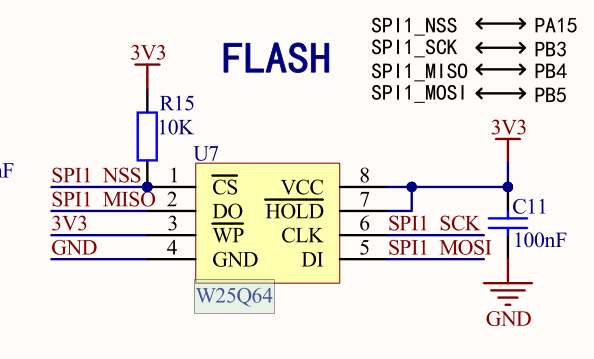
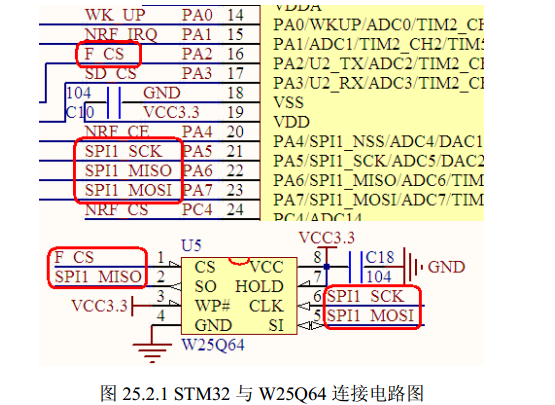
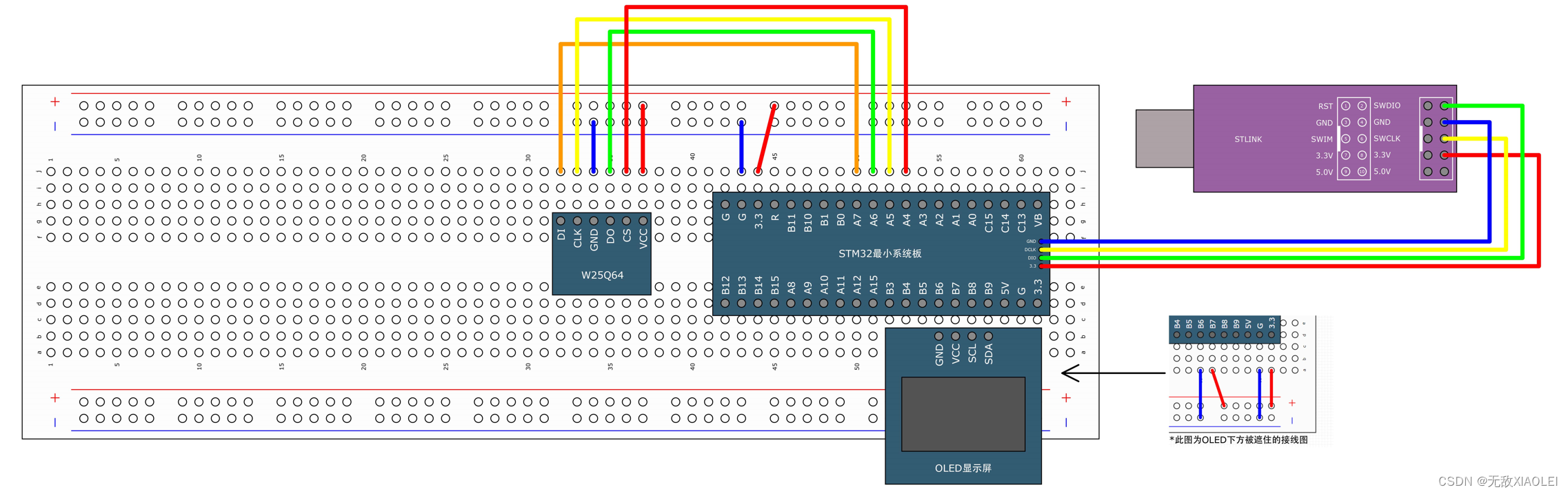
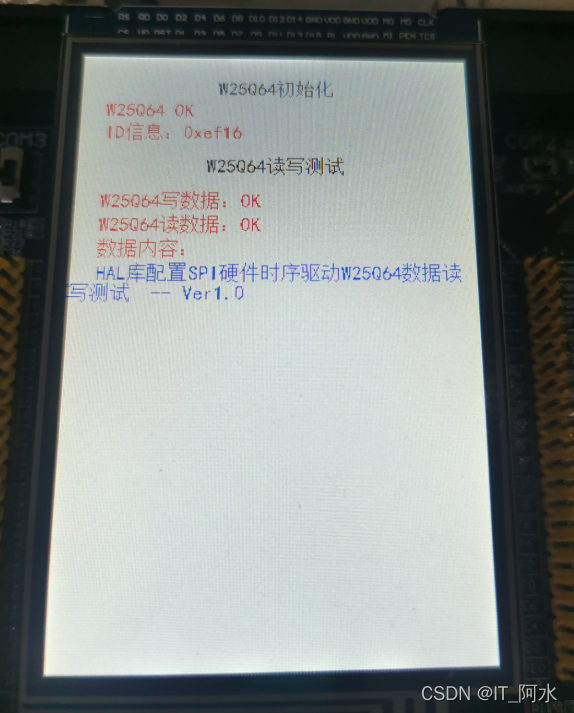
简介
W25Q系列的器件在灵活性和性能方面远远超过普通的串行闪存器件。W25Q64将8M字节的容量分为128个块,每个块大小为64K字节,每个块又分为16个扇区,每个扇区4K个字节。
引脚介绍
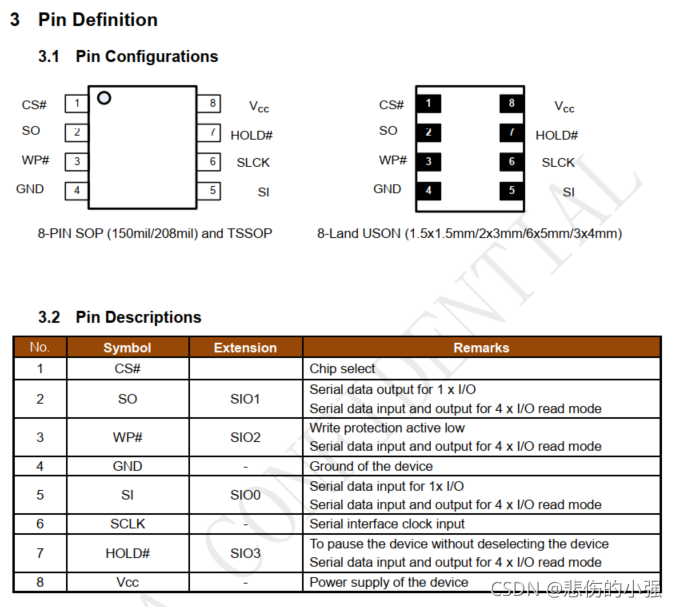
串行数据输入、输出和 IOs(DI、DO 和 IO0、IO1、IO2、IO3)
W25Q64、W25Q16 和 W25Q32 支持标准 SPI、双倍 SPI 和四倍 SPI。标准的 SPI 传输用单向的 DI(输入)引脚连续的写命令、地址或者数据在串行时钟(CLK)的上升沿时写入到芯片内。
写保护(/WP)
写保护引脚(/WP)用来保护状态寄存器。和状态寄存器的块保护位(SEC、TB、BP2、BP1 和BP0)和状态寄存器保护位(SRP)对存储器进行一部分或者全部的硬件保护。/WP 引脚低电平有效。当状态寄存器 2 的 QE 位被置位了,/WP 引脚(硬件写保护)的功能不可用。
保持端(/HOLD)
当/HOLD 引脚是有效时,允许芯片暂停工作。在/CS 为低电平时,当/HOLD 变为低电平,DO 引脚将变为高阻态,在 DI 和 CLK 引脚上的信号将无效。当/HOLD 变为高电平,芯片恢复工作。/HOLD 功能用在当有多个设备共享同一 SPI 总线时。/HOLD 引脚低电平有效。当状态寄存器 2 的 QE 位被置位了,/ HOLD 引脚的功能不可用。
串行时钟(CLK)
串行时钟输入引脚为串行输入和输出操作提供时序。(见 SPI 操作)。
设备数据传输是从高位开始,数据传输的格式为 8bit,数据采样从第二个时间边沿开始,空闲状态时,时钟线 clk 为高电平。
W25Q64操作原理
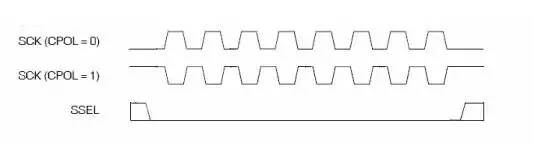
通过SPI接口,用标准的SPI协议发送相应指令给flash,然后flash根据命令进行各种相关操作。
① 写使能:06H
② 读状态寄存器指令:05H
③ 写状态寄存器指令:01H
④ 读数据:03H
⑤ 页写:02H
⑥ 扇区擦除指令:20H
⑦ 块擦除指令:D8H
⑧ 芯片擦除指令:07H
⑨ 掉电指令:B9H
⑩ 读ID指令:90H
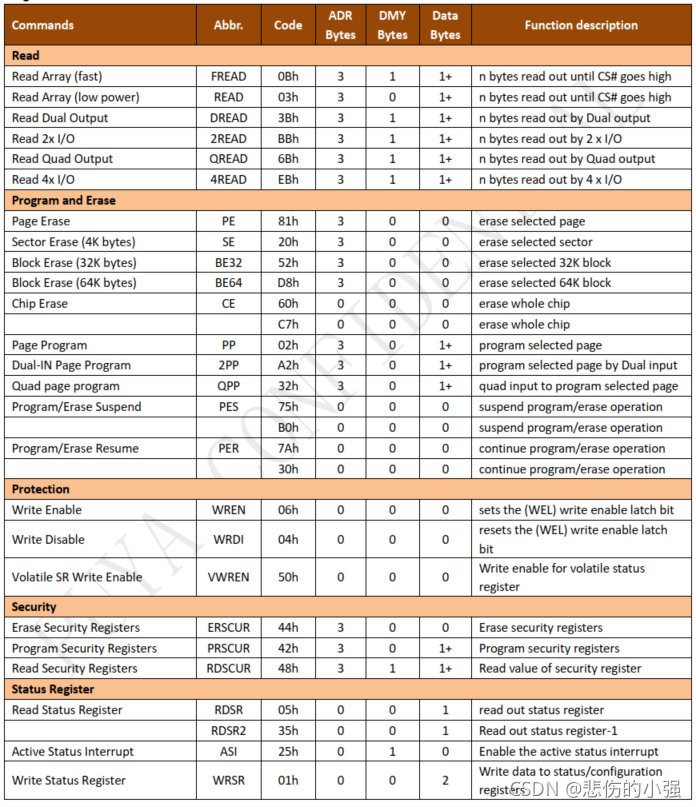

极性CPOL和相位CPHA
(1) CKPOL (Clock Polarity) = CPOL = POL = Polarity = (时钟)极性
(2) CKPHA (Clock Phase) = CPHA = PHA = Phase = (时钟)相位
CPOL和CPHA,分别都可以是0或时1,对应的四种组合就是:

SPI的CPOL,表示当SCLK空闲idle的时候,其电平的值是低电平0还是高电平1:CPOL=0,时钟空闲idle时候的电平是低电平,所以当SCLK有效的时候,就是高电平,就是所谓的active-high。
CPOL=1,时钟空闲idle时候的电平是高电平,所以当SCLK有效的时候,就是低电平,就是所谓的active-low。
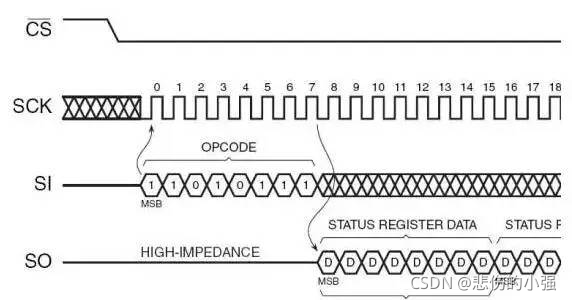
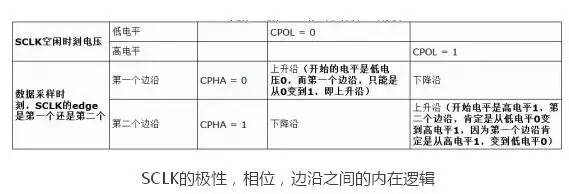
CPHA=0,表示第一个边沿:
对于CPOL=0,idle时候的是低电平,第一个边沿就是从低变到高,所以是上升沿;
对于CPOL=1,idle时候的是高电平,第一个边沿就是从高变到低,所以是下降沿;
CPHA=1,表示第二个边沿:
对于CPOL=0,idle时候的是低电平,第二个边沿就是从高变到低,所以是下降沿;
对于CPOL=1,idle时候的是高电平,第一个边沿就是从低变到高,所以是上升沿;
示例代码
DTSI
w25q64: w25q64@00 {status = "okay";compatible = "rockchip,w25q64";reg = <0x00>;spi-max-frequency = <24000000>;wp-gpio = <&gpio0 12 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; /*GPIO0_B4*/
// spi-cs-high;spi-cpha; /*SPI mode: CPHA = 1*/spi-cpol; /*SPI mode: CPOL = 1*/
};
源码
w25q64.c
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/compat.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_device.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include "w25q64.h"/** This supports access to SPI devices using normal userspace I/O calls.* Note that while traditional UNIX/POSIX I/O semantics are half duplex,* and often mask message boundaries, full SPI support requires full duplex* transfers. There are several kinds of internal message boundaries to* handle chipselect management and other protocol options.** SPI has a character major number assigned. We allocate minor numbers* dynamically using a bitmask. You must use hotplug tools, such as udev* (or mdev with busybox) to create and destroy the /dev/spidevB.C device* nodes, since there is no fixed association of minor numbers with any* particular SPI bus or device.*/
#define SPIDEV_MAJOR 155 /* assigned */
#define N_SPI_MINORS 32 /* ... up to 256 *//*W25Q64 CMD*/
#define WRITE_ENABLE 0x06
#define PAGE_PROGRAM 0x02
#define READ_DATA 0x03
#define WRITE_STATUS_REG 0x01
