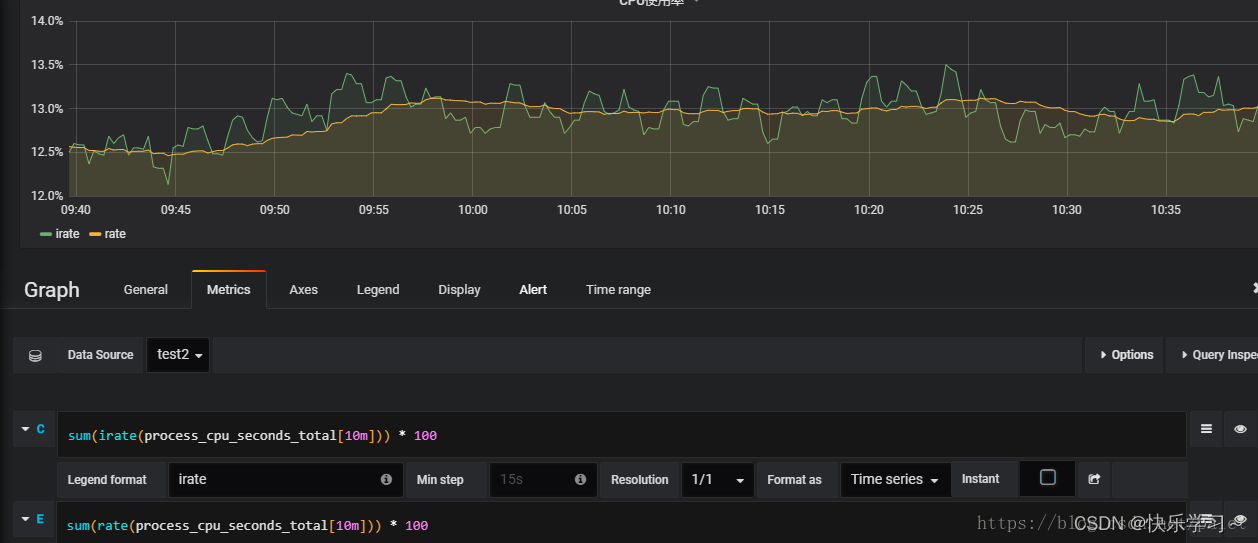
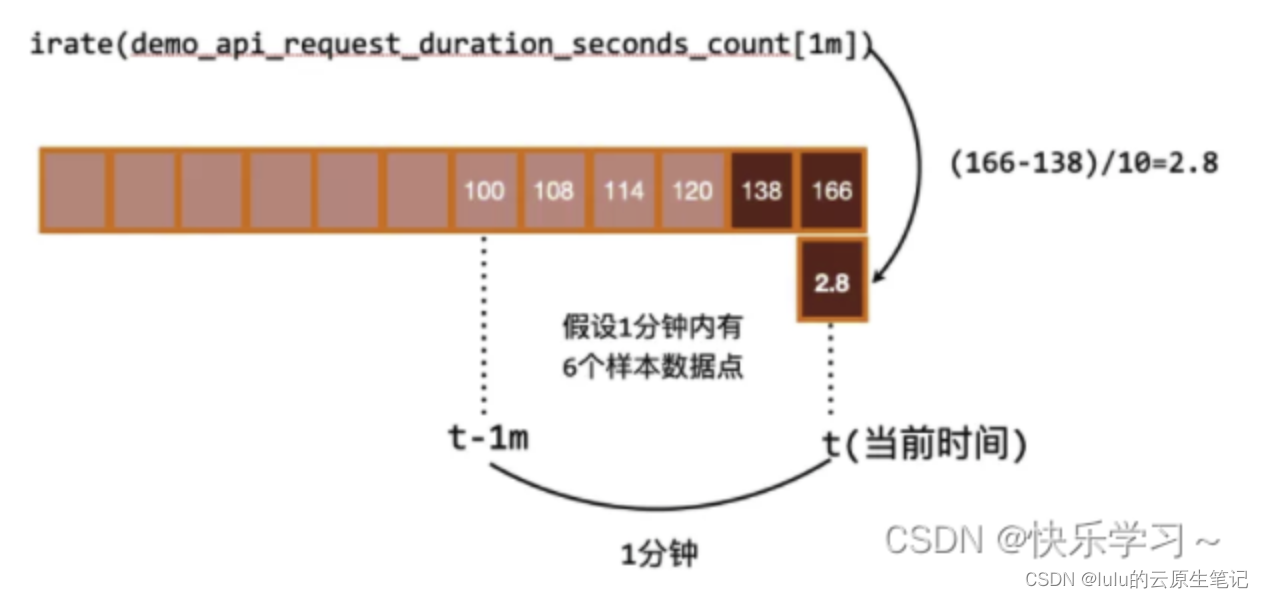
我们先看prometheus的函数格式
一 类型
var Functions = map[string]*Function{..."rate": {Name: "rate",ArgTypes: []ValueType{ValueTypeMatrix},ReturnType: ValueTypeVector,Call: funcRate,},..."irate": {Name: "irate",ArgTypes: []ValueType{ValueTypeMatrix},ReturnType: ValueTypeVector,Call: funcIrate,},...
