文章目录
- 官方文档
- What is flatMap()?
- Why flat a Stream?
- Demo
- 需求1:Find all books
- 需求2:Order and LineItems
- 需求3:Splits the line by spaces
- 需求4: flatMap and primitive type

官方文档
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/stream/Stream.html

What is flatMap()?
# Stream<String[]>
# Stream<Stream<String>>
# String[][][[1, 2],[3, 4],[5, 6]
]
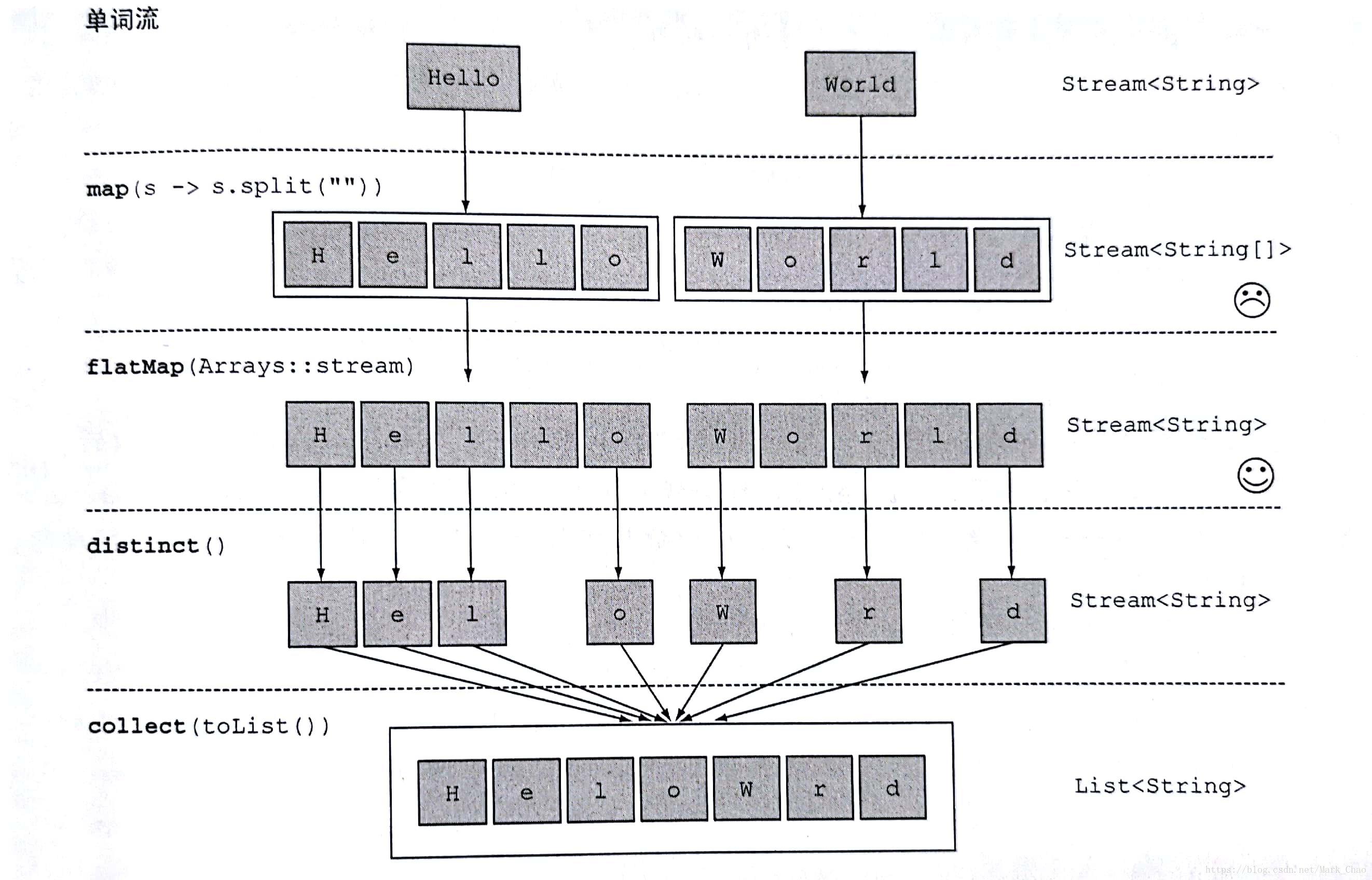
它由一个 2 级 Stream 或一个二维数组组成 。
在 Java 8 中,我们可以使用 flatMap 将上述 2 级 Stream 转换为一级 Stream 或将 二维数组转换为 一维数组。
# Stream<String>
# String[][1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
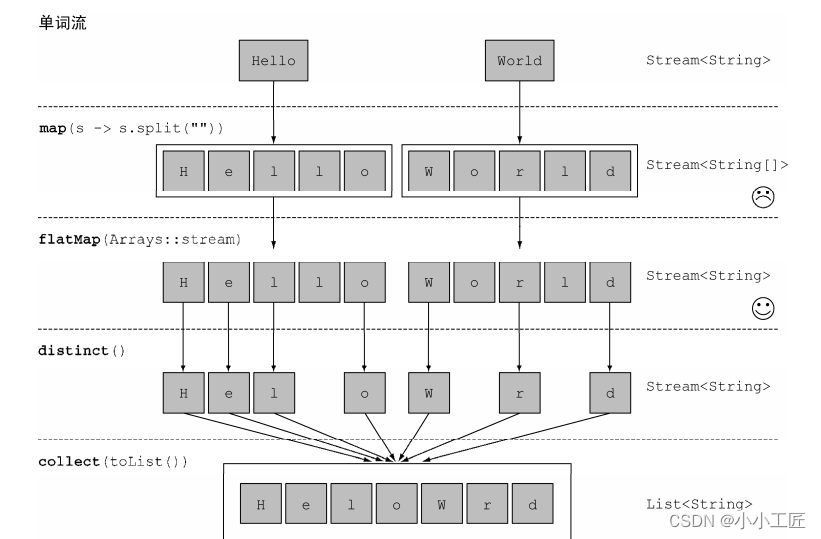
简言之, flatmap方法让你把一个流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有的流连接
起来成为一个流。
看一个简单的例子: 使用flatMap找出单词列表中各不相同的字符
Why flat a Stream?
