目录
1. 线程池是什么
2. 线程池的优点:
3. 线程池的应用场景
4. 线程池的实现
4.1 线程池实现原理
4.2 线程池基本框架
4.3 结构体:
4.4 提供的接口
4.5 线程池测试代码
5 线程池提高demo
thrd_pool.h
thrd_pool.c
main.c
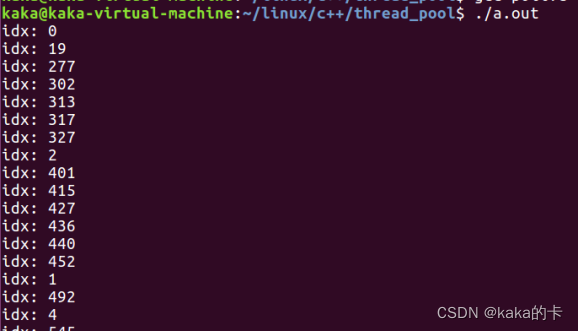
运行结果
6 reactor中线程池
7 nginx 中线程池
8 redis 中线程池
9 skynet 中线程池
1. 线程池是什么

线程池一种线程使用模式。
因为线程过多会带来调度开销,影响缓存局部性和整体性能。线程池是用来维护着多个线程,等待监督管理者分配可并发执行的任务。
2. 线程池的优点:
- 解决在处理短时间任务时创建与销毁线程的代价。
- 线程池不仅能够保证内核充分利用多线程,还能防止过分调度。
注意点:
线程池中可用线程的数量应该取决于可用的并发处理器、处理器内核、内存、网络sockets等的数量。
3. 线程池的应用场景
a. 需要大量的线程来完成任务,并且要求完成任务的时间比较短。
比如Web服务器完成网页请求这样的任务,使用线程池技术是非常合适的。因为单个任务小,而任务数量巨大,你可以想象一个热门网站的点击次数。
b. 对性能要求苛刻的应用,比如要求服务器迅速响应客户请求。
对于长时间的任务,比如Telnet连接请求,线程池的优点就不明显了。因为Telnet会话时间比线程的创建时间大多了。
c. 接受突发性的大量请求,但不至于使服务器因此产生大量线程的应用。
突发性大量客户请求,在没有线程池的情况下,将产生大量线程,虽然理论上大部分操作系统线程数目最大值不是问题,但短时间内产生大量线程可能使内存到达极限,出现错误。
问题:创建的线程越多性能越高?
答:不正确。一开始,程序的运行效率会随着线程数量的增加而逐渐变高。当线程数量增加临界值时,线程数量继续增加,程序的运行效率会减少。(由于线程的频繁切换影响了线程运行效率)。
4. 线程池的实现
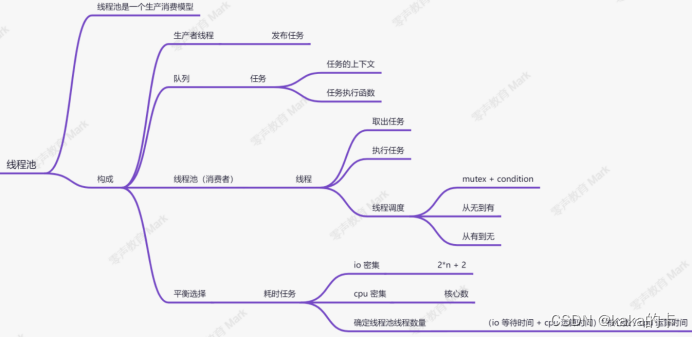
4.1 线程池实现原理
线程池由一个阻塞任务队列加上多个线程实现,线程池中的线程可以从阻塞任务队列中获取任务然后进行任务处理,当线程都处于繁忙状态时可以将任务加入阻塞队列中,等到其它的线程空闲后进行处理。
4.2 线程池基本框架
线程池的主体是一个任务队列和n个线程(工作队列):
a.任务队列用来保存外界传入的需要解决的任务。
b.而线程池中的n个线程负责一直从任务队列中拿出任务并解决。
另外还需要一把互斥锁和一个条件变量:
互斥锁:用来保护任务队列的数据安全,即维护多线程从任务队列中pop任务时的互斥关系。
条件变量:用来维护多线程之间的同步关系,当任务队列为空时要求线程释放互斥锁并在条件变量下等待,这时任务队列中每插入一个任务就唤醒一个线程。
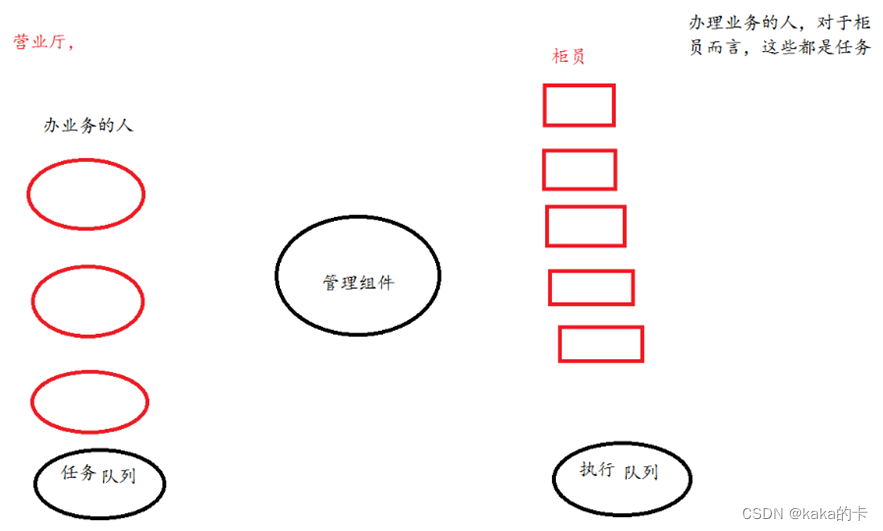
4.3 结构体:

分别为任务队列(生产者)、工作队列(消费者)、管理组件(互斥锁和条件变量)。
//任务队列(生产者) 链表
struct nTask{void (*task_func)(struct nTask* task); //任务函数回调void* user_data; //任务用户数据struct nTask* prev;struct nTask* next;
};//工作队列(消费者) 链表
struct nWorker{pthread_t threadid; //工作线程id struct nManager* manager;struct nWorker* prev;struct nWorker* next;
};//管理互斥锁和条件变量
typedef struct nManager {struct nTask* tasks; //任务队列struct nWorker* workers;//工作队列pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁pthread_cond_t cond; //条件变量
} ThreadPool;4.4 提供的接口
//线程池工作线程创建
int nThreadPoolCreate(ThreadPool* pool, int numWorkers)//唤醒全部工作队列中的线程(销毁线程池)
int nThreadPoolDestory(ThreadPool* pool, int nWorker)//唤醒单个工作队列中的线程
int nThreadPoolPushTask(ThreadPool* pool, struct nTask* task)
4.5 线程池测试代码
创建10个thread线程加入工作队列,阻塞等待。随后创建了1000个task任务,写入 task的数据,去唤醒工作队列中的线程,管理组件判断任务有无,调用task的func来执行任务。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>#define THREADPOOL_INIT_COUNT 20 //工作线程数量
#define TASK_INIT_SIZE 1000 //任务数量//双向链表插入(头插),list为头结点
#define LIST_INSERT(item, list) do{ \item->prev = NULL; \item->next =list; \if((list) != NULL)(list)->prev = item; \(list) = item; \
}while(0)//双向链表删除,list为头结点
