文章目录
- 一、JFFS2介绍
- 1、JFFS2简介
- 2、JFFS2框架
- 二、JFFS2实现
- 1、JFFS2的机制
- 2、JFFS2数据结构
- 1)struct jffs2_sb_info
- 2)struct jffs2_inode_info
- 3)struct jffs2_raw_node_ref
- 4)struct jffs2_inode_cache
- 5)struct jffs2_unknown_node
- 6)struct jffs2_raw_dirent
- 7)struct jffs2_raw_inode
- 8)struct jffs2_full_dirent
- 9)struct jffs2_node_frag
- 10)struct jffs2_full_dnode
- 8)struct jffs2_eraseblock
- 3、其它数据结构
- 1)struct super_block
- 附录
- 1、JFF2疑问
- 2、参考资料
一、JFFS2介绍
1、JFFS2简介
2、JFFS2框架
1)VFS
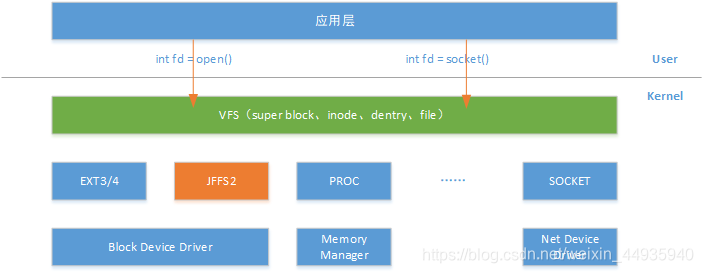
2)MTD
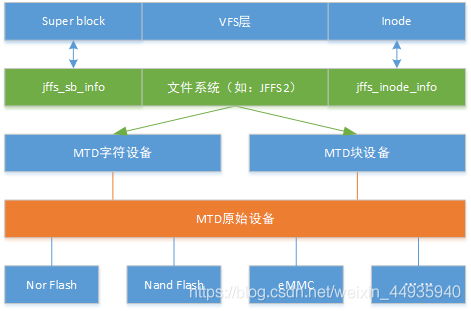
二、JFFS2实现
1、JFFS2的机制
2、JFFS2数据结构
1)struct jffs2_sb_info
该结构体用于描述jffs2文件系统super block的信息。(fs/jffs2/jffs2_fs_sb.h)
struct jffs2_sb_info {/* @mtd: 文件系统所在flash分区的mtd信息 */struct mtd_info *mtd;/* @highest_ino: 记录文件系统内最高的索引结点号,当新建文件时,系统为之分配的* 索引结点号就是highest_ino,并将该字段值递增。 */uint32_t highest_ino;uint32_t check_ino; /* *NEXT* inode to be checked *//* @flags: 挂载文件系统时指定的各种标志,如:JFFS2_SB_FLAG_RO (只读)... */unsigned int flags;struct task_struct *gc_task; /* GC task struct */struct completion gc_thread_start; /* GC thread start completion */struct completion gc_thread_exit; /* GC thread exit completion port */struct mutex alloc_sem; /* Used to protect all the followingfields, and also to protect againstout-of-order writing of nodes. And GC. */uint32_t cleanmarker_size; /* Size of an _inline_ CLEANMARKER(i.e. zero for OOB CLEANMARKER *//* 对应flash分区的大小 */uint32_t flash_size; // copy from @mtd_info.sizeuint32_t used_size;uint32_t dirty_size;uint32_t wasted_size;uint32_t free_size;uint32_t erasing_size;uint32_t bad_size;uint32_t sector_size;uint32_t unchecked_size;uint32_t nr_free_blocks;uint32_t nr_erasing_blocks;/* Number of free blocks there must be before we... */uint8_t resv_blocks_write; /* ... allow a normal filesystem write */uint8_t resv_blocks_deletion; /* ... allow a normal filesystem deletion */uint8_t resv_blocks_gctrigger; /* ... wake up the GC thread */uint8_t resv_blocks_gcbad; /* ... pick a block from the bad_list to GC */uint8_t resv_blocks_gcmerge; /* ... merge pages when garbage collecting *//* Number of 'very dirty' blocks before we trigger immediate GC */uint8_t vdirty_blocks_gctrigger;uint32_t nospc_dirty_size;uint32_t nr_blocks;struct jffs2_eraseblock *blocks; /* The whole array of blocks. Used for getting blocks* from the offset (blocks[ofs / sector_size]) */struct jffs2_eraseblock *nextblock; /* The block we're currently filling *//* @gcblock: 指向当前应该被垃圾收集的擦除块,如果为NULL,可通过 * @jffs2_find_gc_block找到应该被垃圾收集的擦除块。 */struct jffs2_eraseblock *gcblock;struct list_head clean_list; /* Blocks 100% full of clean data */struct list_head very_dirty_list; /* Blocks with lots of dirty space */struct list_head dirty_list; /* Blocks with some dirty space */struct list_head erasable_list; /* Blocks which are completely dirty, and need erasing */struct list_head erasable_pending_wbuf_list; /* Blocks which need erasing but only after the current wbuf is flushed */struct list_head erasing_list; /* Blocks which are currently erasing */struct list_head