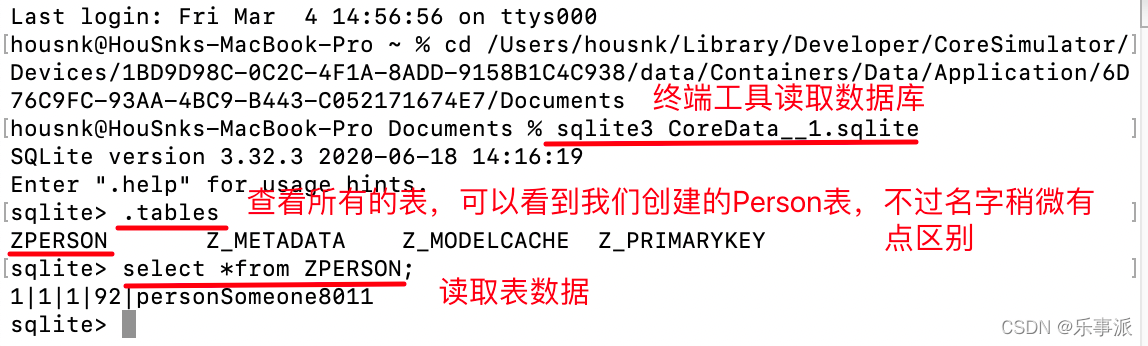
Core Data数据持久化是对SQLite的一个升级,它是ios集成的,在说Core Data之前,我们先说说在CoreData中使用的几个类。
(1)NSManagedObjectModel(被管理的对象模型)
相当于实体,不过它包含 了实体间的关系
(2)NSManagedObjectContext(被管理的对象上下文)
操作实际内容
作用:插入数据 查询 更新 删除
(3)NSPersistentStoreCoordinator(持久化存储助理)
相当于数据库的连接器
(4)NSFetchRequest(获取数据的请求)
相当于查询语句
(5)NSPredicate(相当于查询条件)
(6)NSEntityDescription(实体结构)
(7)后缀名为.xcdatamodel的包
里面的.xcdatamodel文件,用数据模型编辑器编辑
编译后为.momd或.mom文件,这就是为什么文件中没有这个东西,而我们的程序中用到这个东西而不会报错的原因
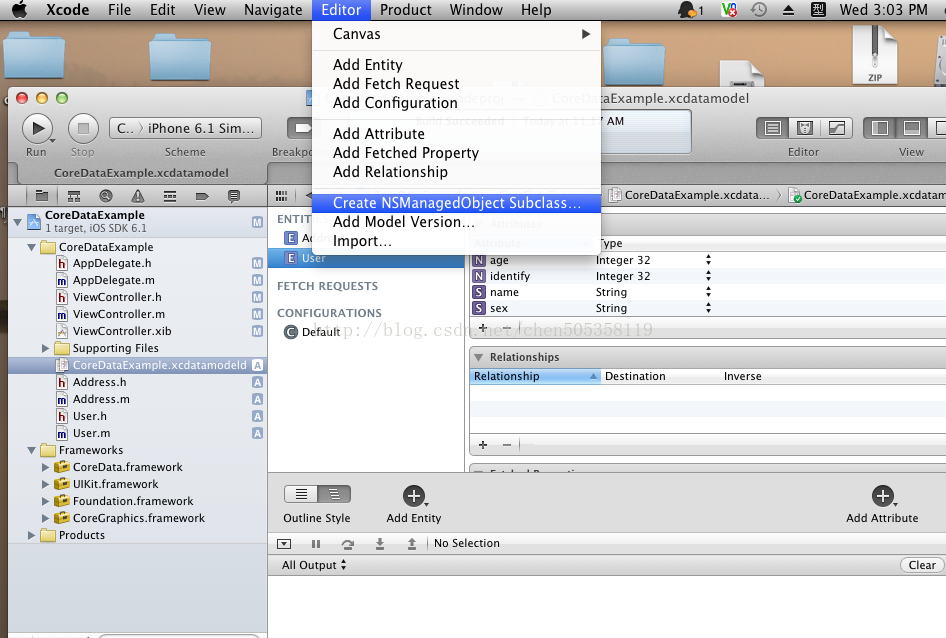
首先我们要建立模型对象
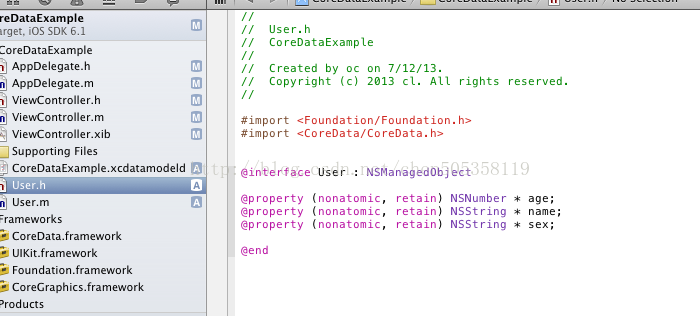
其次我们要生成模型对象的实体User,它是继承NSManagedObjectModel的
点击之后你会发现它会自动的生成User,现在主要说一下,生成的User对象是这种形式的
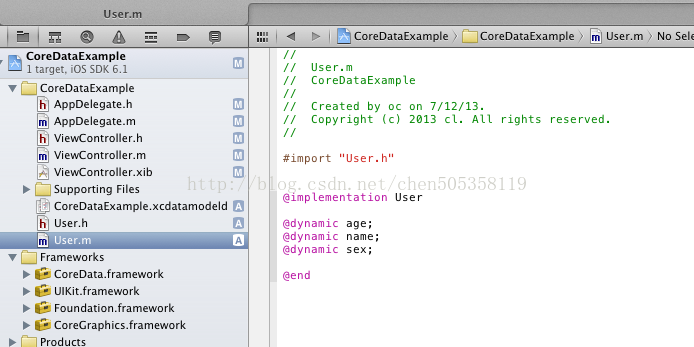
这里解释一下dynamic 平常我们接触的是synthesize
dynamic和synthesize有什么区别呢?它的setter和getter方法不能自已定义
打开CoreData的SQL语句输出开关
1.打开Product,点击EditScheme...2.点击Arguments,在ArgumentsPassed On Launch中添加2项
1> -com.apple.CoreData.SQLDebug
2> 1
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import <CoreData/CoreData.h>
@class ViewController;@interface AppDelegate : UIResponder <UIApplicationDelegate>@property (strong, nonatomic) UIWindow *window;@property (strong, nonatomic) ViewController *viewController;@property(strong,nonatomic,readonly)NSManagedObjectModel* managedObjectModel;@property(strong,nonatomic,readonly)NSManagedObjectContext* managedObjectContext;@property(strong,nonatomic,readonly)NSPersistentStoreCoordinator* persistentStoreCoordinator;
@end#import "AppDelegate.h"#import "ViewController.h"@implementation AppDelegate
@synthesize managedObjectModel=_managedObjectModel;
@synthesize managedObjectContext=_managedObjectContext;
@synthesize persistentStoreCoordinator=_persistentStoreCoordinator;
- (void)dealloc
{[_window release];[_viewController release];[_managedObjectContext release];[_managedObjectModel release];[_persistentStoreCoordinator release];[super dealloc];
}- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{self.window = [[[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]] autorelease];// Override point for customization after application launch.self.viewController = [[[ViewController alloc] initWithNibName:@"ViewController" bundle:nil] autorelease];self.window.rootViewController = self.viewController;[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];return YES;
}- (void)applicationWillResignActive:(UIApplication *)application
{// Sent when the application is about to move from active to inactive state. This can occur for certain types of temporary interruptions (such as an incoming phone call or SMS message) or when the user quits the application and it begins the transition to the background state.// Use this method to pause ongoing tasks, disable timers, and throttle down OpenGL ES frame rates. Games should use this method to pause the game.
}- (void)applicationDidEnterBackground:(UIApplication *)application
{// Use this method to release shared resources, save user data, invalidate timers, and store enough application state information to restore your application to its current state in case it is terminated later. // If your application supports background execution, this method is called instead of applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.
}- (void)applicationWillEnterForeground:(UIApplication *)application
{// Called as part of the transition from the background to the inactive state; here you can undo many of the changes made on entering the background.
}- (void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application
{// Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while the application was inactive. If the application was previously in the background, optionally refresh the user interface.
}- (void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application
{// Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:.
