学习资料参考:
张平.《OpenCV算法精解:基于Python与C++》.[Z].北京.电子工业出版社.2017.
原理
平面的物体若在三维空间发生了旋转,那么这就是投影变换。平面的物体可以借助二维投影变换进行三维变换模型化得到修正。
处理函数
c++中的getPerspectiveTransform(src,dst)函数需要四组对应的坐标变换,返回值类型为CV_64F。
//原坐标
Point2f src[]={Point2f(0,0),Point2f(200.0,0),Point2f(0,200.0),Point2f(200,200)};//投影变换后坐标
Point2f dst[]={Point2f(100,20),Point2f(200,20),Point2f(50,70),Point2f(250,70)};//计算投影变换矩阵
Mat p = getPerspectiveTransform(src,dst);
当然上述是能够确定坐标的情况下的实现,一般情况下,不会这么做。下面提供一种交互的方式确定坐标,完成投影变换:
#include<opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
Mat I;//原图
Mat pI;//投影变换后的图
Point2f IPoint, pIPoint;
int i = 0, j = 0;
Point2f src[4],dst[4]; //原坐标与变换后的坐标
void mouse_I(int event, int x, int y, int flags, void* param) {switch (event) {case EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:IPoint = Point2f(x, y);break;case EVENT_LBUTTONUP:src[i] = IPoint;circle(I, src[i], 7, Scalar(0), 3);i += 1;break;default:break;}
}
void mouse_pI(int event, int x, int y, int flags, void* param) {switch (event) {case EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:pIPoint = Point2f(x, y);break;case EVENT_LBUTTONUP:dst[j] = pIPoint;circle(pI, dst[j], 7, Scalar(0), 3);j += 1;break;default:break;}
}
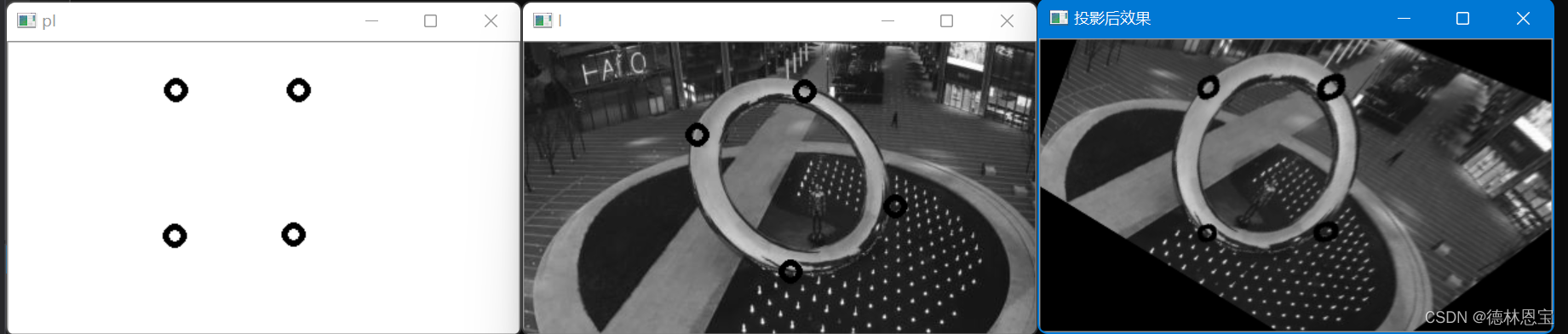
int main() {I = imread("p1.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);if (!I.data)return -1;//输出图像pI = 255 * Mat::ones(I.size(), CV_8UC1);//在原窗口上,定义鼠标事件namedWindow("I", 1);setMouseCallback("I", mouse_I, NULL);//在输出窗口上,定义鼠标事件namedWindow("pI", 1);setMouseCallback("pI", mouse_pI, NULL);imshow("I", I);imshow("pI", pI);while (i != 4 || j != 4) {imshow("I", I);imshow("pI", pI);if (waitKey(50) == 'q')break;}imshow("I", I);imshow("pI", pI);//移除鼠标事件setMouseCallback("I", NULL, NULL);setMouseCallback("pI", NULL, NULL);//计算投影变换矩阵Mat p = getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst);//投影变换Mat result;warpPerspective(I, result, p, pI.size());imshow("投影后效果", result);waitKey(0);return 0;
}
运行结果