#define READ_STATUS_REG 0x05
#define CHIP_ERASE 0xc7
#define SECTOR_ERASE 0x20
#define BLOCK_32KB_ERASE 0x52
#define BLOCK_64KB_ERASE 0xD8
#define READ_DEVICE_ID 0x90
#define READ_UID 0x9Fstatic DECLARE_BITMAP(minors, N_SPI_MINORS);/* Bit masks for spi_device.mode management. Note that incorrect* settings for some settings can cause *lots* of trouble for other* devices on a shared bus:** - CS_HIGH ... this device will be active when it shouldn't be* - 3WIRE ... when active, it won't behave as it should* - NO_CS ... there will be no explicit message boundaries; this* is completely incompatible with the shared bus model* - READY ... transfers may proceed when they shouldn't.** REVISIT should changing those flags be privileged?*/
#define SPI_MODE_MASK (SPI_CPHA | SPI_CPOL | SPI_CS_HIGH \| SPI_LSB_FIRST | SPI_3WIRE | SPI_LOOP \| SPI_NO_CS | SPI_READY | SPI_TX_DUAL \| SPI_TX_QUAD | SPI_RX_DUAL | SPI_RX_QUAD)struct spidev_data {dev_t devt;spinlock_t spi_lock;struct spi_device *spi;struct list_head device_entry;/* TX/RX buffers are NULL unless this device is open (users > 0) */struct mutex buf_lock;unsigned users;u8 *tx_buffer;u8 *rx_buffer;u32 speed_hz;unsigned int cur_addr;unsigned wp_gpio;
};static LIST_HEAD(device_list);
static DEFINE_MUTEX(device_list_lock);static unsigned bufsiz = 4096;
module_param(bufsiz, uint, S_IRUGO);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(bufsiz, "data bytes in biggest supported SPI message");/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/static char spi_w25x_status(struct spi_device *spi)
{ int status;char tbuf[]={READ_STATUS_REG};char rbuf[1] = {1};struct spi_transfer t = {.tx_buf = tbuf,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(tbuf),};struct spi_transfer r = {.rx_buf = rbuf,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(rbuf),};struct spi_message m;spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);spi_message_add_tail(&r, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);return rbuf[0];
}
//modified by xzq degain for retry 5 times @20211105
static int spi_w25x_wait_ready(struct spi_device *spi )
{char retval = 1;int retry = 5;dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "wait ready...");do {retval = spi_w25x_status(spi);retval &= 0xff;retval &= 1;retry --;mdelay(5);}while((retval != 0) && (retry != 0));if(retval)dev_err(&spi->dev,"no ready\n");elsedev_dbg(&spi->dev, "OK\n");return 0;
}
//modified by xzq end
static int spi_w25x_write_enable(struct spi_device *spi)
{ int status;char cmd_buf[1] = {WRITE_ENABLE};struct spi_transfer cmd = {.tx_buf = cmd_buf,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(cmd_buf),};struct spi_message m;spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&cmd, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "write enable\n");return status;
}static int spi_read_w25x_id_0(struct spi_device *spi)
{ int status;char tbuf[]={READ_UID};char rbuf[5];struct spi_transfer t = {.tx_buf = tbuf,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(tbuf),};struct spi_transfer r = {.rx_buf = rbuf,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(rbuf),};struct spi_message m;spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);spi_message_add_tail(&r, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);dev_err(&spi->dev, "ID = %02x %02x %02x %02x %02x\n",rbuf[0], rbuf[1], rbuf[2], rbuf[3], rbuf[4]);return status;