#define LIST_REMOVE(item, list) do{ \if(item->prev != NULL)item->prev->next = item->next;\if(item->next != NULL)item->next->prev = item->prev;\if(item == list)list = item->next;\item->prev = item->next = NULL;\
}while(0)//任务队列(生产者) 链表
struct nTask{void (*task_func)(struct nTask* task); //任务函数回调void* user_data; //任务用户数据struct nTask* prev;struct nTask* next;
};//工作队列(消费者) 链表
struct nWorker{pthread_t threadid; //工作线程id struct nManager* manager;struct nWorker* prev;struct nWorker* next;
};//管理互斥锁和条件变量
typedef struct nManager {struct nTask* tasks; //任务队列struct nWorker* workers;//工作队列pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁pthread_cond_t cond; //条件变量
} ThreadPool;//消费者工作线程
static void* nThreadPoolCallback(void* arg)
{struct nWorker* worker = (struct nWorker*)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->manager->mutex); while(worker->manager->tasks == NULL){ //任务队列为空//解锁,阻塞等待唤醒,唤醒后加锁继续工作pthread_cond_wait(&worker->manager->cond, &worker->manager->mutex);}struct nTask* task = worker->manager->tasks; //从头结点开始消费LIST_REMOVE(task, worker->manager->tasks); //任务队列移除头结点pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->manager->mutex); task->task_func(task); //任务函数回调}free(worker);}//线程池工作线程创建
int nThreadPoolCreate(ThreadPool* pool, int numWorkers)
{if (pool == NULL) return -1;if (numWorkers < 1) numWorkers = 1;memset(pool, 0, sizeof(ThreadPool));pthread_cond_t blank_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; //静态申请 条件变量memcpy(&pool->cond, &blank_cond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));pthread_mutex_t blank_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; //静态申请 互斥锁memcpy(&pool->mutex, &blank_mutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));int i = 0;for(i = 0; i < numWorkers; i++){struct nWorker* worker = (struct nWorker*)malloc(sizeof(struct nWorker));if (worker == NULL) {perror("malloc");return -1;}memset(worker, 0, sizeof(struct nWorker));worker->manager = pool; int ret = pthread_create(&worker->threadid, NULL, nThreadPoolCallback, worker);if (ret) { //失败perror("pthread_create fail");free(worker);return -2;}LIST_INSERT(worker, pool->workers); //工作队列结点插入}return 0;
}//唤醒全部工作队列中的线程(销毁线程池)
int nThreadPoolDestory(ThreadPool* pool, int nWorker)
{struct nWorker* worker = NULL;pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex); //唤醒全部阻塞在条件变量上的工作线程pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex); pool->workers = NULL;pool->tasks = NULL;return 0;
}//唤醒单个工作队列中的线程
