1.概述
好文章,转载防丢失
主要是这里有源码,我遇到问题了,问题是flink在累加器中使用的时候,每次累加最终结果是1,2 每次到了2 就会重新回到1,很郁闷于是看看源码
2.背景
我们经常会统计某个字段的distinct value(DV),比如mysql 的distinct 关键字,但在大数据场景下,考虑空间复杂度,往往需要更少的内存来进行排重逻辑。
HyperLogLog算法就是解决此类问题的算法之一(下文简称DV),如Redis的HyperLogLog结构,ES的distinct语句.
HyperLogLog算法来源于论文
HyperLogLog the analysis of a near-optimal cardinality estimation algorithm
可以使用固定大小的字节计算任意大小的DV。
3.算法原理
HLL 算法的原理会涉及到比较多的数学知识,这边对这些数学原理和证明不会展开。举一个生活中的例子来帮助大家理解HLL算法的原理:比如你在进行一个实验,内容是不停地抛硬币,记录你连续抛到正面的次数(这是数学中的伯努利过程);如果你最多的连抛正面记录是3次,那可以想象你并没有做这个实验太多次,如果你最长的连抛正面记录是 20 次,那你可能进行了这个实验上千次。
一种理论上存在的情况是,你非常幸运,第一次进行这个实验就连抛了 20 次正面,我们也会认为你进行了很多次这个实验才得到了这个记录,这就会导致错误的预估;改进的方式是请 10 位同学进行这项实验,这样就可以观察到更多的样本数据,降低出现上述情况的概率。这就是 HLL 算法的核心思想。
感性认识
| HASH CODE | 发生概率 | 第一个1出现的位置 | 预计实验次数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1xxxxxxx | 1/2 | 1 | 2 |
| 01xxxxxx | 1/4 | 1 | 4 |
| 001xxxxx | 1/8 | 3 | 8 |
| 0001xxxx | 1/16 | 4 | 16 |
分桶
为解决以上错误的预估,改进方法是m个人进行这项实验(数据分成m个均等的部分),分别估计其值,并求其平均数后再乘以m,称之为分桶。这样就能一定程度上避免单一突发事件造成的误差。
公式:DV_{LL} = constantm2^\overline{R}

loglog 算法的基数计算公式
其中
m代表分桶数
桶中数据为最长前导零的个数+1
代表桶的结果的均值

constant 常数,后续源代码介绍。
调和平均数
前面的LogLog算法中我们是使用的是平均数来将每个桶的结果汇总起来,但是平均数有一个广为人知的缺点,就是容易受到大的数值的影响,一个常见的例子是人均GDP。
用调和平均数就可以解决这一问题,调和平均数的结果会倾向于集合中比较小的数(倒数),x1到xn的调和平均数的公式如下:

调和平均数
HyperLogLog算法相比LogLog算法一个重要的改进就是使用调和平均数而不是平均数来聚合每个桶中的结果,HyperLogLog算法的公式如下:

HLL 算法基数计算公式
基中
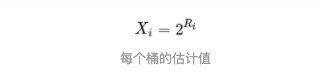
每个桶的估计值
以下为HLL算法的基本原理,关于细节的公式推导,暂不涉及,有兴的小伙伴可以参考上文的论文原文。
RSD
相对标准误差(relative standard deviation,简称RSD)

其中m为桶数,由此可知rsd与m成正比
老外的在线demo 演示

step 1

step 2
HLL源码分析
依赖引用
<groupId>net.agkn</groupId><artifactId>hll</artifactId><version>1.6.0</version>
</dependency>
github
https://github.com/aggregateknowledge/java-hll
依赖类图