}static int
spi_w25x_sector_erase(struct spidev_data *spidev, unsigned long size)
{int status;char cmd[4] = {SECTOR_ERASE};struct spi_device *spi = spidev->spi;struct spi_transfer t = {.tx_buf = cmd,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(cmd),};struct spi_message m;unsigned int flash_addr = spidev->cur_addr;int count = (int)size;for ( ; count > 0; count -= W25Q64_SECTOR) {cmd[1] = (unsigned char)((flash_addr & 0xff0000) >> 16);cmd[2] = (unsigned char)((flash_addr & 0xff00) >> 8);cmd[3] = (unsigned char)(flash_addr & 0xff);spi_w25x_write_enable(spi);spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);spi_w25x_wait_ready(spi);dev_dbg(&spi->dev,"start addr: %x, sector erase OK\n", flash_addr);flash_addr += W25Q64_SECTOR;}return status;
}static int
spi_w25x_32kb_block_erase(struct spidev_data *spidev)
{int status;char cmd[4] = {BLOCK_32KB_ERASE};struct spi_device *spi = spidev->spi;struct spi_transfer t = {.tx_buf = cmd,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(cmd),};struct spi_message m;cmd[1] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff0000) >> 16);cmd[2] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff00) >> 8);cmd[3] = (unsigned char)(spidev->cur_addr & 0xff);spi_w25x_write_enable(spi);spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);spi_w25x_wait_ready(spi);dev_dbg(&spi->dev,"32kb block erase OK\n");return status;
}static int
spi_w25x_64kb_block_erase(struct spidev_data *spidev)
{int status;char cmd[4] = {BLOCK_64KB_ERASE};struct spi_device *spi = spidev->spi;struct spi_transfer t = {.tx_buf = cmd,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(cmd),};struct spi_message m;cmd[1] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff0000) >> 16);cmd[2] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff00) >> 8);cmd[3] = (unsigned char)(spidev->cur_addr & 0xff);spi_w25x_write_enable(spi);spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);spi_w25x_wait_ready(spi);dev_dbg(&spi->dev,"64kb block erase OK\n");return status;
}static int spi_w25x_chip_erase(struct spi_device *spi)
{int status;char chip_erase[1] = {CHIP_ERASE};struct spi_transfer erase = {.tx_buf = chip_erase,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(chip_erase),};struct spi_message m;spi_w25x_write_enable(spi);spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&erase, &m);status = spi_sync(spi, &m);spi_w25x_wait_ready(spi);dev_dbg(&spi->dev,"chip erase OK\n");return status;
}static loff_t
spi_w25x_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t offset, int orig)
{loff_t ret = 0;struct spidev_data *spidev;spidev = filp->private_data;switch (orig) {case SEEK_SET:if (offset < 0) {ret = -EINVAL;break;}if ((unsigned int)offset > W25Q64_SIZE) {ret = -EINVAL;break;}spidev->cur_addr = (unsigned int)offset;ret = spidev->cur_addr;break;case SEEK_CUR:if ((spidev->cur_addr + offset) > W25Q64_SIZE) {ret = -EINVAL;break;}if ((spidev->cur_addr + offset) < 0) {ret = -EINVAL;break;}spidev->cur_addr += offset;ret = spidev->cur_addr;break;default:ret = - EINVAL;break;}dev_dbg(&spidev->spi->dev, "set curr addr:%02X\n", (unsigned int)ret);return ret;}static ssize_t