处理包含多个级别的 Stream ,比如 Stream<String[]> 或 Stream<List<LineItem>> 或 Stream<Stream<String>> 想 将 2 级 Stream 扁平化为一级,如 Stream<String> 或 Stream<LineItem>,这样就可以轻松地循环 Stream 并对其进行处理。
来看个简单的功能实现,以及常犯的一些错误。
需求: 有 {"a", "b"}, {"c", "d"}, {"e", "f"} 三个数组,要求输出 除去a之后的数据
/*** filter out the a and print out all the characters*/private static void filterAndPrintCharacters() {String[][] array = new String[][]{{"a", "b"}, {"c", "d"}, {"e", "f"}};// convert array to a streamStream<String[]> stream = Arrays.stream(array);// array to a stream [same result]Stream<String[]> array1 = Stream.of(array);log.info("==========错误的方式一===============");// x is a String[], not String!List<String[]> result = stream.filter(x -> !x.equals("a")).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info(String.valueOf(result.size()));result.forEach(x -> log.info(Arrays.toString(x)));log.info("==========错误的方式二===============");List<String[]> result1 = Arrays.stream(array).filter(x -> {for (String s : x) { // really?if (s.equals("a")) {return false;}}return true;}).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info(String.valueOf(result1.size()));result1.forEach(x -> log.info(Arrays.toString(x)));log.info("============正确的方式 flatMap=============");log.info("============先测试转换成一维数组=============");// [a, b, c, d, e, f]String[] objects = Arrays.stream(array).flatMap(Stream::of).toArray(String[]::new);Arrays.stream(objects).forEach(x -> log.info("|---->{}", x));log.info("============开始处理=============");List<String> collect = Arrays.stream(array).flatMap(Stream::of).filter(x -> !x.equals("a")).collect(Collectors.toList());collect.forEach(x -> log.info(x));log.info("============处理结束=============");}
我们先看看:
[错误的方式一]
filter(x -> !x.equals("a")) // x 是数组 ,而非字符串
[错误的方式二]
x -> {for (String s : x) { // really?if (s.equals("a")) {return false;}}return true;} // 会把整个 [a, b] 过滤出去,而非我们想要过滤的 a
[正确的方式 ]
// flatMap 将二维数组转换成意味数组, 或者可以说是从 Stream<String[]> 转换成Stream<String>.String[][] array = new String[][]{{"a", "b"}, {"c", "d"}, {"e", "f"}};// Java 8String[] result = Stream.of(array) // Stream<String[]>.flatMap(Stream::of) // Stream<String>.toArray(String[]::new); // [a, b, c, d, e, f]Arrays.stream(objects).forEach(x -> log.info("|---->{}", x));接下来我们就可以很轻松地过滤出来 a了, 就得到了一下最终版本
List<String> collect = Arrays.stream(array).flatMap(Stream::of).filter(x -> !x.equals("a")).collect(Collectors.toList());collect.forEach(x -> log.info(x));
【小结】
Stream#flatMap 可以将 2 levels Stream 转换成 1 level Stream.
