前言:
关系型数据库已经红火了很久,但是其弊端也是显而易见的,对于很多非结构数据以及半结构化数据很难有效地管理,而且RDBMS的固定式的Schema往往很难接受,太呆板不灵活,因此基于可自由伸缩的schema的数据库随之而来了,这个就是文档数据库,伴随着云计算技术的发展,支持MapReduce以及多点复制、反向搜索引擎技术的文档数据库正在渐渐地成为了主流,其中的开源娇娇者有 Hadoop, CouchDB, MongoDB等众多的数据库,不过各个数据都有自己的特点。
Wikipedia论述:
A document-oriented database is a computer program designed for document-oriented applications. These systems may be implemented as a layer above arelational database or an object database.
For example here's a document:
- FirstName="Bob", Address="5 Oak St.", Hobby="sailing".
Another document could be:
- FirstName="Jonathan", Address="15 Wanamassa Point Road", Children=[{Name:"Michael",Age:10}, {Name:"Jennifer", Age:8}, {Name:"Samantha", Age:5}, {Name:"Elena", Age:2}].
Notice that both documents have some similar information and some different - but unlike a relational database where each record would have the same set of fields and unused fields might be kept empty, there are no empty 'fields' in either document (record) in this case. This system allows new information to be added and it doesn't require explicitly stating if other pieces of information are left out, as in relational databases.
It is noteworthy here that using XML, YAML or JSON for information storage has advantages similar to document oriented database. In these languages each record can have a non-standard amount of information. Such information is properly calledsemi structured data.
Another advantage of document oriented databases is the ease of usage and programming so that untrained business users, for example, can create applications and design their own databases. Information can be added without worrying about the "record size" and so programmers simply need to build an interface to allow the information to be entered easily.
Contents[hide]
|
Implementations
Name | Publisher | License | Language | Notes | RESTful API |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lotus Notes | IBM | Proprietary | (unknown) | ||
| askSam | askSam Systems | Proprietary | (unknown) | ||
| Apstrata | Apstrata | Proprietary | (unknown) | ||
| Datawasp | Significant Data Systems | Proprietary | (unknown) | ||
| CRX | Day Software | Proprietary | (unknown) | ||
| MUMPS Database[1] | Proprietary and GNU Affero GPL[2] | MUMPS | Commonly used in health applications. | (unknown) | |
| UniVerse | Rocket Software | Proprietary | Yes (Beta) | ||
| UniData | Rocket Software | Proprietary | Yes (Beta) | ||
| Jackrabbit | Apache | Apache License | Java | (unknown) | |
| CouchDB | Apache | Apache License | Erlang | JSON over HTTP | Yes |
| FleetDB | FleetDB | MIT License | Clojure | A JSON-based schema-free database optimized for agile development. | (unknown) |
| MongoDB | GNU AGPL v3.0[3] | C++ | Fast, document-oriented database optimized for highly transient data. | (unknown) | |
| GemFire Enterprise[2] | VMWare | Commercial | Java, .NET, C++ | Memory-oriented, fast, key-value database with indexing and querying support. | Yes |
| OrientDB | OrientDB | Apache License | Java | JSON over HTTP | Yes |
| RavenDB | RavenDB | commercial or GNU AGPL v3.0 | .NET | A .NET LINQ-enabled Document Database, focused on providing high performance, transactional, schema-less, flexible and scalable NoSQL data store for the .NET and Windows platforms. | Yes |
| Redis | BSD License | ANSI C | Key-value store supporting lists and sets with fast, simple and binary-safe protocol. | (unknown) | |
| StrokeDB | [3] | MIT License | Alpha software. | (unknown) | |
| Terrastore | Apache License | Java | JSON/HTTP | (unknown) | |
| ThruDB | BSD License | C++, Java | Built on top of Apache Thrift framework that provides indexing and document storage services for building and scaling websites. Alternate implementation is being developed in Java.Alpha software. | (unknown) | |
| Persevere | Persevere | BSD License | A JSON database and JavaScript Application Server. Provides RESTful JSON interface for Create, read, update, and delete access to data. Also supports JSONQuery/JSONPath querying. | Yes | |
| DBSlayer | DBSlayer | Apache License | C | database abstraction layer (overMySQL) used by the New York Times. JSON over HTTP. | (unknown) |
| Eloquera DB | Eloquera | Proprietary | .NET | High performance. Based on Dynamic objects. Supports LINQ, SQL queries. | (unknown) |
XML database implementations
All XML databases are document-oriented databases.
| | This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2011) |
| | This article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. Please improve this article by removing excessive and inappropriate external links. (August 2011) |
An XML database is a data persistence software system that allows data to be stored in XML format. This data can then be queried, exported and serialized into the desired format.
Two major classes of XML database exist:
- XML-enabled: these map all XML to a traditional database (such as arelational database[4]), accepting XML as input and rendering XML as output. This term implies that the database does the conversion itself (as opposed to relying on middleware).
- Native XML (NXD): the internal model of such databases depends on XML and uses XML documents as the fundamental unit of storage, which are, however, not necessarily stored in the form of text files.