}
//托管对象
-(NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel
{if (_managedObjectModel!=nil) {return _managedObjectModel;}
// NSURL* modelURL=[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"CoreDataExample" withExtension:@"momd"];
// _managedObjectModel=[[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];_managedObjectModel=[[NSManagedObjectModel mergedModelFromBundles:nil] retain];return _managedObjectModel;
}
//托管对象上下文
-(NSManagedObjectContext *)managedObjectContext
{if (_managedObjectContext!=nil) {return _managedObjectContext;}NSPersistentStoreCoordinator* coordinator=[self persistentStoreCoordinator];if (coordinator!=nil) {_managedObjectContext=[[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] initWithConcurrencyType:NSMainQueueConcurrencyType];[_managedObjectContext setPersistentStoreCoordinator:coordinator];}return _managedObjectContext;
}
//持久化存储协调器
-(NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator
{if (_persistentStoreCoordinator!=nil) {return _persistentStoreCoordinator;}
// NSURL* storeURL=[[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"CoreaDataExample.CDBStore"];
// NSFileManager* fileManager=[NSFileManager defaultManager];
// if(![fileManager fileExistsAtPath:[storeURL path]])
// {
// NSURL* defaultStoreURL=[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"CoreDataExample" withExtension:@"CDBStore"];
// if (defaultStoreURL) {
// [fileManager copyItemAtURL:defaultStoreURL toURL:storeURL error:NULL];
// }
// }NSString* docs=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject];NSURL* storeURL=[NSURL fileURLWithPath:[docs stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"CoreDataExample.sqlite"]];NSLog(@"path is %@",storeURL);NSError* error=nil;_persistentStoreCoordinator=[[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {NSLog(@"Error: %@,%@",error,[error userInfo]);}return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
//-(NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory
//{
// return [[[NSFileManager defaultManager] URLsForDirectory:NSDocumentDirectory inDomains:NSUserDomainMask] lastObject];
//}
@end#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import "AppDelegate.h"
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *nameText;
@property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *ageText;
@property (retain, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *sexText;
@property(nonatomic,retain)AppDelegate* myAppDelegate;
- (IBAction)addIntoDataSource:(id)sender;
- (IBAction)query:(id)sender;
- (IBAction)update:(id)sender;
- (IBAction)del:(id)sender;#import "ViewController.h"
#import "User.h"
@interface ViewController ()@end@implementation ViewController- (void)viewDidLoad
{[super viewDidLoad];// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib._myAppDelegate=(AppDelegate *)[[UIApplication sharedApplication] delegate];
}- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning
{[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}- (void)dealloc {[_nameText release];[_ageText release];[_sexText release];[super dealloc];
}
//插入数据
- (IBAction)addIntoDataSource:(id)sender {User* user=(User *)[NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"User" inManagedObjectContext:self.myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext];[user setName:_nameText.text];[user setAge:[NSNumber numberWithInteger:[_ageText.text integerValue]]];[user setSex:_sexText.text];NSError* error;BOOL isSaveSuccess=[_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext save:&error];if (!isSaveSuccess) {NSLog(@"Error:%@",error);}else{NSLog(@"Save successful!");}}
//查询
- (IBAction)query:(id)sender {NSFetchRequest* request=[[NSFetchRequest alloc] init];NSEntityDescription* user=[NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"User" inManagedObjectContext:_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext];[request setEntity:user];
// NSSortDescriptor* sortDescriptor=[[NSSortDescriptor alloc] initWithKey:@"name" ascending:YES];
// NSArray* sortDescriptions=[[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:sortDescriptor, nil];
// [request setSortDescriptors:sortDescriptions];
// [sortDescriptions release];
// [sortDescriptor release];NSError* error=nil;NSMutableArray* mutableFetchResult=[[_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext executeFetchRequest:request error:&error] mutableCopy];if (mutableFetchResult==nil) {NSLog(@"Error:%@",error);}NSLog(@"The count of entry: %i",[mutableFetchResult count]);for (User* user in mutableFetchResult) {NSLog(@"name:%@----age:%@------sex:%@",user.name,user.age,user.sex);}[mutableFetchResult release];[request release];
}
//更新
- (IBAction)update:(id)sender {NSFetchRequest* request=[[NSFetchRequest alloc] init];NSEntityDescription* user=[NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"User" inManagedObjectContext:_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext];[request setEntity:user];//查询条件NSPredicate* predicate=[NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name==%@",@"chen"];[request setPredicate:predicate];NSError* error=nil;NSMutableArray* mutableFetchResult=[[_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext executeFetchRequest:request error:&error] mutableCopy];if (mutableFetchResult==nil) {NSLog(@"Error:%@",error);}NSLog(@"The count of entry: %i",[mutableFetchResult count]);//更新age后要进行保存,否则没更新for (User* user in mutableFetchResult) {[user setAge:[NSNumber numberWithInt:12]];}[_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext save:&error];[mutableFetchResult release];[request release];}
//删除
- (IBAction)del:(id)sender {NSFetchRequest* request=[[NSFetchRequest alloc] init];NSEntityDescription* user=[NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"User" inManagedObjectContext:_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext];[request setEntity:user];NSPredicate* predicate=[NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name==%@",@"chen"];[request setPredicate:predicate];NSError* error=nil;NSMutableArray* mutableFetchResult=[[_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext executeFetchRequest:request error:&error] mutableCopy];if (mutableFetchResult==nil) {NSLog(@"Error:%@",error);}NSLog(@"The count of entry: %i",[mutableFetchResult count]);for (User* user in mutableFetchResult) {[_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext deleteObject:user];}if ([_myAppDelegate.managedObjectContext save:&error]) {NSLog(@"Error:%@,%@",error,[error userInfo]);}
}
@end对于多线程它是不安全的,需要进行特殊处理下次再说吧