Stream<String[]> -> flatMap -> Stream<String>
Stream<Set<String>> -> flatMap -> Stream<String>
Stream<List<String>> -> flatMap -> Stream<String>
Stream<List<Object>> -> flatMap -> Stream<Object>

Demo
需求1:Find all books
分析: 使用 stream 将List转换为对象流,每个对象都包含一组书籍,使用flatMap生成包含所有对象中所有书籍的流。过滤掉包含单词cloud的书,并收集一个Set以便于删除重复的书。
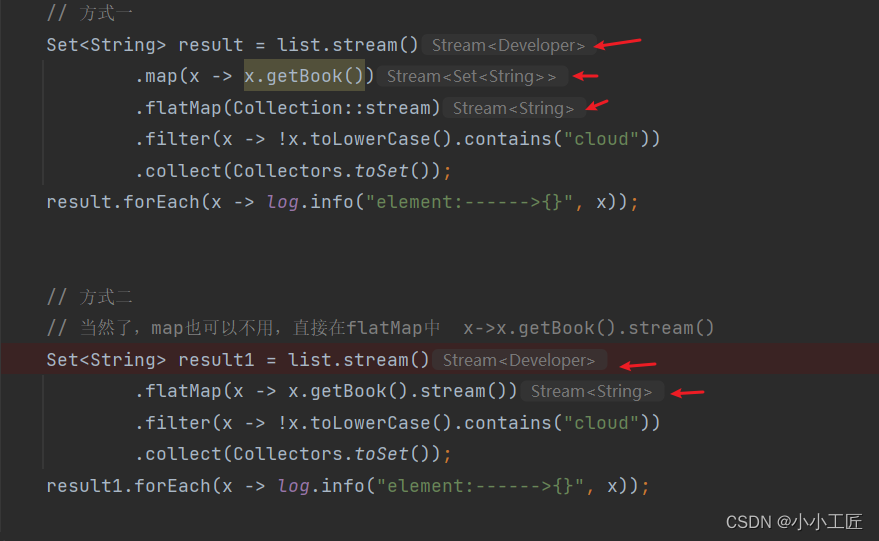