Rationale for XML in databases
O'Connell (2005, 9.2) gives one reason for the use of XML in databases: the increasingly common use of XML fordata transport, which has meant that "data is extracted from databases and put into XML documents and vice-versa". It may prove more efficient (in terms of conversion costs) and easier to store the data in XML format.
Native XML databases
The term "native XML database" (NXD) can lead to confusion. Many NXDs do not function as standalone databases at all, and do not really store the native (text) form.
The formal definition from the XML:DB initiative (which appears to be inactive since 2003[5]) states that a native XML database:
- Defines a (logical) model for an XML document — as opposed to the data in that document — and stores and retrieves documents according to that model. At a minimum, the model must include elements, attributes,PCDATA, and document order. Examples of such models include theXPath data model, the XML Infoset, and the models implied by the DOM and the events in SAX 1.0.
- Has an XML document as its fundamental unit of (logical) storage, just as arelational database has a row in a table as its fundamental unit of (logical) storage.
- Need not have any particular underlying physical storage model. For example, NXDs can use relational,hierarchical, or object-oriented database structures, or use a proprietary storage format (such as indexed, compressed files).
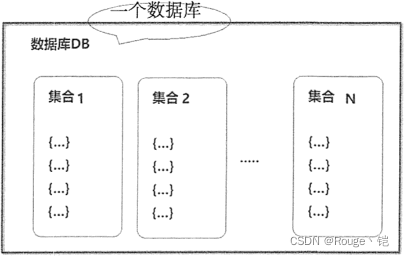
Additionally, many XML databases provide a logical model of grouping documents, called "collections". Databases can set up and manage many collections at one time. In some implementations, a hierarchy of collections can exist, much in the same way that an operating system's directory-structure works.
All XML databases now[update] support at least one form of querying syntax. Minimally, just about all of them support XPath for performing queries against documents or collections of documents. XPath provides a simple pathing system that allows users to identify nodes that match a particular set of criteria.
In addition to XPath, many XML databases support XSLT as a method of transforming documents or query-results retrieved from the database. XSLT provides adeclarative language written using an XML grammar. It aims to define a set of XPathfilters that can transform documents (in part or in whole) into other formats includingPlain text, XML, or HTML.
Many XML databases also support XQuery to perform querying. XQuery includes XPath as a node-selection method, but extends XPath to provide transformational capabilities. Users sometimes refer to its syntax as "FLWOR" (pronounced 'Flower') because the query may include the following clauses: 'for', 'let', 'where', 'order by' and 'return'. Traditional RDBMS vendors (who traditionally had SQL only engines), are now shipping with hybrid SQL and XQuery engines. Hybrid SQL/XQuery engines help to query XML data alongside the relational data, in the same query expression. This approach helps in combining relational and XML data.
Some XML databases support an API called the XML:DB API (or XAPI) as a form of implementation-independent access to the XMLdatastore. In XML databases, XAPI resemblesODBC and JDBC as used with relational databases. On the 24th of June 2009, The Java Community Process released the final version of the XQuery API for Java specification (XQJ) - "a common API that allows an application to submit queries conforming to the W3C XQuery 1.0 specification and to process the results of such queries".
XML Databases with database APIs (XQJ, XML:DB, RESTful)
XML Database | License | Language | XQJ API | XML:DB API | RESTful API |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaseX | BSD License | Java | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| xDB | Commercial | Java | Yes | No | No |
| eXist | LGPL License | Java | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| MarkLogic Server | Commercial | C++ | Yes | No | Yes |
| MonetDB/XQuery | Proprietary | C++ | No | Yes | No |
| Oracle | Commercial | C++ | Yes | No | No |
| Sedna | Apache License | C++ | Yes | Yes | No |
References
- ^ Extreme Database programming with MUMPS Globals
- ^ GTM MUMPS FOSS on SourceForge
- ^ [1]
- ^ Mustafa Atay and Shiyong Lu, “Storing and Querying XML: An Efficient Approach Using Relational Databases”,ISBN 3-639-11581-3, VDM Verlag, 2009.
- ^ http://xmldb-org.sourceforge.net/faqs.html
External references
- XML Databases - The Business Case, Charles Foster, June 2008 - Talks about the current state of Databases and data persistence, how the current Relational Database model is starting to crack at the seams and gives an insight into a strong alternative for today's requirements.
- An XML-based Database of Molecular Pathways (2005-06-02) Speed / Performance comparisons of eXist, X-Hive, Sedna and Qizx/open
- XML Native Database Systems: Review of Sedna, Ozone, NeoCoreXMS 2006
- XML Data Stores: Emerging Practices
- Bhargava, P.; Rajamani, H.; Thaker, S.; Agarwal, A. (2005) XML Enabled Relational Databases, Texas, The University of Texas at Austin.
- O'Connell, S. Advanced Databases Course Notes, Southampton, University of Southampton, 2005
- Initiative for XML Databases
- XML and Databases, Ronald Bourret, September 2005
- XML Database Products, Ronald Bourret, 2000–2009
- The State of Native XML Databases, Elliotte Rusty Harold, August 13, 2007







![[模板]详细设计说明书(整理版)【申明:来源于网络】](https://img-blog.csdn.net/20161211224152607?watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQveWVhckhlYXZlbg==/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0JBQkFCMA==/dissolve/70/gravity/SouthEast)