int nThreadPoolPushTask(ThreadPool* pool, struct nTask* task)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex); LIST_INSERT(task, pool->tasks);//唤醒至少一个阻塞在条件变量上的线程pthread_cond_signal(&pool->cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex); }//任务执行回调函数
void task_etry(struct nTask* task)
{int idx = *(int*)task->user_data;printf("idx: %d\n", idx);free(task->user_data);free(task);
}int main(void)
{ThreadPool pool = {0};//线程池工作线程创建nThreadPoolCreate(&pool, THREADPOOL_INIT_COUNT);for(int i = 0; i < TASK_INIT_SIZE; i++){struct nTask* task = (struct nTask*)malloc(sizeof(struct nTask)); if (task == NULL) {perror("malloc");exit(1);}memset(task, 0, sizeof(struct nTask));task->task_func = task_etry; //注册回调task->user_data = malloc(sizeof(int));*(int*)task->user_data = i;//唤醒单个工作队列中的线程nThreadPoolPushTask(&pool, task); }getchar();
}
5 线程池提高demo
thrd_pool.h
#ifndef _THREAD_POOL_H
#define _THREAD_POOL_H//声明结构体,不暴露出来
typedef struct thread_pool_t thread_pool_t;
//任务函数指针
typedef void (*handler_pt) (void *);/*线程池创建*/
thread_pool_t *thread_pool_create(int thrd_count, int queue_size);/*线程池抛出出任务*/
int thread_pool_post(thread_pool_t *pool, handler_pt func, void *arg);/*线程池销毁*/
int thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *pool);/*线程池线程join*/
int wait_all_done(thread_pool_t *pool);#endifthrd_pool.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "thrd_pool.h"/*任务*/
typedef struct task_t {handler_pt func; //任务执行函数void * arg; //上下文参数
} task_t;/*任务队列结构体*/
typedef struct task_queue_t {uint32_t head; //uint32_t tail; //uint32_t count; //当前有多少个任务task_t *queue; //任务队列
} task_queue_t;/*线程池结构体*/
struct thread_pool_t {pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁pthread_cond_t condition; //条件变量pthread_t *threads; //线程数 数组task_queue_t task_queue; //任务队列结构体int closed; //标记线程池退出int started; // 当前运行的线程数int thrd_count; //线程数int queue_size; //任务队列最大值
};static void * thread_worker(void *thrd_pool);
static void thread_pool_free(thread_pool_t *pool);thread_pool_t * thread_pool_create(int thrd_count, int queue_size) {thread_pool_t *pool;if (thrd_count <= 0 || queue_size <= 0) {return NULL;}pool = (thread_pool_t*) malloc(sizeof(thread_pool_t));if (pool == NULL) {return NULL;}//初始化线程池pool->thrd_count = 0;pool->queue_size = queue_size;pool->started = pool->closed = 0;pool->threads = (pthread_t*) malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * thrd_count);if (pool->threads == NULL) {// TODO: free poolreturn NULL;}//初始化任务队列pool->task_queue.head = 0;pool->task_queue.tail = 0;pool->task_queue.count = 0;pool->task_queue.queue = (task_t*)malloc(sizeof(task_t)*queue_size);if (pool->task_queue.queue == NULL) {// TODO: free poolreturn NULL;}//启动线程int i = 0;for (; i < thrd_count; i++) {if (pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, thread_worker, (void*)pool) != 0) {// TODO: free poolreturn NULL;}pool->thrd_count++;pool->started++;}return pool;