依赖类图
package net.agkn.hll;
…
public class HLL implements Cloneable {
翻译
一种概率性的集合,集合的元素为 long 型的hash值,这种数据结构(算法适用于使用相对很小的存储来近似地计算数据流的基数。
根据 HLL论文实现的改近版本,HLL的数据结构和算法都被采用了,并结合概率性和非概率性的技术来改进预测的精度和原始算法的存储需求(空间复杂度低)
更具体地说
- HLL初始化时,会分配一个EMPTY的空集合
- 接着加入几个值之后会升级为EXPLICIT的HashSet
- 为了减少内存的占用,会牺牲精度:EXPLICIT类型会升级为基于映射的SPARSE(稀疏)
- 当更多的桶(register)被占用时,基于映射的HLL会转换成基于位封装的结构(FULL)
/**...public HLL(final int log2m, final int regwidth, final int expthresh, final boolean sparseon, final HLLType type)
翻译
- @param log2m 桶数的log-base-2 比如桶数为64, 则log2m=6,该参数为4到30之间
- @param regwidth 每个桶的位数,该参数在1到8之间,即最大为一个字节
- @param expthresh 当EXPLICIT提升为SPARSE的阈值,取值范围为1-18
expthresh 含义
| expthresh | 含义 |
|---|---|
| -1 | Promote at whatever cutoff makes sense for optimal memory usage. |
| 0 | Skip EXPLICIT representation in hierarchy |
| 1-18 | Promote at 2expthresh - 1 cardinality |
if(expthresh == -1) {
//Promote at whatever cutoff makes sense for optimal memory usage. this.explicitAuto = true;this.explicitOff = false;// NOTE: This math matches the size calculation in the PostgreSQL impl.所有桶点的字节数final long fullRepresentationSize = (this.regwidth * (long)this.m + 7/*round up to next whole byte*/)/Byte.SIZE;
//所有桶占用的long 类型数组lengthfinal int numLongs = (int)(fullRepresentationSize / 8/*integer division to round down*/);if(numLongs > MAXIMUM_EXPLICIT_THRESHOLD) {this.explicitThreshold = MAXIMUM_EXPLICIT_THRESHOLD;} else {this.explicitThreshold = numLongs;}} else if(expthresh == 0) {
// Skip `EXPLICIT` representation in hierarchythis.explicitAuto = false;this.explicitOff = true;this.explicitThreshold = 0;} else if((expthresh > 0) && (expthresh <= MAXIMUM_EXPTHRESH_PARAM)){this.explicitAuto = false;this.explicitOff = false;
//Promote at pow(2,expthresh - 1) cardinalitythis.explicitThreshold = (1 << (expthresh - 1));} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("'expthresh' must be at least " + MINIMUM_EXPTHRESH_PARAM + " and at most " + MAXIMUM_EXPTHRESH_PARAM + " (was: " + expthresh + ")");}
@param sparseon 标识SPARSE是否被使用,false则skip SPARSE
this.sparseOff = !sparseon;if(this.sparseOff) {this.sparseThreshold = 0;}
@param type 在提升层次关系中的起始类型
不同存储介质
private void initializeStorage(final HLLType type) {this.type = type;switch(type) {case EMPTY:// nothing to be donebreak;case EXPLICIT:
//精确存储,基于long 的hashsetthis.explicitStorage = new LongOpenHashSet();break;case SPARSE:
//稀疏类型,因为数据量不是很大时,大部分的桶为空,为节省空间,则只保存有值的桶this.sparseProbabilisticStorage = new Int2ByteOpenHashMap();break;case FULL:
//当大部分的桶有值时,用位向量来保存所有的桶的内容,以节省空间this.probabilisticStorage = new BitVector(regwidth, m);break;default:throw new RuntimeException("Unsupported HLL type " + type);}}
ADD
根据上文类的注释不难理解ADD会提升存储类型
*** Adds <code>rawValue</code> directly to the HLL.* rawValue 必须被hash,官方建议用google guave的Murmur3_128HashFunction * @param rawValue the value to be added. It is very important that this* value <em>already be hashed</em> with a strong (but not* necessarily cryptographic) hash function. For instance, the* Murmur3 implementation in* <a href="http://guava-libraries.googlecode.com/git/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Murmur3_128HashFunction.java">* Google's Guava</a> library is an excellent hash function for this* purpose and, for seeds greater than zero, matches the output* of the hash provided in the PostgreSQL implementation.*/public void addRaw(final long rawValue) {switch(type) {case EMPTY: {// NOTE: EMPTY type is always promoted on #addRaw()
//explicitThreshold==0 时则skip EXPLICTif(explicitThreshold > 0) {initializeStorage(HLLType.EXPLICIT);explicitStorage.add(rawValue);
//sparseOff==true 时,则skip SPARSE} else if(!sparseOff) {initializeStorage(HLLType.SPARSE);addRawSparseProbabilistic(rawValue);} else {
