分2步,第一步是首先转换为device_node,第二步device_node转换为platform_device。
第一步
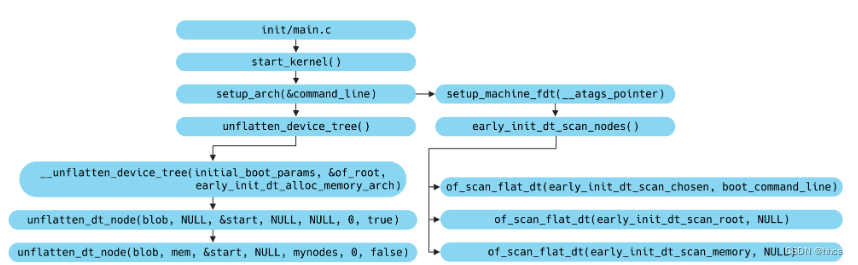
/*** unflatten_device_tree - create tree of device_nodes from flat blob** unflattens the device-tree passed by the firmware, creating the* tree of struct device_node. It also fills the "name" and "type"* pointers of the nodes so the normal device-tree walking functions* can be used.*/
void __init unflatten_device_tree(void)//dtb-->内存设备树结构
{__unflatten_device_tree(initial_boot_params, &of_root,early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch);/* Get pointer to "/chosen" and "/aliases" nodes for use everywhere */of_alias_scan(early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch);
}执行后,of_root 是设备树的根 。
struct property {//node的 属性,读到内存中的属性char *name;//keyint length;//value's lengthvoid *value;//value, for key = valuestruct property *next;//单链表指向下一个属性unsigned long _flags;unsigned int unique_id;struct bin_attribute attr;//for sys
};struct device_node {//最终在内存中形成一个树形的设备信息const char *name; /* node的名称,取最后一次“/”和“@”之间子串 */const char *type; /*设备类型,来自节点中的device_type属性, 如果没有该属性, 则设为"NULL"*/phandle phandle;//u32 phandleconst char *full_name; /* 指向该结构体结束的位置,存放node的路径全名*/struct fwnode_handle fwnode;struct property *properties;/*指向该节点下的第一个属性,其他属性与该属性链表相接 */struct property *deadprops; /* removed properties */struct device_node *parent;//parent nodestruct device_node *child;//childstruct device_node *sibling;//same level nodestruct kobject kobj;//kobjunsigned long _flags;//node flag,see flag descriptions@current filevoid *data;
};第二步:
设备树的device_node到platform_device转换中,必须满足以下条件:
- 一般情况下,只对设备树中根的一级子节点进行转换,也就是多级子节点(子节点的子节点)并不处理。但是存在一种特殊情况,就是当某个根子节点的compatible属性为"simple-bus"、"simple-mfd"、"isa"、"arm,amba-bus"时,当前节点中的一级子节点将会被转换成platform_device节点。
- 节点中必须有compatible属性。
arch_initcall_sync(arm64_device_init);---以常见的arm64平台
static int __init arm64_device_init(void)
{of_iommu_init();of_platform_populate(NULL, of_default_bus_match_table, NULL, NULL);//device_node--->platformreturn 0;
}/*** of_platform_populate() - Populate platform_devices from device tree data* @root: parent of the first level to probe or NULL for the root of the tree* @matches: match table, NULL to use the default* @lookup: auxdata table for matching id and platform_data with device nodes* @parent: parent to hook devices from, NULL for toplevel** Similar to of_platform_bus_probe(), this function walks the device tree* and creates devices from nodes. It differs in that it follows the modern* convention of requiring all device nodes to have a 'compatible' property,* and it is suitable for creating devices which are children of the root* node (of_platform_bus_probe will only create children of the root which* are selected by the @matches argument).** New board support should be using this function instead of* of_platform_bus_probe().** Returns 0 on success, < 0 on failure.*/
int of_platform_populate(struct device_node *root,const struct of_device_id *matches,const struct of_dev_auxdata *lookup,struct device *parent)//populate platform_devices from device tree data
{struct device_node *child;int rc = 0;root = root ? of_node_get(root) : of_find_node_by_path("/");if (!root)return -EINVAL;for_each_child_of_node(root, child) {/* 为根节点下面的每一个节点创建platform_device结构体 */rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, parent, true);if (rc)break;}of_node_set_flag(root, OF_POPULATED_BUS);//set 已填充 flagof_node_put(root);return rc;
}*** of_platform_bus_create() - Create a device for a node and its children.* @bus: device node of the bus to instantiate* @matches: match table for bus nodes* @lookup: auxdata table for matching id and platform_data with device nodes* @parent: parent for new device, or NULL for top level.* @strict: require compatible property** Creates a platform_device for the provided device_node, and optionally* recursively create devices for all the child nodes.*/
static int of_platform_bus_create(struct device_node *bus,const struct of_device_id *matches,const struct of_dev_auxdata *lookup,struct device *parent, bool strict)
{const struct of_dev_auxdata *auxdata;struct device_node *child;struct platform_device *dev;const char *bus_id = NULL;void *platform_data = NULL;int rc = 0;/* Make sure it has a compatible property */if (strict && (!of_get_property(bus, "compatible", NULL))) {/* 只有包含"compatible"属性的node节点才会生成相应的platform_device结构体 */pr_debug("%s() - skipping %s, no compatible prop\n",__func__, bus->full_name);return 0;}auxdata = of_dev_lookup(lookup, bus);if (auxdata) {bus_id = auxdata->name;platform_data = auxdata->platform_data;}if (of_device_is_compatible(bus, "arm,primecell")) {/** Don't return an error here to keep compatibility with older* device tree files.*/of_amba_device_create(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);return 0;}/* 针对节点下面得到status = "ok" 或者status = "okay"或者不存在status属性的节点分配内存并填充platform_device结构体 */dev = of_platform_device_create_pdata(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent);//platform_data一般是nullif (!dev || !of_match_node(matches, bus))return 0;for_each_child_of_node(bus, child) {pr_debug(" create child: %s\n", child->full_name);rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, &dev->dev, strict);//父节点下的子设备节点创建if (rc) {of_node_put(child);break;}}of_node_set_flag(bus, OF_POPULATED_BUS);return rc;