private static void findAllBooks() {Developer o1 = new Developer();o1.setName("artisan");o1.addBook("Java 8 in Action");o1.addBook("Spring Boot in Action");o1.addBook("Effective Java (3nd Edition)");Developer o2 = new Developer();o2.setName("小工匠");o2.addBook("Spring Cloud");o2.addBook("Effective Java (3nd Edition)");List<Developer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(o1);list.add(o2);// 这....Set of Set...(Set<Set<String>>)咋处理?Set<Set<String>> collect = list.stream().map(x -> x.getBook()).collect(Collectors.toSet());// 方式一Set<String> result = list.stream().map(x -> x.getBook()).flatMap(Collection::stream).filter(x -> !x.toLowerCase().contains("cloud")).collect(Collectors.toSet());result.forEach(x -> log.info("element:------>{}", x));// 方式二// 当然了,map也可以不用,直接在flatMap中 x->x.getBook().stream()Set<String> result1 = list.stream().flatMap(x -> x.getBook().stream()).filter(x -> !x.toLowerCase().contains("cloud")).collect(Collectors.toSet());result1.forEach(x -> log.info("element:------>{}", x));}
当然了 有个内部类
@Data
static class Developer {private Integer id;private String name;private Set<String> book;public void addBook(String book) {if (this.book == null) {this.book = new HashSet<>();}this.book.add(book);}}
我们来来拆解下 【方式一】的处理过程如下
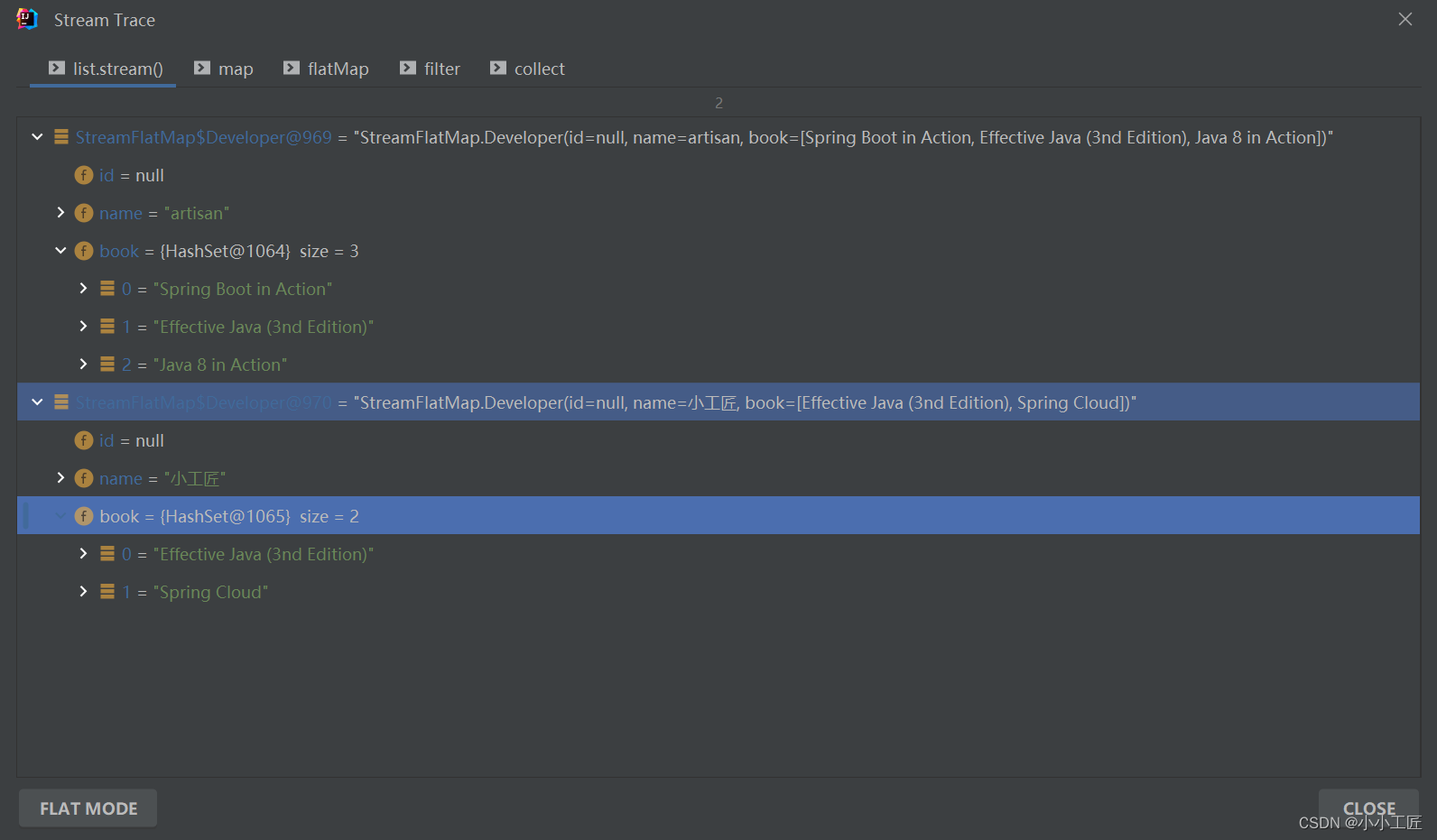
