ssms,新建查询设置字体
SQLCMD Mode allows creating, testing, executing SQLCMD commands or scripts in SQL Server Management Studio directly in the query editor. This option is available since SQL Server 2005.
SQLCMD模式允许直接在查询编辑器中在SQL Server Management Studio中创建,测试,执行SQLCMD命令或脚本。 从SQL Server 2005开始,此选项可用。
This article will explain some of the SQLCMD script keywords that the Database Engine Query Editor supports.
本文将解释数据库引擎查询编辑器支持的一些SQLCMD脚本关键字。
To write or edit SQLCMD scripts in the query editor, the SQLCMD mode needs to be enabled. By default, this mode is turned off.
要在查询编辑器中编写或编辑SQLCMD脚本,需要启用SQLCMD模式。 默认情况下,此模式是关闭的。
To enable SQLCMD mode, click the SQLCMD Mode option under the Query menu:
若要启用SQLCMD模式,请单击“ 查询”菜单下的“ SQLCMD模式”选项:

Another way to enable the SQLCMD Mode is by using a combination of keys ALT+Q+M from the keyboard.
启用SQLCMD模式的另一种方法是组合使用键盘上的ALT + Q + M键。
In SSMS, there is an option to set the query windows to be opened in the SQLCMD mode by default. To do that, go to the SSMS main menu and under the Tools menu choose the Options command:
在SSMS中,有一个选项可以设置默认情况下在SQLCMD模式下打开查询窗口。 为此,请转到SSMS主菜单,然后在“ 工具”菜单下选择“ 选项”命令:

This will open the Options window. From the list, choose the Query Execution -> SQL Server -> General and check the “By default, open new queries in SQLCMD mode” checkbox:
这将打开“ 选项”窗口。 从列表中,选择查询执行-> SQL Server->常规,然后选中“默认情况下,以SQLCMD模式打开新查询”复选框:

When using SQLCMD mode the IntelliSense and Transact-SQL debugger are turned off in the Database Engine Query Editor.
使用SQLCMD模式时,在数据库引擎查询编辑器中将关闭IntelliSense和Transact-SQL 调试器。
In the SQLCMD mode, two types of statement can be entered: the first are the SQLCMD and second are T-SQL statements.
在SQLCMD模式下,可以输入两种类型的语句:第一种是SQLCMD,第二种是T-SQL语句。
In the example below, some of the SQLCMD script keywords will be explained:
在下面的示例中,将解释一些SQLCMD脚本关键字:
:CONNECT ZIVKO\ZIVKO2014 :OUT C:\Users\Marko\Data.txt
:CONNECT ZIVKO \ ZIVKO2014 :OUT C:\ Users \ Marko \ Data.txt
USE AdventureWorks2014; SELECT a.City, a.PostalCode FROM Person.Address a
使用 AdventureWorks2014; 从个人中选择 a.City,a.PostalCode。 地址 a
When executing the code, the result in the query editor will be:
执行代码时,查询编辑器中的结果将是:
The SQLCMD commands are automatically highlighted in gray and the T-SQL statements appear normal as it appears in the regular query.
SQLCMD命令将自动以灰色突出显示,并且T-SQL语句显示为常规查询中的正常状态。
Most of the SQLCMD commands begin with a colon (:). For a few SQLCMD commands, such as QUIT and EXIT though, a colon (:) can be omitted.
大多数SQLCMD命令以冒号(:)开头。 对于一些SQLCMD命令,例如QUIT和EXIT,可以省略冒号(:)。
For example, the quit command will work the same as the command : quit.
例如, quit命令将与命令quit相同。
This is enabled because of backward compatibility with the osql utility.
由于与osql实用程序具有向后兼容性,因此启用了此功能。
Only one SQLCMD command can be in each line. If two or more SQLCMD commands appear in one line:
每行中只能有一个SQLCMD命令。 如果一行中出现两个或更多SQLCMD命令:
:connect ZIVKO\ZIVKO2014 :out C:\Users\Marko\Data.txt
:connect ZIVKO \ ZIVKO2014:out C:\ Users \ Marko \ Data.txt
the following error will appear:
将出现以下错误:
A fatal scripting error occurred.
Incorrect syntax was encountered while parsing :setvar.
发生致命的脚本错误。
解析:setvar时遇到语法错误。
:connect SQLCMD script keyword
:connect SQLCMD脚本关键字
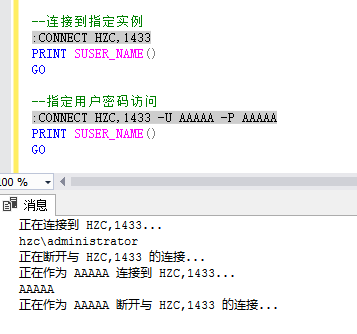
This creates a connection to a SQL Server instance. If the instance is the default one, or if is specified by the server/instance name, then SQLCMD uses Windows authentication for connecting to SQL Server with a current account:
这将创建到SQL Server实例的连接。 如果实例是默认实例,或者由服务器/实例名称指定,则SQLCMD使用Windows身份验证使用当前帐户连接到SQL Server:
:connect (local) or
:connect ZIVKO\ZIVKO2014
:connect(本地)或
:连接ZIVKO \ ZIVKO2014
SQLCMD also allows specifying a username and password when connecting to an instance. To include a username, add -U switch and then the name of a user. To include a password, use -P switch and enter a password:
SQLCMD还允许在连接到实例时指定用户名和密码。 要包含用户名,请添加-U开关,然后添加用户名。 要包含密码,请使用-P开关并输入密码:
:connect ZIVKO\ZIVKO2014 -U <username> -P <password>
:connect ZIVKO \ ZIVKO2014 -U <用户名> -P <密码>
:out SQLCMD script keyword
:out SQLCMD脚本关键字
This command provides a location where the query results will be redirected. In this example, the results will be redirected to the Data.txt file:
该命令提供了将查询结果重定向的位置。 在此示例中,结果将被重定向到Data.txt文件:
:out C:\Users\Marko\Data.txt
:out C:\ Users \ Marko \ Data.txt