spidev_sync(struct spidev_data *spidev, struct spi_message *message)
{DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);int status;struct spi_device *spi;spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);spi = spidev->spi;spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);if (spi == NULL)status = -ESHUTDOWN;elsestatus = spi_sync(spi, message);if (status == 0)status = message->actual_length;return status;
}static inline ssize_t
spidev_sync_write(struct spidev_data *spidev, size_t len)
{int status;char cmd[1] = {PAGE_PROGRAM};unsigned char addr[3];struct spi_transfer c[] = {{.tx_buf = cmd,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(cmd),},{.tx_buf = addr,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(addr),},};struct spi_transfer t = {.tx_buf = spidev->tx_buffer,.len = len,.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz,};struct spi_message m;addr[0] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff0000) >> 16);addr[1] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff00) >> 8);addr[2] = (unsigned char)(spidev->cur_addr & 0xff);spi_w25x_write_enable(spidev->spi);spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&c[0], &m);spi_message_add_tail(&c[1], &m);spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);status = spidev_sync(spidev, &m);spi_w25x_wait_ready(spidev->spi);return status;
}static inline ssize_t
spidev_sync_read(struct spidev_data *spidev, size_t len)
{int status;char cmd[] = {READ_DATA};unsigned char addr[3];struct spi_transfer t[] = {{.tx_buf = cmd,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(cmd),.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz,},{.tx_buf = addr,.len = ARRAY_SIZE(addr),},{.rx_buf = spidev->rx_buffer,.len = len,.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz,}};struct spi_message m;addr[0] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff0000) >> 16);addr[1] = (unsigned char)((spidev->cur_addr & 0xff00) >> 8);addr[2] = (unsigned char)(spidev->cur_addr & 0xff);spi_message_init(&m);spi_message_add_tail(&t[0], &m);spi_message_add_tail(&t[1], &m);spi_message_add_tail(&t[2], &m);status = spidev_sync(spidev, &m);spi_w25x_wait_ready(spidev->spi);return status;
}/* Read-only message with current device setup */
static ssize_t
spidev_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{struct spidev_data *spidev;ssize_t status = 0;/* chipselect only toggles at start or end of operation */if (count > bufsiz)return -EMSGSIZE;spidev = filp->private_data;mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);status = spidev_sync_read(spidev, count);if (status > 0) {unsigned long missing;missing = copy_to_user(buf, spidev->rx_buffer, status);if (missing == status)status = -EFAULT;elsestatus = status - missing;}mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);return status;