}int thread_pool_post(thread_pool_t *pool, handler_pt func, void *arg) {if (pool == NULL || func == NULL) {return -1;}task_queue_t *task_queue = &(pool->task_queue);if (pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0) {return -2;}if (pool->closed) {pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));return -3;}if (task_queue->count == pool->queue_size) {pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));return -4;}task_queue->queue[task_queue->tail].func = func;task_queue->queue[task_queue->tail].arg = arg;task_queue->tail = (task_queue->tail + 1) % pool->queue_size;task_queue->count++;if (pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->condition)) != 0) {pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));return -5;}pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));return 0;
}static void
thread_pool_free(thread_pool_t *pool) {if (pool == NULL || pool->started > 0) {return;}if (pool->threads) {free(pool->threads);pool->threads = NULL;pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->condition);}if (pool->task_queue.queue) {free(pool->task_queue.queue);pool->task_queue.queue = NULL;}free(pool);
}int
wait_all_done(thread_pool_t *pool) {int i, ret=0;for (i=0; i < pool->thrd_count; i++) {if (pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL) != 0) {ret=1;}}return ret;
}int thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *pool) {if (pool == NULL) {return -1;}if (pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0) {return -2;}if (pool->closed) {thread_pool_free(pool);return -3;}//终止线程池pool->closed = 1;//唤醒所有休眠线程if (pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->condition)) != 0 || pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0) {thread_pool_free(pool);return -4;}//等待唤醒线程退出wait_all_done(pool);thread_pool_free(pool);return 0;
}static void * thread_worker(void *thrd_pool) {thread_pool_t *pool = (thread_pool_t*)thrd_pool;task_queue_t *que;task_t task;for (;;) {pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));que = &pool->task_queue;// 虚假唤醒 linux pthread_cond_signal// linux 可能被信号唤醒// 业务逻辑不严谨,被其他线程抢了该任务while (que->count == 0 && pool->closed == 0) { //如果没有任务// pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex))// 阻塞在 condition// ===================================// 