}
func getFunction(name string) (*Function, bool) {function, ok := Functions[name]return function, ok
}
//通过getfunc 传递name 我们拿到func 并且调用
二 irate
那么我们具体看一下rate是如何实现的
func funcIrate(vals []Value, args Expressions, enh *EvalNodeHelper) Vector {return instantValue(vals, enh.out, true)
}
func instantValue(vals []Value, out Vector, isRate bool) Vector {samples := vals[0].(Matrix)[0]/*type Matrix []Seriestype Series struct {Metric labels.Labels `json:"metric"`Points []Point `json:"values"`}type Point struct {T int64V float64}type Vector []Sampletype Sample struct {PointMetric labels.Labels}也就是说samples = Series type*/// No sense in trying to compute a rate without at least two points. Drop// this Vector element.//试图计算一个没有至少两个点的速率是没有意义的。删除这个向量元素if len(samples.Points) < 2 {return out}// 2个值以上//倒数第一个值lastSample := samples.Points[len(samples.Points)-1]//倒数第二个值previousSample := samples.Points[len(samples.Points)-2]//声明一个新的valuevar resultValue float64//如果是rate 并且倒数第一个值小于倒数第二个值if isRate && lastSample.V < previousSample.V {// Counter reset.//那么 把倒数第一个值赋予我们新的变量resultValue = lastSample.V} else {//否则就算差值resultValue = lastSample.V - previousSample.V}//采样时间间隔等于 两个值的时间差sampledInterval := lastSample.T - previousSample.Tfmt.Println("\n\n")fmt.Printf("vals %#v\n",vals)fmt.Printf("out %#v\n",out)fmt.Println("last",lastSample.T)fmt.Println("pre",previousSample.T)fmt.Println("samp",sampledInterval)fmt.Println("len",len(vals[0].(Matrix)[0].Points))fmt.Println("\n\n")//时间间隔为0 就直接返回outif sampledInterval == 0 {// Avoid dividing by 0.return out}//这里是irate 传递的是true 详情见funcIrateif isRate {// Convert to per-second.//转换为每s// a = float64(sampledInterval) / 1000// resultValue = resultValue / a//这里sampledInterval 是我们计算的时间差resultValue /= float64(sampledInterval) / 1000}return append(out, Sample{Point: Point{V: resultValue},})
}
我这里prome配置的采集间隔为20s
irate(go_memstats_alloc_bytes_total[1m])

irate(go_memstats_alloc_bytes_total[2m])

根据代码以及promeql不难看出 1m 3个采集点 也就是说20 * 3 ,2m 6个采集点 也就是说20 * 6
根据代码是从采集点中首先判断如果低于2个指标直接返回,如果2个以上取最后两个并且判断大小 如果后续大于上一个 那么就取差值,并且除以采集间隔,算出每秒的数据 counter是只增不减的数据类型
三 rate
func funcRate(vals []Value, args Expressions, enh *EvalNodeHelper) Vector {return extrapolatedRate(vals, args, enh, true, true)
}
/*
extrapolatedRate是用于速率/增加/增量的实用函数。
它计算速率(如果isCounter为true,则允许计数器重置),
如果第一个/最后一个采样接近边界,则进行推断,
并以每秒(如果isRate为true)或总体形式返回结果。*/
//rate 传递的参数为extrapolatedRate(vals, args, enh, true, true)
//由此可以理解rate一般用于Counter类型
func extrapolatedRate(vals []Value, args Expressions, enh *EvalNodeHelper, isCounter bool, isRate bool) Vector {ms := args[0].(*MatrixSelector)/*type MatrixSelector struct {// 如果解析器未返回错误,则可以假定这是一个VectorSelector。VectorSelector ExprRange time.DurationEndPos Pos}type Expr interface {Node// Type返回表达式求值的类型。 它不会执行深入检查,因为这是在解析时完成的。Type() ValueType//expr确保没有其他类型的接口意外实现。expr()}type ValueType stringtype Node interface {// 当作为有效查询的一部分进行解析时,返回给定节点的节点的字符串表示形式。String() string//PositionRange返回AST节点在查询字符串中的位置。