}/* Write-only message with current device setup */
static ssize_t
spidev_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{struct spidev_data *spidev;ssize_t status = 0;unsigned long missing;/* chipselect only toggles at start or end of operation */if (count > bufsiz)return -EMSGSIZE;spidev = filp->private_data;gpio_set_value(spidev->wp_gpio, 1);mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);missing = copy_from_user(spidev->tx_buffer, buf, count);if (missing == 0)status = spidev_sync_write(spidev, count);elsestatus = -EFAULT;mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);gpio_set_value(spidev->wp_gpio, 0);return status;
}static long
spidev_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{int err = 0;int retval = 0;struct spidev_data *spidev;struct spi_device *spi;u32 tmp;/* Check type and command number */if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != W25Q64_MAGIC)return -ENOTTY;/* Check access direction once here; don't repeat below.* IOC_DIR is from the user perspective, while access_ok is* from the kernel perspective; so they look reversed.*/if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_READ)err = !access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE,(void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));if (err == 0 && _IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_WRITE)err = !access_ok(VERIFY_READ,(void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));if (err)return -EFAULT;/* guard against device removal before, or while,* we issue this ioctl.*/spidev = filp->private_data;spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);spi = spi_dev_get(spidev->spi);spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);if (spi == NULL)return -ESHUTDOWN;/* use the buffer lock here for triple duty:* - prevent I/O (from us) so calling spi_setup() is safe;* - prevent concurrent SPI_IOC_WR_* from morphing* data fields while SPI_IOC_RD_* reads them;* - SPI_IOC_MESSAGE needs the buffer locked "normally".*/mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);switch (cmd) {/* read requests */case W25Q64_IOC_SECTOR_ERASE:retval = spi_w25x_sector_erase(spidev, arg);break;case W25Q64_IOC_32KB_BLOCK_ERASE:retval = spi_w25x_32kb_block_erase(spidev);break;case W25Q64_IOC_64KB_BLOCK_ERASE:retval = spi_w25x_64kb_block_erase(spidev);break;case W25Q64_IOC_CHIP_ERASE:retval = spi_w25x_chip_erase(spi);break;case SPI_IOC_RD_MODE:retval = __put_user(spi->mode & SPI_MODE_MASK,(__u8 __user *)arg);break;case SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32:retval = __put_user(spi->mode & SPI_MODE_MASK,(__u32 __user *)arg);break;case SPI_IOC_RD_LSB_FIRST:retval = __put_user((spi->mode & SPI_LSB_FIRST) ? 