//都skip则初始化为FULLinitializeStorage(HLLType.FULL);addRawProbabilistic(rawValue);}return;}case EXPLICIT: {explicitStorage.add(rawValue);// promotion, if necessaryif(explicitStorage.size() > explicitThreshold) {if(!sparseOff) {initializeStorage(HLLType.SPARSE);for(final long value : explicitStorage) {addRawSparseProbabilistic(value);}} else {initializeStorage(HLLType.FULL);for(final long value : explicitStorage) {addRawProbabilistic(value);}}explicitStorage = null;}return;}case SPARSE: {addRawSparseProbabilistic(rawValue);// promotion, if necessaryif(sparseProbabilisticStorage.size() > sparseThreshold) {initializeStorage(HLLType.FULL);for(final int registerIndex : sparseProbabilisticStorage.keySet()) {final byte registerValue = sparseProbabilisticStorage.get(registerIndex);probabilisticStorage.setMaxRegister(registerIndex, registerValue);}sparseProbabilisticStorage = null;}return;}case FULL:addRawProbabilistic(rawValue);return;default:throw new RuntimeException("Unsupported HLL type " + type);}}
EXPLICIT LongOpenHashSet
该类型为long 类型的hash set
public boolean add(long k) {int pos;
//根据 hash值找到位置for(pos = (int)HashCommon.murmurHash3(k ^ (long)this.mask) & this.mask; this.used[pos]; pos = pos + 1 & this.mask) {
//如果已经存在则退出if (this.key[pos] == k) {return false;}}this.used[pos] = true;this.key[pos] = k;
//如果超过最大值 Math.min((int)Math.ceil((double)((float)n * f)), n - 1);,则重hashif (this.size++ >= this.maxFill) {this.rehash(HashCommon.arraySize(this.size + 1, this.f));}return true;}
SPARSE 稀疏概率预测存储
/*** Adds the raw value to the {@link #sparseProbabilisticStorage}.* {@link #type} must be {@link HLLType#SPARSE}.** @param rawValue the raw value to add to the sparse storage.*/private void addRawSparseProbabilistic(final long rawValue) {// p(w): position of the least significant set bit (one-indexed)// By contract: p(w) <= 2^(registerValueInBits) - 1 (the max register value)//// By construction of pwMaxMask (see #Constructor()),// lsb(pwMaxMask) = 2^(registerValueInBits) - 2,// thus lsb(any_long | pwMaxMask) <= 2^(registerValueInBits) - 2,// thus 1 + lsb(any_long | pwMaxMask) <= 2^(registerValueInBits) -1.
//hash code中移掉桶的标志位,剩下的value标志位final long substreamValue = (rawValue >>> log2m);final byte p_w;if(substreamValue == 0L) {// The paper does not cover p(0x0), so the special value 0 is used.// 0 is the original initialization value of the registers, so by// doing this the multiset simply ignores it. This is acceptable// because the probability is 1/(2^(2^registerSizeInBits)).p_w = 0;} else {
// 取value 标志位的最低小有效位p_w = (byte)(1 + BitUtil.leastSignificantBit(substreamValue| pwMaxMask));}// Short-circuit if the register is being set to zero, since algorithmically// this corresponds to an "unset" register, and "unset" registers aren't// stored to save memory. (The very reason this sparse implementation// exists.) If a register is set to zero it will break the #algorithmCardinality// code.if(p_w == 0) {return;}// NOTE: no +1 as in paper since 0-based indexing
//取桶的索引final int j = (int)(rawValue & mBitsMask);
//当前桶中的值final byte currentValue = sparseProbabilisticStorage.get(j);
//当前值比桶中的值大,则替换if(p_w > currentValue) {sparseProbabilisticStorage.put(j, p_w);}}
FULL BitVector
插入逻辑同上
/*** Adds the raw value to the {@link #probabilisticStorage}.* {@link #type} must be {@link HLLType#FULL}.** @param rawValue the raw value to add to the full probabilistic storage.*/private void addRawProbabilistic(final long rawValue) {// p(w): position of the least significant set bit (one-indexed)// By contract: p(w) <= 2^(registerValueInBits) - 1 (the max register value)//// By construction of pwMaxMask (see #Constructor()),// lsb(pwMaxMask) = 2^(registerValueInBits) - 2,// thus lsb(any_long | pwMaxMask) <= 2^(registerValueInBits) - 2,// thus 1 + lsb(any_long | pwMaxMask) <= 2^(registerValueInBits) -1.final long substreamValue = (rawValue >>> log2m);final byte p_w;if (substreamValue == 0L) {// The paper does not cover p(0x0), so the special value 0 is used.