解除阻塞// pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->condition), &(pool->mutex)); //睡眠,自动解锁}if (pool->closed == 1) break;task = que->queue[que->head];que->head = (que->head + 1) % pool->queue_size;que->count--;pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));(*(task.func))(task.arg);}pool->started--;pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));pthread_exit(NULL);return NULL;
}main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>#include "thrd_pool.h"int nums = 0;
int done = 0;pthread_mutex_t lock;void do_task(void *arg) {usleep(10000);pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);done++;printf("doing %d task\n", done);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}int main(int argc, char **argv) {int threads = 8;int queue_size = 256;if (argc == 2) {threads = atoi(argv[1]);if (threads <= 0) {printf("threads number error: %d\n", threads);return 1;}} else if (argc > 2) {threads = atoi(argv[1]);queue_size = atoi(argv[1]);if (threads <= 0 || queue_size <= 0) {printf("threads number or queue size error: %d,%d\n", threads, queue_size);return 1;}}thread_pool_t *pool = thread_pool_create(threads, queue_size);if (pool == NULL) {printf("thread pool create error!\n");return 1;}while (thread_pool_post(pool, &do_task, NULL) == 0) {pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);nums++;pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);}printf("add %d tasks\n", nums);wait_all_done(pool);printf("did %d tasks\n", done);thread_pool_destroy(pool);return 0;
}
运行结果

6 reactor中线程池
在一个事件循环中,可以处理多个就绪事件,这些就绪事件在reactor 模型中时串行执行的,一个事件处理若耗时较长,会延迟其他同时触发的事件的处理(对于客户端而言,响应会变得较慢)。
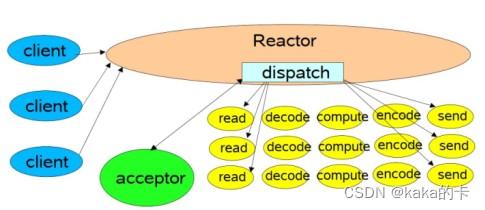
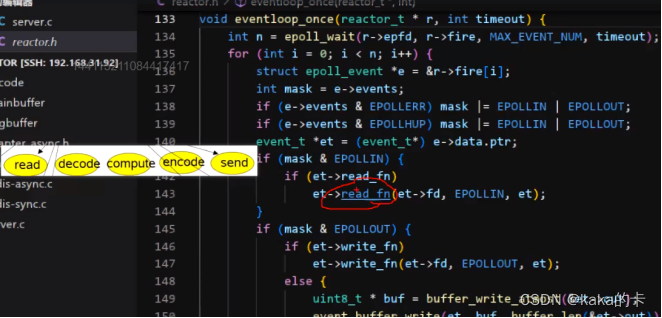
7 nginx 中线程池
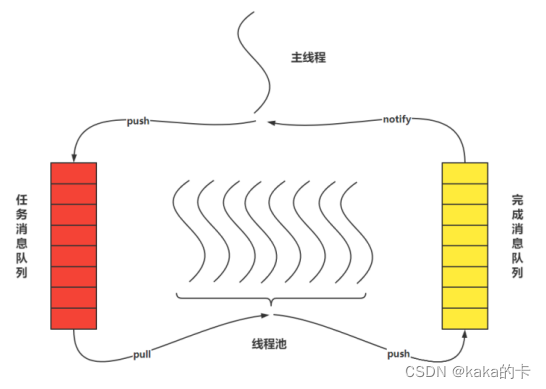
作用:处理文件缓冲;
线程池作用阶段

开启线程池
# 线程池默认关闭,configure 时,需要 --with-threads
来指定;
./configure --with-pcre-jit --withhttp_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --withhttp_stub_status_module --with-http_v2_module --
with-threads# 解决 gdb 远程权限的问题
echo 0 | sudo tee
/proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope# 创建名为 mark 的线程池
thread_pool mark threads=32 max_queue=65535;
location / {
root /img;
aio threads=mark;
}
location / {
sendfile on;
sendfile_max_chunk 128k; # 默认是没有限制的
}
location / {
directio 8m;
} 
8 redis 中线程池
作用:读写 io 处理以及数据包解析、压缩;
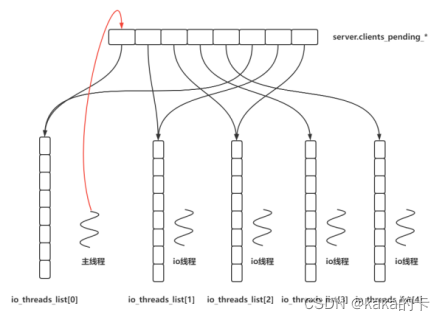
线程池作用阶段

9 skynet 中线程池
作用:处理读写 io 、数据包解压缩、业务逻辑处理;特别地:当同一个 io 在多个线程处理时,将写 io 转由网络线程处理;
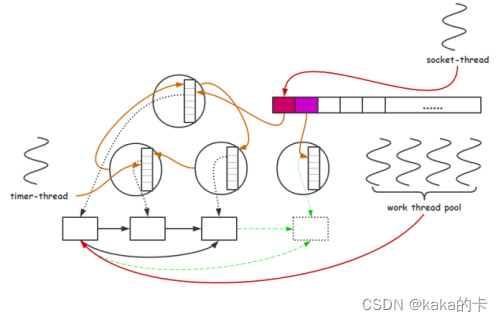
线程池作用阶段