Callable
创建线程有四种方式:
- 继承Thread类
- 实现Runnable接口
- Callable接口
- 线程池
前两种前面说过了, Runnable接口是比较常用的, 因为在Java中继承是很重要的, 不能随便使用, 但是Runnable接口有一个缺点, run()方法没有返回值, 也就是当线程结束时, 不能返回结果, 为了能返回结果, 在JDK1.5以后出现了Callable接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {/*** Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.** @return computed result* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result*/V call() throws Exception;
}
Callable接口中的call()方法可以用来处理任务并返回一个结果, 如果无法处理, 则会抛出异常。
Runnable和Callable的区别:
- Callable规定的方法是call(), Runnable规定的方法是run()
- Callable的任务执行后可返回值, 而Runnable的任务是不能返回值
- call()方法可以抛出异常, run()方法不能
下面就写一个简单的类实现Callable接口:
//返回一个10以内的随机数
class GetNumber implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {return new Random().nextInt(10);}
}
但是当我们想要去创建这样一个线程去测试的时候发现, Thread的构造方法里没有一个是需要传入Callable接口的, 只能传入Runnable接口, 那么有什么方法可以让Callable接口转成Runnable接口呢?
FutureTask
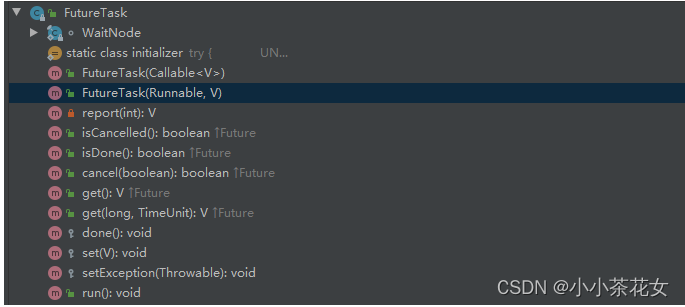
先来看一下FutureTask的继承结构
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-srzBASld-1650026154305)(/img/2022-04-06/01.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c343f0c4e0ab4e4c86f91eb3bda491f9.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBAYVl1SXNBeVU=,size_12,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
FutureTask是Runnable的一个实现类, 再来看一下FutureTask的构造方法
/*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Callable}.** @param callable the callable task* @throws NullPointerException if the callable is null*/
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {if (callable == null)throw new NullPointerException();this.callable = callable;this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
需要传入一个Callable接口, 那么使用FutureTask就可以将Callable接口转成Runnable接口了
再来看一下FutureTask的另一个构造方法
/*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Runnable}, and arrange that {@code get} will return the* given result on successful completion.** @param runnable the runnable task* @param result the result to return on successful completion. If* you don't need a particular result, consider using* constructions of the form:* {@code Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Void>(runnable, null)}* @throws NullPointerException if the runnable is null*/
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
创建一个FutureTask将在运行, 执行给定Runnable, 安排get()将返回给定的成功完成。
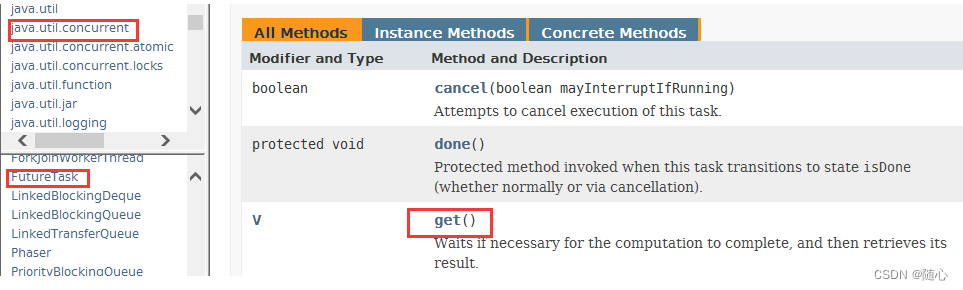
最后看一下FutureTask的常用方法
get(), 如果有必要等待计算完成, 然后获取它的结果isDone(), 如果正常终止, 或是发生异常, 或是手动取消, 返回true
使用FutureTask来完成我们的案例
public class CallableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//普通创建FutureTask<Integer> integerFutureTask1 = new FutureTask<>(new GetNumber());//Lambda表达式创建FutureTask<Integer> integerFutureTask2 = new FutureTask<>(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " come in callable!");//返回一个10以内的随机数return new Random().nextInt(10);});//创建线程new Thread(integerFutureTask1, "tom").start();new Thread(integerFutureTask2, "jerry").start();//打印结果System.out.println("tom get " + integerFutureTask1.get());System.out.println("jerry get " + integerFutureTask2.get());//主线程结束System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " over!");}
}
class GetNumber implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " come in callable!");//返回一个10以内的随机数return new Random().nextInt(10);}
}
查看运行结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-d6OCOpIi-1650026154307)(/img/2022-04-06/02.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/985feee2af9d4134a07cbffa83fc79e6.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBAYVl1SXNBeVU=,size_17,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
运行成功!
我的个人主页: www.ayu.link
本文连接: ┏ (゜ω゜)=☞