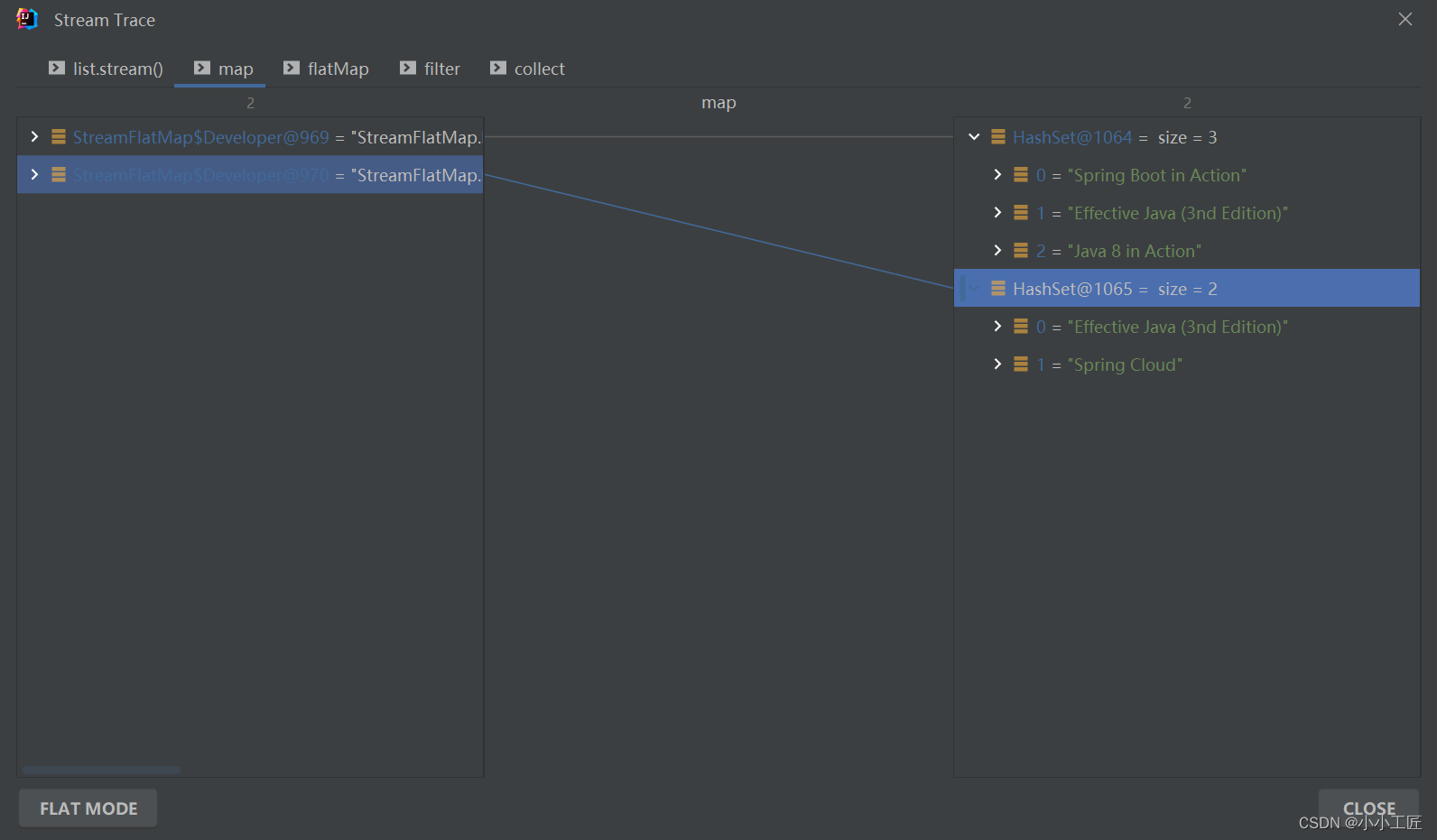
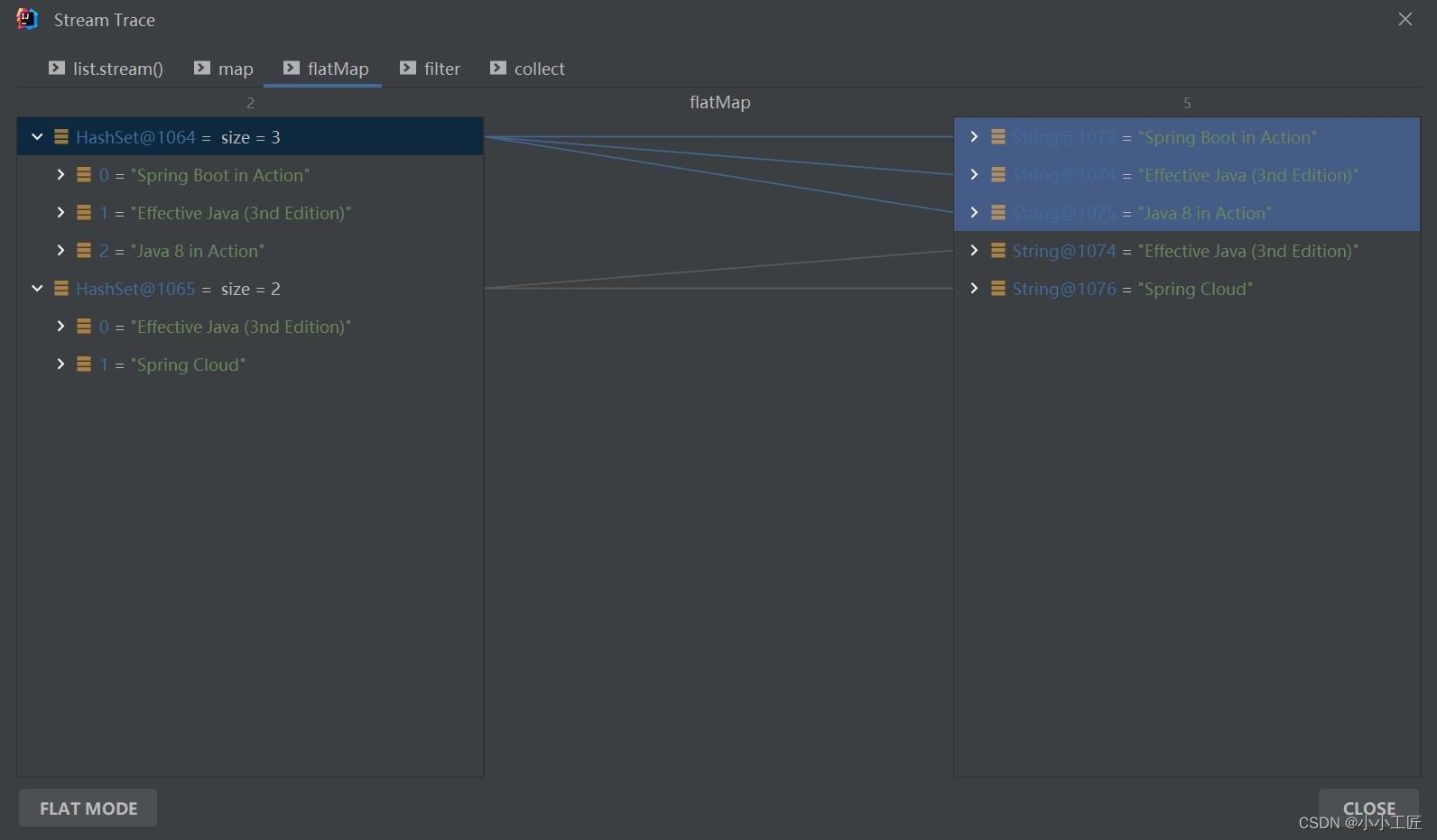
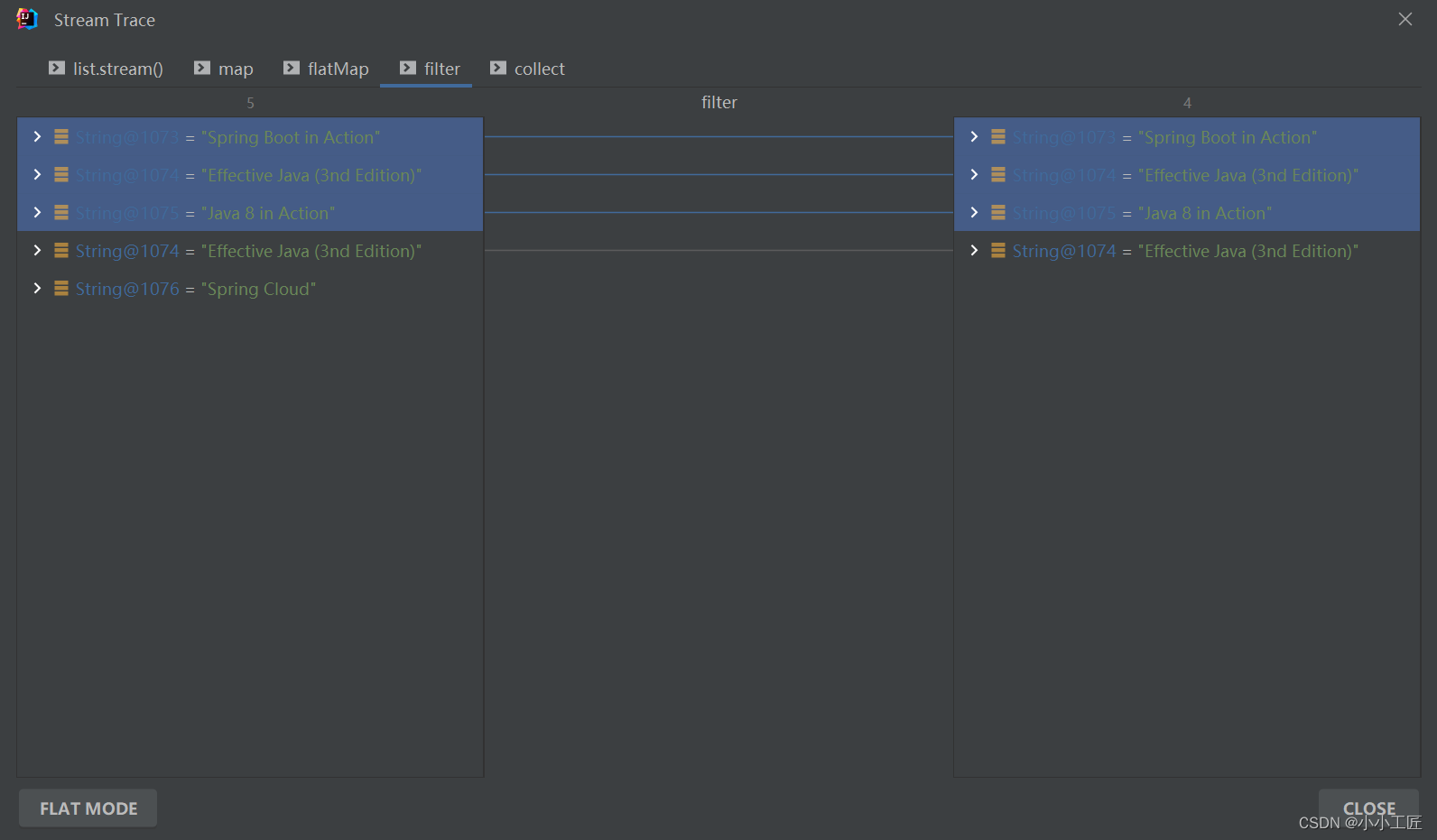
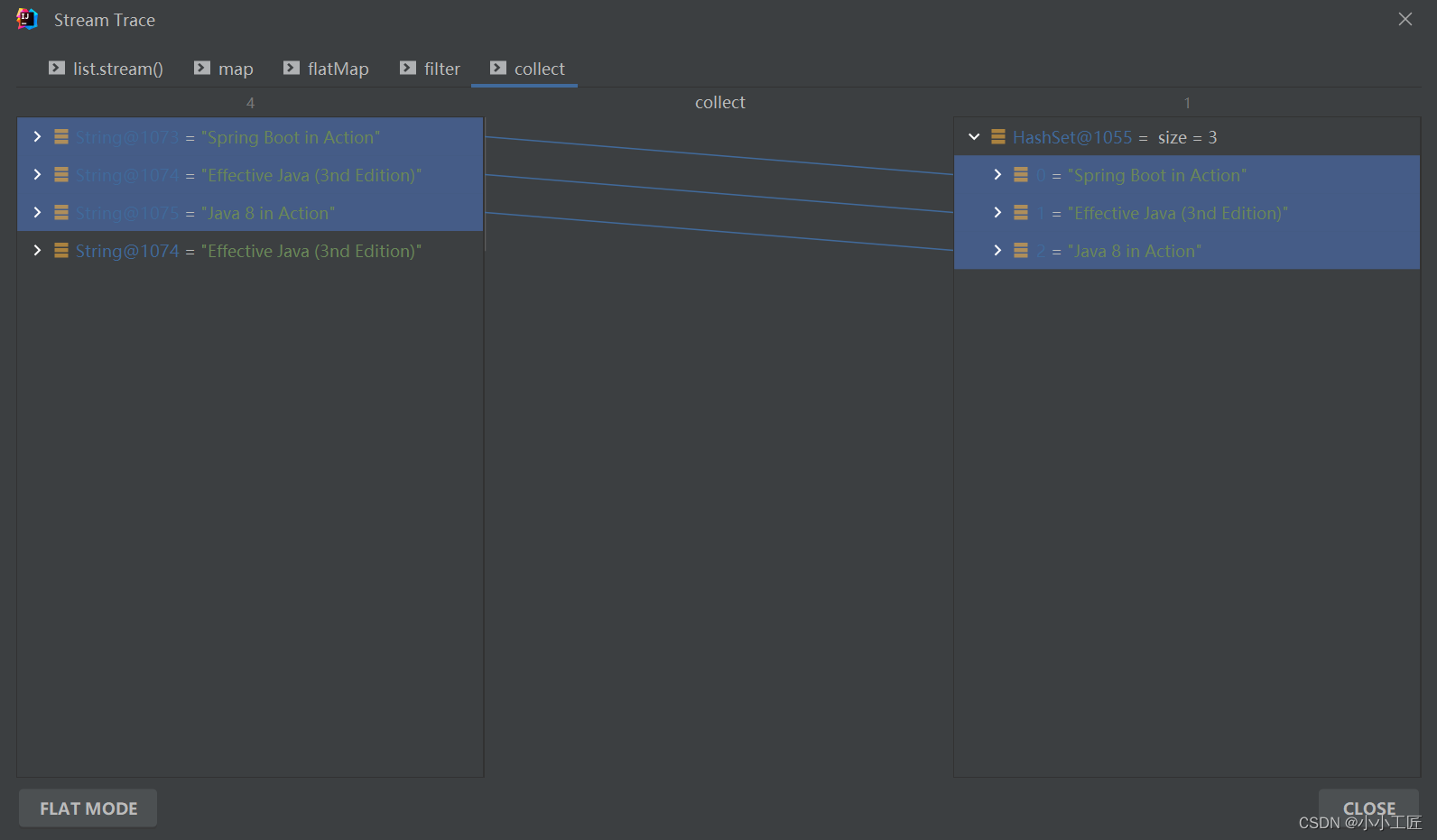
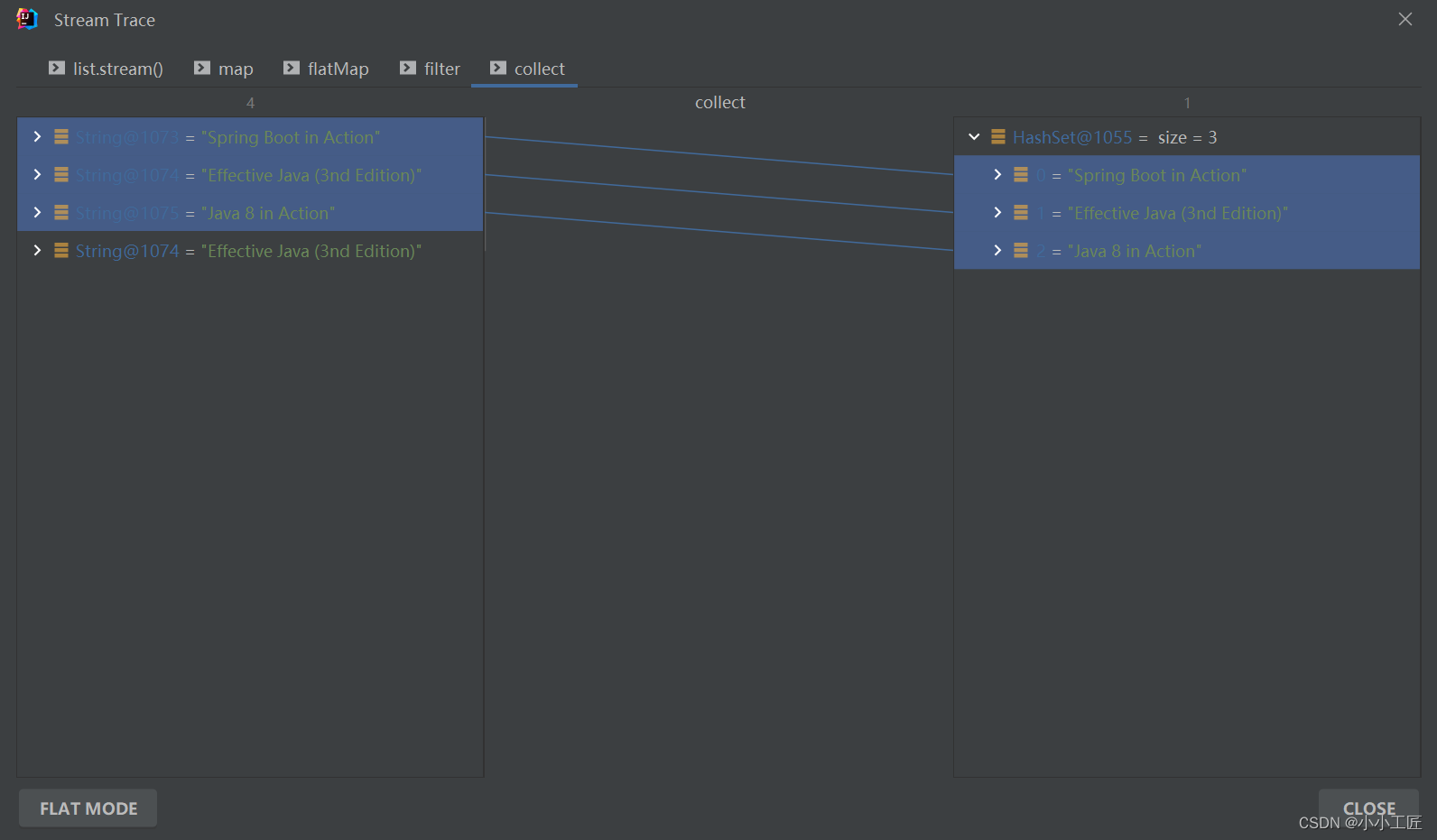
总结下每一步的输出:
需求2:Order and LineItems
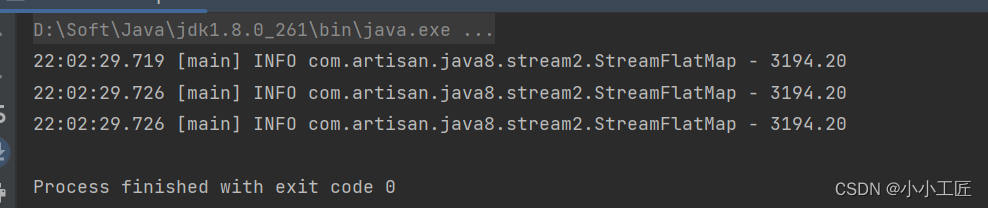
订单是一个采购订单流,每个采购订单都包含一组行项目,然后使用flatMap生成一个包含所有订单中所有行项目的stream或Stream<LineItem>。此外,还添加了一个reduce操作来合计行项目的总金额 .