To change the appearance of the results in the Data.txt file, go to Tools -> Options -> Query Results -> SQL Server -> Results to Text and from the Output format combo box, choose for example the Comma delimited option:
要更改结果在Data.txt文件中的外观,请转到“工具”->“选项”->“查询结果”->“ SQL Server”->“结果为文本”,然后从“ 输出格式”组合框中,选择“ 逗号分隔”选项:

After executing the same T-SQL statement, the result will be:
执行相同的T-SQL语句后,结果将是:
SQLCMD is very useful when it needs to execute the same code on multiple databases or servers. In the example below, it is shown how a user can be added on multiple databases.
当需要在多个数据库或服务器上执行相同的代码时,SQLCMD非常有用。 在下面的示例中,显示了如何在多个数据库上添加用户。
Open a new query editor, switch to the SQLCMD mode (QuerySQLCMD Mode) and paste the following code:
打开一个新的查询编辑器,切换到SQLCMD模式(QuerySQLCMD模式)并粘贴以下代码:
:setvar username “Marko” :setvar login “Zivko”
:setvar用户名“ Marko” :setvar登录“ Zivko”
EXEC sp_grantdbaccess ‘$(login)’, ‘$(username)’ GO
EXEC sp_grantdbaccess'$ {登录)','$ {用户名)' GO
Save this code as the User.sql file on this location “C:\User”.
将此代码另存为“ C:\ User”位置上的User.sql文件。
sp_grantdbaccess –Stored procedure that adds a user to the current database.
sp_grantdbaccess –将用户添加到当前数据库的存储过程。
Setvar脚本关键字 (Setvar script keyword)
Example
例
:setvar <var> <value>
:setvar <var> <值>
This defines sqlcmd variables. The first item is the name of the sqlcmd variable (<var>) and the second item is the value of the sqlcmd variable (<value>). Variable names (<var>) are case insensitive.
这定义了sqlcmd变量。 第一项是sqlcmd变量(<var>)的名称,第二项是sqlcmd变量(<value>)的值。 变量名称(<var>)不区分大小写。
Variable name cannot have blank spaces. The following sqlcmd variable name:
变量名称不能有空格。 以下sqlcmd变量名称:
:setvar user name “Marko”
:setvar用户名“ Marko”
will raise this error:
将引发此错误:
A fatal scripting error occurred.
Incorrect syntax was encountered while parsing :setvar.
发生致命的脚本错误。
解析:setvar时遇到语法错误。
变量标识符 (Variable identifier )
Example
例
$(<var>)
$(<var>)
The variable identifier can be used as a database name, table names, column names, values in queries etc:
变量标识符可以用作数据库名称,表名称,列名称,查询中的值等:
:setvar Table Person.Person :setvar Database AdventureWorks2014 :setvar Value “FirstName +’ ‘+ LastName AS Name”
:setvar表Person.Person :setvar数据库AdventureWorks2014 :setvar值“名字+''+姓氏AS名称”
USE $(Database) SELECT $(Value) FROM $(Table)
使用 $ (数据库) 从 $ (表)中 选择 $(值)
The result will be:
结果将是:

