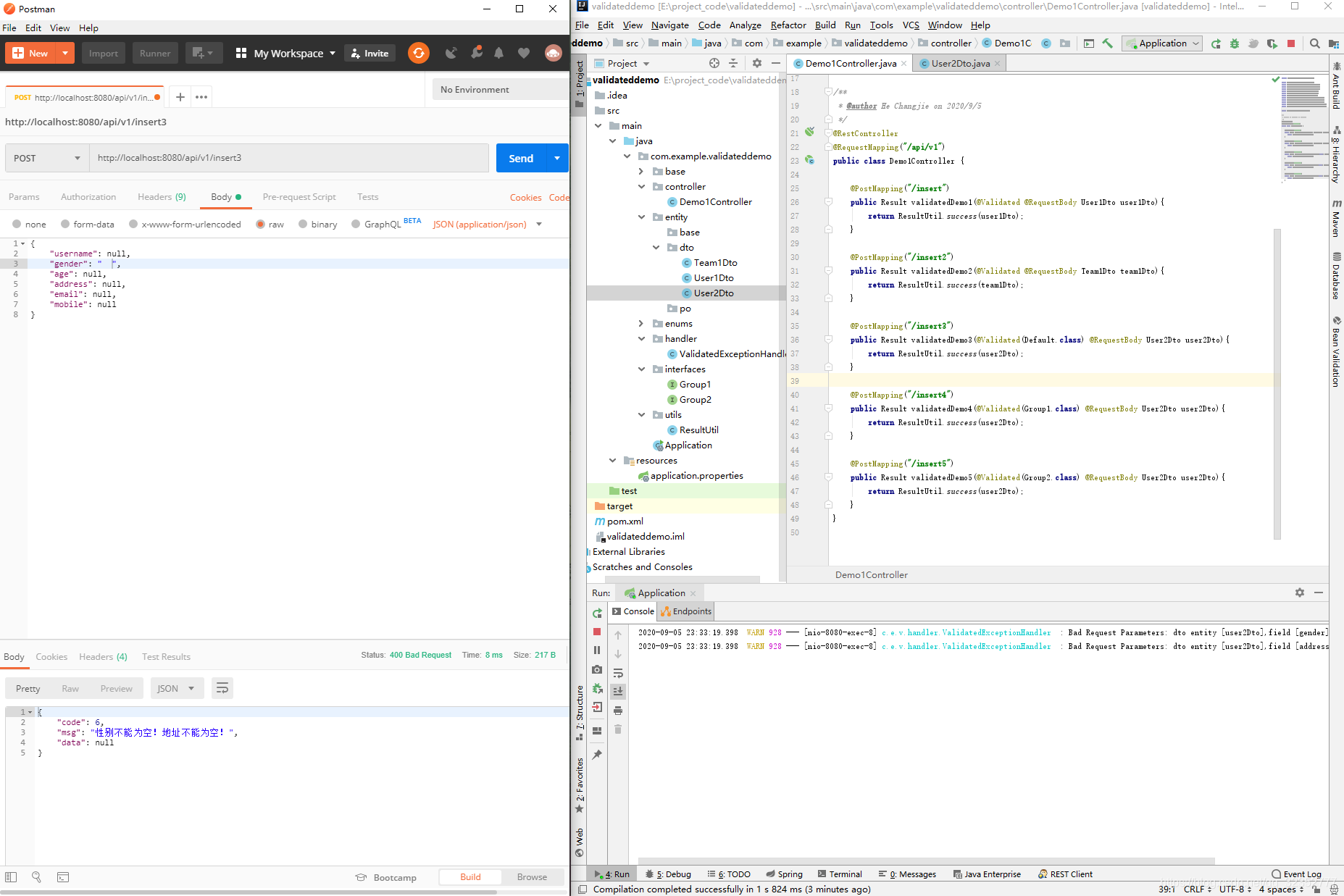
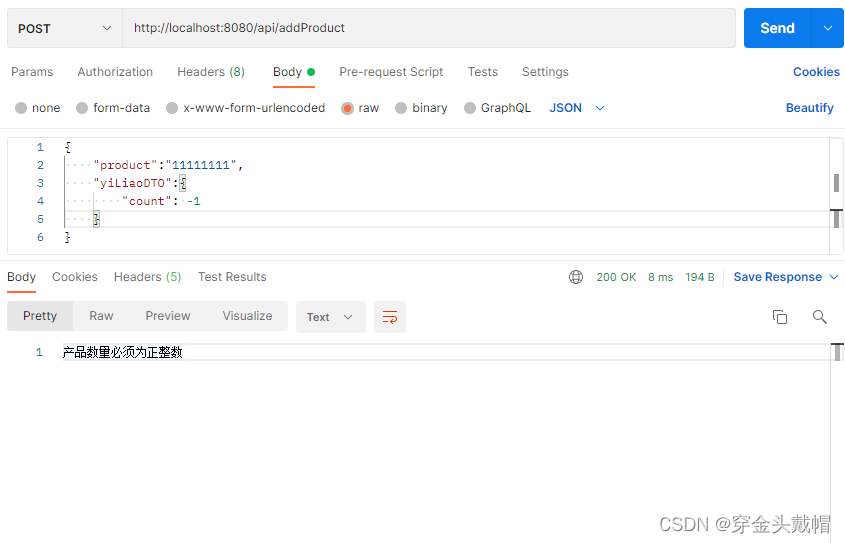
3、实战使用
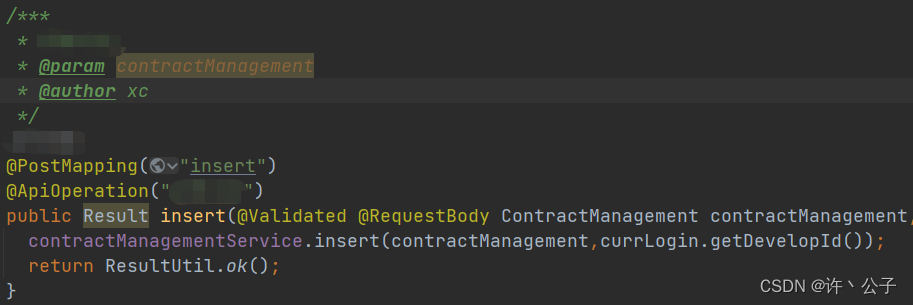
a>在控制层声明注解
b>对实体类的参数注解标注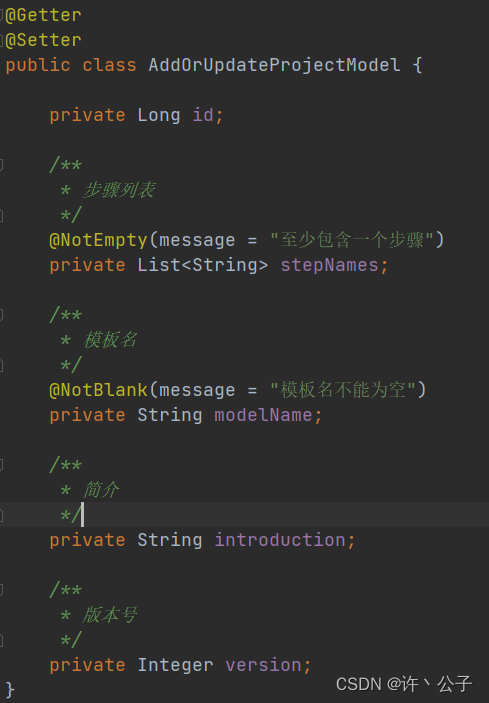
c>测试

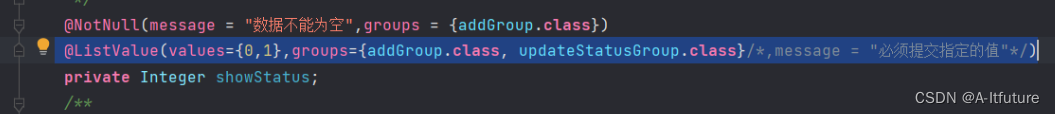
4、自定义参数注解
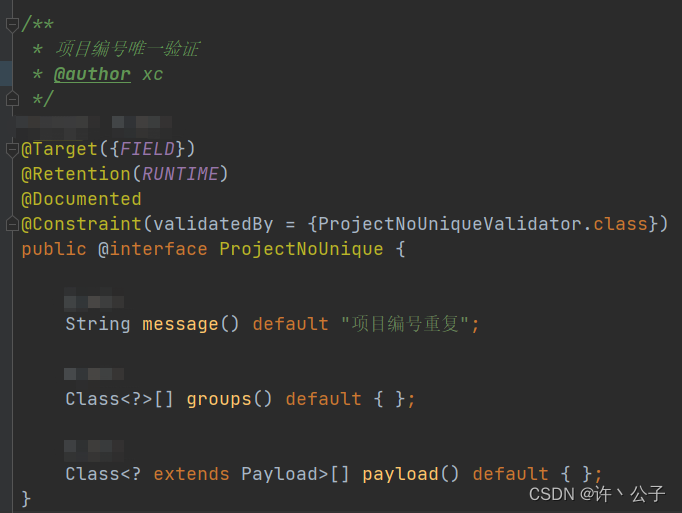
public class ProjectNoUniqueValidator implements ConstraintValidator<ProjectNoUnique, String> {@Overridepublic void initialize(ProjectNoUnique constraintAnnotation) {}@Overridepublic boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {}5、groups的校验
a>先定义groups的分组接口Create和Update
import javax.validation.groups.Default;
public interface Create extends Default {
}
import javax.validation.groups.Default;
public interface Update extends Default{
}
b>再在需要校验的地方@Validated声明校验组
/**
* 走参数校验注解的 groups 组合校验
*
* @param userDTO
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/update/groups")
public RspDTO update(@RequestBody @Validated(Update.class) UserDTO userDTO) {
userService.updateById(userDTO);
return RspDTO.success();
}
c>在DTO中的字段上定义好groups = {}的分组类型
@Data
public class UserDTO implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/*** 用户ID*/
@NotNull(message = "用户id不能为空", groups = Update.class)
private Long userId;
/**
* 用户名
*/
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空")
@Length(max = 20, message = "用户名不能超过20个字符", groups = {Create.class, Update.class})
@Pattern(regexp = "^[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9\\*]*$", message = "用户昵称限制:最多20字符,包含文字、字母和数字")
private String username;
/**
* 手机号
*/
@NotBlank(message = "手机号不能为空")
@Pattern(regexp = "^[1][3,4,5,6,7,8,9][0-9]{9}$", message = "手机号格式有误", groups = {Create.class, Update.class})
private String mobile;
/**
* 性别
*/
private String sex;
/**
* 邮箱
*/
@NotBlank(message = "联系邮箱不能为空")
@Email(message = "邮箱格式不对")
private String email;
/**
* 密码
*/
private String password;
/*** 创建时间 */
@Future(message = "时间必须是将来时间", groups = {Create.class})
private Date createTime;
}