PositionRange() PositionRange}*/vs := ms.VectorSelector.(*VectorSelector)/*type VectorSelector struct {Name stringOffset time.DurationLabelMatchers []*labels.Matcher//在查询准备时填充未扩展的seriesSet。unexpandedSeriesSet storage.SeriesSetseries []storage.SeriesPosRange PositionRange}*/var (samples = vals[0].(Matrix)[0]//durationMilliseconds//d/ (s/ns)//int64(d / (time.Millisecond / time.Nanosecond))rangeStart = enh.ts - durationMilliseconds(ms.Range+vs.Offset)rangeEnd = enh.ts - durationMilliseconds(vs.Offset))// 在没有至少两个点的情况下尝试计算速率没有任何意义。 删除此Vector元素。if len(samples.Points) < 2 {return enh.out}var (counterCorrection float64lastValue float64)fmt.Printf("%#v\n",ms)fmt.Printf("%#v\n",vs)fmt.Printf("%#v\n",samples.Points)//这里主要是为了防止不是counter类型的 会出现忽大忽小for _, sample := range samples.Points {if isCounter && sample.V < lastValue {counterCorrection += lastValue}lastValue = sample.V}//拿到第一个根最后一个的中间差resultValue := lastValue - samples.Points[0].V + counterCorrection// Duration between first/last samples and boundary of range.//第一个/最后一个样本与范围边界之间的持续时间。durationToStart := float64(samples.Points[0].T-rangeStart) / 1000durationToEnd := float64(rangeEnd-samples.Points[len(samples.Points)-1].T) / 1000sampledInterval := float64(samples.Points[len(samples.Points)-1].T-samples.Points[0].T) / 1000averageDurationBetweenSamples := sampledInterval / float64(len(samples.Points)-1)if isCounter && resultValue > 0 && samples.Points[0].V >= 0 {// Counters cannot be negative. If we have any slope at// all (i.e. resultValue went up), we can extrapolate// the zero point of the counter. If the duration to the// zero point is shorter than the durationToStart, we// take the zero point as the start of the series,// thereby avoiding extrapolation to negative counter// values.//计数器不能为负。//如果我们有任何斜率(即resultValue上升),我们可以外推计数器的零点。//如果到零点的持续时间比durationToStart短,我们将零点作为序列的开始,从而避免外推到负计数器值。durationToZero := sampledInterval * (samples.Points[0].V / resultValue)if durationToZero < durationToStart {durationToStart = durationToZero}}// If the first/last samples are close to the boundaries of the range,// extrapolate the result. This is as we expect that another sample// will exist given the spacing between samples we've seen thus far,// with an allowance for noise.//如果第一个/最后一个样本接近范围的边界,则外推结果。//就像我们期望的那样,考虑到到目前为止我们看到的样本之间的间隔,还会有另一个样本存在,并且要考虑到噪声。extrapolationThreshold := averageDurationBetweenSamples * 1.1extrapolateToInterval := sampledIntervalif durationToStart < extrapolationThreshold {extrapolateToInterval += durationToStart} else {extrapolateToInterval += averageDurationBetweenSamples / 2}if durationToEnd < extrapolationThreshold {extrapolateToInterval += durationToEnd} else {extrapolateToInterval += averageDurationBetweenSamples / 2}resultValue = resultValue * (extrapolateToInterval / sampledInterval)if isRate {resultValue = resultValue / ms.Range.Seconds()}return append(enh.out, Sample{Point: Point{V: resultValue},})
}