1 : 0,(__u8 __user *)arg);break;case SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD:retval = __put_user(spi->bits_per_word, (__u8 __user *)arg);break;case SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ:retval = __put_user(spidev->speed_hz, (__u32 __user *)arg);break;/* write requests */case SPI_IOC_WR_MODE:case SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32:if (cmd == SPI_IOC_WR_MODE)retval = __get_user(tmp, (u8 __user *)arg);elseretval = __get_user(tmp, (u32 __user *)arg);if (retval == 0) {u32 save = spi->mode;if (tmp & ~SPI_MODE_MASK) {retval = -EINVAL;break;}tmp |= spi->mode & ~SPI_MODE_MASK;spi->mode = (u16)tmp;retval = spi_setup(spi);if (retval < 0)spi->mode = save;elsedev_dbg(&spi->dev, "spi mode %x\n", tmp);}break;case SPI_IOC_WR_LSB_FIRST:retval = __get_user(tmp, (__u8 __user *)arg);if (retval == 0) {u32 save = spi->mode;if (tmp)spi->mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;elsespi->mode &= ~SPI_LSB_FIRST;retval = spi_setup(spi);if (retval < 0)spi->mode = save;elsedev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%csb first\n",tmp ? 'l' : 'm');}break;case SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD:retval = __get_user(tmp, (__u8 __user *)arg);if (retval == 0) {u8 save = spi->bits_per_word;spi->bits_per_word = tmp;retval = spi_setup(spi);if (retval < 0)spi->bits_per_word = save;elsedev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%d bits per word\n", tmp);}break;case SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ:retval = __get_user(tmp, (__u32 __user *)arg);if (retval == 0) {u32 save = spi->max_speed_hz;spi->max_speed_hz = tmp;retval = spi_setup(spi);if (retval >= 0)spidev->speed_hz = tmp;elsedev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%d Hz (max)\n", tmp);spi->max_speed_hz = save;}break;default:return -EINVAL;}mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);spi_dev_put(spi);return retval;
}#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
static long
spidev_compat_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{return spidev_ioctl(filp, cmd, (unsigned long)compat_ptr(arg));
}
#else
#define spidev_compat_ioctl NULL
#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */static int spidev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{struct spidev_data *spidev;int status = -ENXIO;mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);list_for_each_entry(spidev, &device_list, device_entry) {if (spidev->devt == inode->i_rdev) {status = 0;break;}}if (status) {pr_debug("spidev: nothing for minor %d\n", iminor(inode));goto err_find_dev;}if (!spidev->tx_buffer) {spidev->tx_buffer = kmalloc(bufsiz, GFP_KERNEL);if (!spidev->tx_buffer) {dev_err(&spidev->spi->dev, "open/ENOMEM\n");status = -ENOMEM;goto err_find_dev;}}if (!spidev->rx_buffer) {spidev->rx_buffer = kmalloc(bufsiz, GFP_KERNEL);if (!spidev->rx_buffer) {dev_err(&spidev->spi->dev, "open/ENOMEM\n");status = -ENOMEM;goto err_alloc_rx_buf;}}spidev->users++;filp->private_data = spidev;mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);return 0;err_alloc_rx_buf:kfree(spidev->tx_buffer);spidev->tx_buffer = NULL;
err_find_dev:mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);return status;