}
const struct of_device_id of_default_bus_match_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "simple-bus", },
{ .compatible = "simple-mfd", },
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM_AMBA
{ .compatible = "arm,amba-bus", },
#endif /* CONFIG_ARM_AMBA */
{} /* Empty terminated list */
};对于dts中定义的device node,只有其所属的parent node所属的compatible属性和调用of_platform_populate时传入的of_device_id(红色)相互匹配,则说明如果当前的device node只要包含有compatible属性就会被创建为platform device,其他不会帮你自动创建,需要自己写代码创建
/*** of_platform_device_create_pdata - Alloc, initialize and register an of_device* @np: pointer to node to create device for* @bus_id: name to assign device* @platform_data: pointer to populate platform_data pointer with* @parent: Linux device model parent device.** Returns pointer to created platform device, or NULL if a device was not* registered. Unavailable devices will not get registered.*/
static struct platform_device *of_platform_device_create_pdata(struct device_node *np,const char *bus_id,void *platform_data,struct device *parent)
{struct platform_device *dev;if (!of_device_is_available(np) || //status ok,okay,或者没写of_node_test_and_set_flag(np, OF_POPULATED))return NULL;dev = of_device_alloc(np, bus_id, parent);// Allocate and initialize an of platform_deviceif (!dev)goto err_clear_flag;dev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;//关键,platform device所在总线是platform busdev->dev.platform_data = platform_data;of_dma_configure(&dev->dev, dev->dev.of_node);of_msi_configure(&dev->dev, dev->dev.of_node);if (of_device_add(dev) != 0) {of_dma_deconfigure(&dev->dev);platform_device_put(dev);goto err_clear_flag;}return dev;err_clear_flag:of_node_clear_flag(np, OF_POPULATED);return NULL;
}/*** of_device_alloc - Allocate and initialize an of_device* @np: device node to assign to device* @bus_id: Name to assign to the device. May be null to use default name.* @parent: Parent device.*/
struct platform_device *of_device_alloc(struct device_node *np,const char *bus_id,struct device *parent)
{struct platform_device *dev;int rc, i, num_reg = 0, num_irq;struct resource *res, temp_res;dev = platform_device_alloc("", -1);if (!dev)return NULL;/* count the io and irq resources */while (of_address_to_resource(np, num_reg, &temp_res) == 0)//统计reg属性的数量num_reg++;num_irq = of_irq_count(np);//统计中断irq属性的数量/* Populate the resource table */if (num_irq || num_reg) {res = kzalloc(sizeof(*res) * (num_irq + num_reg), GFP_KERNEL);//根据num_irq和num_reg的数量申请相应的struct resource内存空间if (!res) {platform_device_put(dev);return NULL;}dev->num_resources = num_reg + num_irq;dev->resource = res;for (i = 0; i < num_reg; i++, res++) {rc = of_address_to_resource(np, i, res);//dts reg-->res.start,end,name(reg-name),flagsWARN_ON(rc);}if (of_irq_to_resource_table(np, res, num_irq) != num_irq)pr_debug("not all legacy IRQ resources mapped for %s\n",np->name);}dev->dev.of_node = of_node_get(np);//关联设备树节点和设备之间的指针,以后就可以platform来找到node节点和它的属性信息dev->dev.parent = parent ? : &platform_bus;if (bus_id)dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "%s", bus_id);elseof_device_make_bus_id(&dev->dev);return dev;
}
/*** platform_device_alloc - create a platform device* @name: base name of the device we're adding* @id: instance id** Create a platform device object which can have other objects attached* to it, and which will have attached objects freed when it is released.*/
struct platform_device *platform_device_alloc(const char *name, int id)
{struct platform_object *pa;pa = kzalloc(sizeof(*pa) + strlen(name) + 1, GFP_KERNEL);//this,1 is \0if (pa) {strcpy(pa->name, name);pa->pdev.name = pa->name;pa->pdev.id = id;device_initialize(&pa->pdev.dev);//设备初始化pa->pdev.dev.release = platform_device_release;arch_setup_pdev_archdata(&pa->pdev);}return pa ? &pa->pdev : NULL;
}
struct platform_device {const char *name;int id;bool id_auto;struct device dev;//dev.of_node代表dts节点u32 num_resources;//reg + irqstruct resource *resource;//设备资源资源,中断,regconst struct platform_device_id *id_entry;char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match *//* MFD cell pointer */struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;/* arch specific additions */struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};