erase_checking_list; /* Blocks which are being checked and marked */struct list_head erase_pending_list; /* Blocks which need erasing now */struct list_head erase_complete_list; /* Blocks which are erased and need the clean marker written to them */struct list_head free_list; /* Blocks which are free and ready to be used */struct list_head bad_list; /* Bad blocks. */struct list_head bad_used_list; /* Bad blocks with valid data in. */spinlock_t erase_completion_lock; /* Protect free_list and erasing_listagainst erase completion handler */wait_queue_head_t erase_wait; /* For waiting for erases to complete */wait_queue_head_t inocache_wq;int inocache_hashsize;struct jffs2_inode_cache **inocache_list;spinlock_t inocache_lock;/* Sem to allow jffs2_garbage_collect_deletion_dirent todrop the erase_completion_lock while it's holding a pointerto an obsoleted node. I don't like this. Alternatives welcomed. */struct mutex erase_free_sem;uint32_t wbuf_pagesize; /* 0 for NOR and other flashes with no wbuf */#ifdef CONFIG_JFFS2_FS_WBUF_VERIFYunsigned char *wbuf_verify; /* read-back buffer for verification */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_JFFS2_FS_WRITEBUFFERunsigned char *wbuf; /* Write-behind buffer for NAND flash */uint32_t wbuf_ofs;uint32_t wbuf_len;struct jffs2_inodirty *wbuf_inodes;struct rw_semaphore wbuf_sem; /* Protects the write buffer */struct delayed_work wbuf_dwork; /* write-buffer write-out work */unsigned char *oobbuf;int oobavail; /* How many bytes are available for JFFS2 in OOB */
#endifstruct jffs2_summary *summary; /* Summary information */struct jffs2_mount_opts mount_opts;#ifdef CONFIG_JFFS2_FS_XATTR
#define XATTRINDEX_HASHSIZE (57)uint32_t highest_xid;uint32_t highest_xseqno;struct list_head xattrindex[XATTRINDEX_HASHSIZE];struct list_head xattr_unchecked;struct list_head xattr_dead_list;struct jffs2_xattr_ref *xref_dead_list;struct jffs2_xattr_ref *xref_temp;struct rw_semaphore xattr_sem;uint32_t xdatum_mem_usage;uint32_t xdatum_mem_threshold;
#endif/* OS-private pointer for getting back to master superblock info */void *os_priv;
};
2)struct jffs2_inode_info
该结构体用于描述jffs2文件系统inode的信息。(fs/jffs2/jffs2_fs_i.h)
struct jffs2_inode_info {/* We need an internal mutex similar to inode->i_mutex.Unfortunately, we can't used the existing one, becauseeither the GC would deadlock, or we'd have to release itbefore letting GC proceed. Or we'd have to put uglinessinto the GC code so it didn't attempt to obtain the i_mutexfor the inode(s) which are already locked */struct mutex sem;/* The highest (datanode) version number used for this ino */uint32_t highest_version;/* List of data fragments which make up the file */struct rb_root fragtree;/* There may be one datanode which isn't referenced by any of theabove fragments, if it contains a metadata update but no actualdata - or if this is a directory inode *//* This also holds the _only_ dnode for symlinks/device nodes,etc. */struct jffs2_full_dnode *metadata;/* Directory entries */struct jffs2_full_dirent *dents;/* The target path if this is the inode of a symlink */unsigned char *target;/* Some stuff we just have to keep in-core at all times, for each inode. */struct jffs2_inode_cache *inocache;uint16_t flags;uint8_t usercompr;struct inode vfs_inode;