If the sqlcmd value contains blank spaces, the values must be enclosed in quotation marks:
如果sqlcmd值包含空格,则必须将这些值用引号引起来:
:setvar Value “FirstName +’ ‘+ LastName AS Name”
:setvar值“名字+''+姓氏AS名称”
Otherwise the following error will appear:
否则将出现以下错误:
A fatal scripting error occurred.
Incorrect syntax was encountered while parsing :setvar.
发生致命的脚本错误。
解析:setvar时遇到语法错误。
In a new query window, paste the following code:
在新的查询窗口中,粘贴以下代码:
:setvar SQLFile “User.sql” :setvar Error “Errors.txt” :setvar Path “C:\User\” – -specify the path of the error file :error $(Path)$(Error)
:setvar SQLFile“ User.sql” :setvar错误“ Errors.txt” :setvar路径“ C:\ User \” –-指定错误文件的路径 :error $(Path)$(Error)
USE AdventureWorks2014 – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test 1 – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE [Adventure – Works] – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile)
USE AdventureWorks2014 – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test 1 – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path )$(SQLFile) USE [冒险–工作] – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile)
错误脚本关键字 (Error script keyword)
Example
例
:error < filename >
:错误<文件名>
Redirect all errors that occur during execution to the specified file name, in this case, this will be the Errors.txt file on this location C:\User\”.
将执行期间发生的所有错误重定向到指定的文件名,在这种情况下,这将是此位置C:\ User \”上的Errors.txt文件。
< filename >
<文件名>
This file is automatically created and records all errors that appear during the execution of the code:
该文件是自动创建的,并记录了在执行代码期间出现的所有错误:
If this file already exists, the content from the previous session will be truncated.
如果此文件已经存在,则上一个会话的内容将被截断。
:r < filename > script keyword
:r <文件名>脚本关键字
This sqlcmd command reads input from <filename>, in this example, from the User.sql file and loads it into the statement cache.
此sqlcmd命令从<文件名>(在本示例中)从User.sql文件读取输入,并将其加载到语句高速缓存中。
其他SQLCMD命令 (Other SQLCMD commands)
错误脚本关键字 (On error script keyword)
Example
例
:on error [exit | ignore] script keyword
:on错误[退出| [忽略]脚本关键字
With this sqlcmd command, an action can be set that will be performed when an error occurred.
使用此sqlcmd命令,可以设置将在发生错误时执行的操作。
:on error exit
:错误退出
When the exit option is set the sqlcmd exits with an error message. If the user already exists in the database and the code below is executed:
设置退出选项后,sqlcmd退出并显示一条错误消息。 如果用户已经存在于数据库中,并且执行以下代码:
:setvar SQLFile “User.sql” :setvar Error “Errors.txt” :setvar Path “C:\User\” – -specify the path of the error file :error $(Path)$(Error) :setvar Report “Report.txt”
:setvar SQLFile“ User.sql” :setvar错误“ Errors.txt” :setvar路径“ C:\ User \” –指定错误文件的路径 :error $(Path)$(Error) :setvar报告“ Report 。文本”
:out $(Path)$(Report) :on error exit
:out $ {Path)$ {Report) :错误退出
USE AdventureWorks2014 – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test 1 – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE [Adventure – Works] – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile)
USE AdventureWorks2014 – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test 1 – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path )$(SQLFile) USE [冒险–工作] – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile)
the error message will be:
错误消息将是:
:on error ignore
:错误忽略
When the ignore option is set, sqlcmd ignores the error and continues to execute the script.
当设置了ignore选项时,sqlcmd将忽略该错误并继续执行脚本。
:reset script keyword
:reset脚本关键字
Throw away the statement cache
丢弃语句缓存
:quit script keyword
:quit脚本关键字
Stops sqlcmd immediately
立即停止sqlcmd
:exit script keyword
:exit脚本关键字
Exits sqlcmd immediately and returns no value
立即退出sqlcmd ,不返回任何值
:exit() script keyword
:exit()脚本关键字
Executes the batch, then exit and returns no value.
执行批处理,然后退出并不返回任何值。
:exit(query) script keyword
:exit(query)脚本关键字
Executes a batch that includes the query, returns the results of the query and then quits:
执行包含查询的批处理,返回查询结果,然后退出:
:setvar SQLFile “User.sql” :setvar Error “Errors.txt” :setvar Path “C:\User\” – -specify the path of the error file :error $(Path)$(Error) :setvar Report “Report.txt”
:setvar SQLFile“ User.sql” :setvar错误“ Errors.txt” :setvar路径“ C:\ User \” –指定错误文件的路径 :error $(Path)$(Error) :setvar报告“ Report 。文本”
:out $(Path)$(Report) :exit(Select * from Person.AddressType)
: out $ {Path)$ {Report) : exit(从Person.AddressType中选择*)
USE AdventureWorks2014 – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test 1 – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE [Adventure – Works] – – Set the database name :r $(Path)$(SQLFile)
USE AdventureWorks2014 – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile) USE Test 1 – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path )$(SQLFile) USE [冒险–工作] – –设置数据库名称 :r $(Path)$(SQLFile)
The results in the Report.txt will be:
Report.txt中的结果将是:

翻译自: https://www.sqlshack.com/use-sqlcmd-commands-ssms-query-editor/
ssms,新建查询设置字体