}static int spidev_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{struct spidev_data *spidev;mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);spidev = filp->private_data;filp->private_data = NULL;/* last close? */spidev->users--;if (!spidev->users) {int dofree;kfree(spidev->tx_buffer);spidev->tx_buffer = NULL;kfree(spidev->rx_buffer);spidev->rx_buffer = NULL;spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);if (spidev->spi)spidev->speed_hz = spidev->spi->max_speed_hz;/* ... after we unbound from the underlying device? */dofree = (spidev->spi == NULL);spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);if (dofree)kfree(spidev);}mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);return 0;
}static const struct file_operations spidev_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,/* REVISIT switch to aio primitives, so that userspace* gets more complete API coverage. It'll simplify things* too, except for the locking.*/.write = spidev_write,.read = spidev_read,.unlocked_ioctl = spidev_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = spidev_compat_ioctl,.open = spidev_open,.release = spidev_release,.llseek = spi_w25x_llseek,
};/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*//* The main reason to have this class is to make mdev/udev create the* /dev/spidevB.C character device nodes exposing our userspace API.* It also simplifies memory management.*/static struct class *spidev_class;#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static const struct of_device_id spidev_dt_ids[] = {{ .compatible = "rockchip,w25q64" },{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, spidev_dt_ids);
#endif/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/static int spidev_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
{struct spidev_data *spidev;struct device_node *np = spi->dev.of_node;int status;unsigned long minor;dev_err(&spi->dev, "probe,rk3399.0\n");/** spidev should never be referenced in DT without a specific* compatible string, it is a Linux implementation thing* rather than a description of the hardware.*/if (spi->dev.of_node && !of_match_device(spidev_dt_ids, &spi->dev)) {dev_err(&spi->dev, "buggy DT: spidev listed directly in DT\n");WARN_ON(spi->dev.of_node &&!of_match_device(spidev_dt_ids, &spi->dev));}/* Allocate driver data */spidev = kzalloc(sizeof(*spidev), GFP_KERNEL);if (!spidev)return -ENOMEM;/* Initialize the driver data */spidev->spi = spi;spin_lock_init(&spidev->spi_lock);mutex_init(&spidev->buf_lock);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&spidev->device_entry);/* If we can allocate a minor number, hook up this device.* Reusing minors is fine so long as udev or mdev is working.*/mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);minor = find_first_zero_bit(minors, N_SPI_MINORS);if (minor < N_SPI_MINORS) {struct device *dev;spidev->devt = MKDEV(SPIDEV_MAJOR, minor);dev = device_create(spidev_class, &spi->dev, spidev->devt,spidev, "w25q64");status = PTR_ERR_OR_ZERO(dev);} else {dev_err(&spi->dev, "no minor number available!\n");status = -ENODEV;}if (status == 0) {set_bit(minor, minors);list_add(&spidev->device_entry, &device_list);}mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);spidev->speed_hz = spi->max_speed_hz;if (status == 0)spi_set_drvdata(spi, spidev);elsekfree(spidev);spidev->wp_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(np, "wp-gpio", 0);if (!gpio_is_valid(spidev->wp_gpio)) {dev_err(&spi->dev, "wp-gpio: %d is invalid\n", spidev->wp_gpio);return -ENODEV;}status = gpio_request(spidev->wp_gpio, "wp-gpio");if (status) {dev_err(&spi->dev, "wp-gpio: %d request failed!\n", spidev->wp_gpio);gpio_free(spidev->wp_gpio);return -ENODEV;}gpio_direction_output(spidev->wp_gpio, 0);gpio_export(spidev->wp_gpio, 0);spi_read_w25x_id_0(spi);return status;