};
3)struct jffs2_raw_node_ref
一个文件对应一个 jffs2_inode_cache,同时对应多个jffs2_raw_node_ref。
struct jffs2_raw_node_ref
{/* @next_in_ino: 单向链表,指向下一个raw_node_ref,如果这是最后一个成员,* 则会指向 @jffs2_inode_cache,参见函数jffs2_raw_ref_to_ic(),* 如此一来,每个 @jffs2_raw_node_ref 都知道自己所在的文件了。*/struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *next_in_ino;/* @flash_offset: 表示相应数据实体在flash分区上的物理地址 */uint32_t flash_offset;
#undef TEST_TOTLEN
#ifdef TEST_TOTLENuint32_t __totlen; /* This may die; use ref_totlen(c, jeb, ) below */
#endif
};
4)struct jffs2_inode_cache
struct jffs2_inode_cache {/* First part of structure is shared with other objects whichcan terminate the raw node refs' next_in_ino list -- whichcurrently struct jffs2_xattr_datum and struct jffs2_xattr_ref. */struct jffs2_full_dirent *scan_dents; /* Used during scan to holdtemporary lists of dirents, and later must be set toNULL to mark the end of the raw_node_ref->next_in_inochain. */struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *nodes;uint8_t class; /* It's used for identification *//* end of shared structure */uint8_t flags;uint16_t state;/* @ino: 文件在文件系统中唯一的索引结点号 */uint32_t ino;/* @next: 链表,连接管理每一个inode缓存节点 */struct jffs2_inode_cache *next;
#ifdef CONFIG_JFFS2_FS_XATTRstruct jffs2_xattr_ref *xref;
#endif/* @pino_nlink: 如果是目录,则存储上级目录的inode号,否则存储链接个数,* 0表示没有链接 */uint32_t pino_nlink;
};
5)struct jffs2_unknown_node
所有jffs2节点的起始信息如下所示:(include/uapi/linux/jffs2.h)
struct jffs2_unknown_node
{/* @magic: 魔术位掩码,表明是否为jffs2文件系统 */jint16_t magic; // JFFS2_MAGIC_BITMASK/* @nodetype: 数据结点的具体类型,如: JFFS2_NODETYPE_DIRENT... */jint16_t nodetype;jint32_t totlen; /* So we can skip over nodes we don't grok *//* @hdr_crc: crc校验,具体从哪个开始计算呢??? */jint32_t hdr_crc;
};
6)struct jffs2_raw_dirent
一个文件是由若干jffs2_raw_dirent或者jffs2_raw_inode数据实体组成。(include/uapi/linux/jffs2.h)
struct jffs2_raw_dirent
{jint16_t magic;jint16_t nodetype; /* == JFFS2_NODETYPE_DIRENT */jint32_t totlen;jint32_t hdr_crc;/* @pino: 存放该文件的目录的索引结点号,用于表明自己所属的目录文件 */jint32_t pino;/* @version: 版本号是相对于某一文件内部的概念,当向文件某个区域写入新的数据时,* 它的版本号就会不断递增。一个文件的所有数据实体的最高版本号由* @jffs2_inode_info中highest_version字段记录。 */jint32_t version;/* @ino: 文件的索引结点号 */jint32_t ino; /* == zero for unlink */jint32_t mctime;__u8 nsize;__u8 type;__u8 unused[2];jint32_t node_crc;jint32_t name_crc;__u8 name[0];
};
7)struct jffs2_raw_inode
(include/uapi/linux/jffs2.h)
struct jffs2_raw_inode
{jint16_t magic; /* A constant magic number. */jint16_t nodetype; /* == JFFS2_NODETYPE_INODE */jint32_t totlen; /* Total length of this node (inc data, etc.) */jint32_t hdr_crc;jint32_t ino; /* Inode number. */jint32_t version; /* Version number. */jmode_t mode; /* The file's type or mode. */jint16_t uid; /* The file's owner. */jint16_t gid; /* The file's group. */jint32_t isize; /* Total resultant size of this inode (used for truncations) */jint32_t