private static void orderAndLineItems() {List<Order> orders = findAll();// sum the order's total amount// 计算 order的total 总和BigDecimal reduce = orders.stream().map(Order::getTotal).reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);log.info(reduce.toString());// sum the line items' total amount// 计算 全部的 line的 price 总和// 方式一 先 map 再flatMapBigDecimal reduce1 = orders.stream().map(Order::getLineItems).flatMap(Collection::stream).map(line -> line.getTotal()).reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);// 方式二 直接 flatMapBigDecimal reduce2 = orders.stream().flatMap(order -> order.getLineItems().stream()).map(line -> line.getTotal()).reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);log.info(reduce1.toString());log.info(reduce2.toString());}/*** 模拟数据** @return*/private static List<Order> findAll() {LineItem item1 = new LineItem(1, "apple", 1, new BigDecimal("1.20"), new BigDecimal("1.20"));LineItem item2 = new LineItem(2, "orange", 2, new BigDecimal(".50"), new BigDecimal("1.00"));Order order1 = new Order(1, "A0000001", Arrays.asList(item1, item2), new BigDecimal("2.20"));LineItem item3 = new LineItem(3, "monitor BenQ", 5, new BigDecimal("99.00"), new BigDecimal("495.00"));LineItem item4 = new LineItem(4, "monitor LG", 10, new BigDecimal("120.00"), new BigDecimal("1200.00"));Order order2 = new Order(2, "A0000002", Arrays.asList(item3, item4), new BigDecimal("1695.00"));LineItem item5 = new LineItem(5, "One Plus 8T", 3, new BigDecimal("499.00"), new BigDecimal("1497.00"));Order order3 = new Order(3, "A0000003", Arrays.asList(item5), new BigDecimal("1497.00"));return Arrays.asList(order1, order2, order3);}@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic static class Order {private Integer id;private String invoice;private List<LineItem> lineItems;private BigDecimal total;}@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic static class LineItem {private Integer id;private String item;private Integer qty;private BigDecimal price;private BigDecimal total;}输出
需求3:Splits the line by spaces
读取一个文本文件,计算单词数量
文本文件
hello world Java
hello world Python
hello world Node JS
hello world Rust
hello world Flutter
@SneakyThrowsprivate static void splitLinesBySpaces() {Path path = Paths.get("D:\\IdeaProjects\\boot2\\java8review\\src\\main\\java\\com\\artisan\\java8\\stream2\\a.txt");// 按行读取Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);// stream of array...hard to process.// Stream<String[]> stream = lines.map(line -> line.split(" +"));// stream of stream of string....hmm...better flat to one level.// Stream<Stream<String>> words = lines.map(line -> Stream.of(line.split(" +")));// +、*、|、\等符号在正则表达示中有相应的不同意义// 加号可用于与字符匹配 1 次或多次。例如,'bre+' 匹配 bre 和 bree,但不匹配 br// " +" 匹配空格// result a stream of words, good! 方式一Stream<String> words = Files.lines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8).flatMap(line -> Stream.of(line.split(" +")));System.out.println(words.count());// 方式二long count = Files.lines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8).map(line -> line.split(" +")).flatMap(line -> Stream.of(line)).count();System.out.println(count);}需求4: flatMap and primitive type

private static void flatMap2PrimitiveType() {int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};//Stream<int[]>Stream<int[]> streamArray = Stream.of(array);//Stream<int[]> -> flatMap -> IntStreamIntStream intStream = streamArray.flatMapToInt(x -> Arrays.stream(x));intStream.forEach(System.out::println);// flatMapToLong -> LongStreamlong[] array2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};Stream<long[]> longArray = Stream.of(array2);LongStream longStream = longArray.flatMapToLong(x -> Arrays.stream(x));System.out.println(longStream.count());}