}static int spidev_remove(struct spi_device *spi)
{struct spidev_data *spidev = spi_get_drvdata(spi);gpio_free(spidev->wp_gpio);/* make sure ops on existing fds can abort cleanly */spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);spidev->spi = NULL;spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);/* prevent new opens */mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);list_del(&spidev->device_entry);device_destroy(spidev_class, spidev->devt);clear_bit(MINOR(spidev->devt), minors);if (spidev->users == 0)kfree(spidev);mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);return 0;
}static struct spi_driver spidev_spi_driver = {.driver = {.name = "w25q64",.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(spidev_dt_ids),},.probe = spidev_probe,.remove = spidev_remove,/* NOTE: suspend/resume methods are not necessary here.* We don't do anything except pass the requests to/from* the underlying controller. The refrigerator handles* most issues; the controller driver handles the rest.*/
};/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/static int __init spidev_init(void)
{int status;/* Claim our 256 reserved device numbers. Then register a class* that will key udev/mdev to add/remove /dev nodes. Last, register* the driver which manages those device numbers.*/BUILD_BUG_ON(N_SPI_MINORS > 256);status = register_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, "w25q64", &spidev_fops);if (status < 0)return status;spidev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "w25q64");if (IS_ERR(spidev_class)) {unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);return PTR_ERR(spidev_class);}status = spi_register_driver(&spidev_spi_driver);if (status < 0) {class_destroy(spidev_class);unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);}return status;
}
module_init(spidev_init);static void __exit spidev_exit(void)
{spi_unregister_driver(&spidev_spi_driver);class_destroy(spidev_class);unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);
}
module_exit(spidev_exit);MODULE_AUTHOR("Yubel");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("User mode SPI device interface");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");w25q64.h
#ifndef W25Q64_H
#define W25Q64_H#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>#define W25Q64_SIZE 0x800000
#define W25Q64_PAGE_LENGTH 256
#define W25Q64_SECTOR 4096
#define W25Q64_32KB_BLOCK 32768
#define W25Q64_64KB_BLOCK 65536/* IOCTL commands */
#define W25Q64_MAGIC 'k'/*Erase SPI Flash*/
#define W25Q64_IOC_SECTOR_ERASE _IOW(W25Q64_MAGIC, 6, __u32)
#define W25Q64_IOC_32KB_BLOCK_ERASE _IOW(W25Q64_MAGIC, 7, __u32)
#define W25Q64_IOC_64KB_BLOCK_ERASE _IOW(W25Q64_MAGIC, 8, __u32)
#define W25Q64_IOC_CHIP_ERASE _IOW(W25Q64_MAGIC, 9, __u32)#endif /* W25Q64_H */