atime; /* Last access time. */jint32_t mtime; /* Last modification time. */jint32_t ctime; /* Change time. *//* @offset: 文件内部的偏移,该jffs2_raw_inode在flash分区中的偏移由内核描述符* jffs2_raw_node_ref中flash_offset字段表示 */jint32_t offset;/* @csize: 压缩后的数据长度 */jint32_t csize;/* @dsize: 解压后的数据长度 */jint32_t dsize;__u8 compr; /* Compression algorithm used */__u8 usercompr; /* Compression algorithm requested by the user */jint16_t flags; /* See JFFS2_INO_FLAG_* */jint32_t data_crc; /* CRC for the (compressed) data. */jint32_t node_crc; /* CRC for the raw inode (excluding data) */__u8 data[0];
};
8)struct jffs2_full_dirent
struct jffs2_full_dirent
{union {struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *raw;struct jffs2_inode_cache *ic; /* Just during part of build */};struct jffs2_full_dirent *next;uint32_t version;uint32_t ino; /* == zero for unlink */unsigned int nhash;unsigned char type;unsigned char name[0];
};
9)struct jffs2_node_frag
struct jffs2_node_frag
{/* @rb: 用于组织红黑树,目的??? */struct rb_node rb;struct jffs2_full_dnode *node; /* NULL for holes *//* @size, @ofs: 从jffs2_full_dnode中复制而来,表示数据结点所代表的区域在* 文件内的偏移和长度。 */uint32_t size;uint32_t ofs; /* The offset to which this fragment belongs */
};
10)struct jffs2_full_dnode
struct jffs2_full_dnode
{struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *raw;uint32_t ofs; /* The offset to which the data of this node belongs */uint32_t size;uint32_t frags; /* Number of fragments which currently referto this node. When this reaches zero,the node is obsolete. */
};
8)struct jffs2_eraseblock
该结构体称为擦除块描述符,用于描述flash某个擦除块的信息。所有擦除块的描述符都存放载blocks[]中。另外,根据擦除块的状态,如是否由数据、数据是否过时等情况,还会将擦除块描述符组织在不同的链表中,以供文件系统的读写和 GC 使用(fs/jffs2/nodelist.h)
struct jffs2_eraseblock
{struct list_head list;int bad_count;uint32_t offset; /* of this block in the MTD */uint32_t unchecked_size;/* @used_size: 表示当前擦除块内有效数实体的空间大小 */uint32_t used_size;/* @dirty_size: 表示当前擦除块内过时数实体的空间大小 */uint32_t dirty_size;/* @wasted_size: 表示当前擦除块内无法利用的空间大小,由于flash数据* 结点必须4字节地址对齐导致。 */uint32_t wasted_size;/* @free_size: 表示当前擦除块内剩余空间大小 */uint32_t free_size; /* Note that sector_size - free_sizeis the address of the first free space */uint32_t allocated_refs;struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *first_node;struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *last_node;struct jffs2_raw_node_ref *gc_node; /* Next node to be garbage collected */
};
3、其它数据结构
1)struct super_block
VFS 描述文件系统使用超级块和inode的方式,所谓超级块就是对所有文件系统的管理机构,每种文件系统都要把自己的信息挂到super_blocks这么一个全局链表上。因此,每个super_blocks结构体可以代表一个文件系统。
struct super_block {/* @s_list: 双向链表,连接linux上所有文件系统对应的super_block */struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first */dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t */...
} __randomize_layout;
附录
1、JFF2疑问
Q1:为什么JFF2文件系统在挂载的时候需要遍历整个flash分区?
A1: JFF2是一种日志型文件系统,该文件系统下的一个文件所有的数据实体可能分布在flash的任何位置上,每个文件对应若干jffs2_raw_inode结点,每个结点都各自描述自己的后继数据。正因为缺少类似ext2_inode的“索引”机制,所以在挂载jffs2时不得不白哪里整个flash分区,从而找到每个文件的所有数据实体,并建立它们的内核描述符jffs2_raw_node_ref并组织到文件的jffs2_inode_cache所在的nodes链表中。
2、参考资料
- 以上源码内容参考自:Linux-4.15.18