// 0 is the original initialization value of the registers, so by// doing this the multiset simply ignores it. This is acceptable// because the probability is 1/(2^(2^registerSizeInBits)).p_w = 0;} else {p_w = (byte)(1 + BitUtil.leastSignificantBit(substreamValue| pwMaxMask));}// Short-circuit if the register is being set to zero, since algorithmically// this corresponds to an "unset" register, and "unset" registers aren't// stored to save memory. (The very reason this sparse implementation// exists.) If a register is set to zero it will break the #algorithmCardinality// code.if(p_w == 0) {return;}// NOTE: no +1 as in paper since 0-based indexingfinal int j = (int)(rawValue & mBitsMask);probabilisticStorage.setMaxRegister(j, p_w);}
基数计算
// Cardinality/*** Computes the cardinality of the HLL.** @return the cardinality of HLL. This will never be negative.*/public long cardinality() {switch(type) {case EMPTY:return 0/*by definition*/;case EXPLICIT:return explicitStorage.size();case SPARSE:return (long)Math.ceil(sparseProbabilisticAlgorithmCardinality());case FULL:return (long)Math.ceil(fullProbabilisticAlgorithmCardinality());default:throw new RuntimeException("Unsupported HLL type " + type);}}
Sparse Probabilistic Algorithm Cardinality
稀疏和FULL两种情况计算公式一致
/*** Computes the exact cardinality value returned by the HLL algorithm when* represented as a {@link HLLType#SPARSE} HLL. Kept* separate from {@link #cardinality()} for testing purposes. {@link #type}* must be {@link HLLType#SPARSE}.** @return the exact, unrounded cardinality given by the HLL algorithm*//*package, for testing*/ double sparseProbabilisticAlgorithmCardinality() {final int m = this.m/*for performance*/;// compute the "indicator function" -- sum(2^(-M[j])) where M[j] is the// 'j'th register value
计算sum(2^(-M[j])),基中M[j]为第j个桶的值double sum = 0;int numberOfZeroes = 0/*"V" in the paper*/;for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {final long register = sparseProbabilisticStorage.get(j);sum += 1.0 / (1L << register);if(register == 0L) numberOfZeroes++;}// apply the estimate and correction to the indicator function
//alphaMSquared 为alphaMSquared方法中计算的值,有兴趣的小伙伴可以对照公上公司,这里计算公式与上边公式描述一致。final double estimator = alphaMSquared / sum;if((numberOfZeroes != 0) && (estimator < smallEstimatorCutoff)) {return HLLUtil.smallEstimator(m, numberOfZeroes);} else if(estimator <= largeEstimatorCutoff) {return estimator;} else {return HLLUtil.largeEstimator(log2m, regwidth, estimator);}}
alpha-m-square 为常量,即上文公式中提到的常量
/*** Computes the 'alpha-m-squared' constant used by the HyperLogLog algorithm.** @param m this must be a power of two, cannot be less than* 16 (2<sup>4</sup>), and cannot be greater than 65536 (2<sup>16</sup>).* @return gamma times <code>registerCount</code> squared where gamma is* based on the value of <code>registerCount</code>.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if <code>registerCount</code> is less* than 16.*/public static double alphaMSquared(final int m) {switch(m) {case 1/*2^0*/:case 2/*2^1*/:case 4/*2^2*/:case 8/*2^3*/:throw new IllegalArgumentException("'m' cannot be less than 16 (" + m + " < 16).");case 16/*2^4*/:return 0.673 * m * m;case 32/*2^5*/:return 0.697 * m * m;case 64/*2^6*/:return 0.709 * m * m;default/*>2^6*/:return (0.7213 / (1.0 + 1.079 / m)) * m * m;}}
参考资料
https://www.jianshu.com/p/55defda6dcd2
https://github.com/aggregateknowledge/java-hll
作者:zh_harry
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/27d9a7912fce
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。