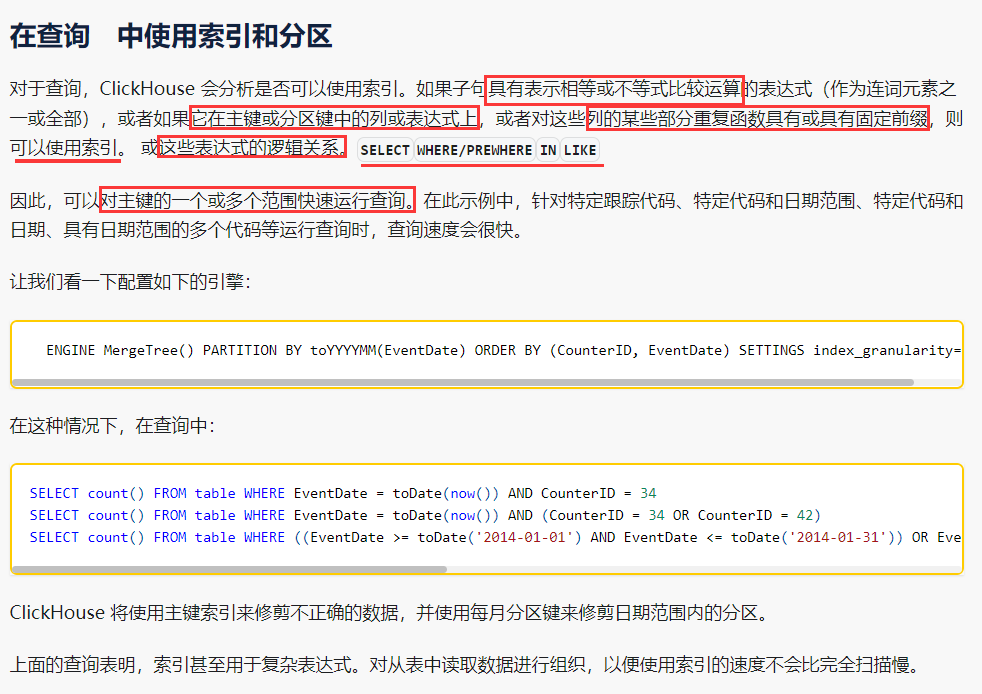
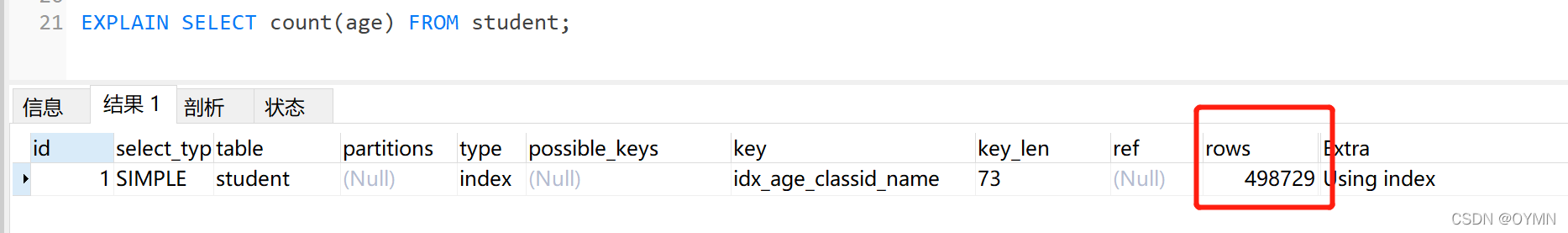
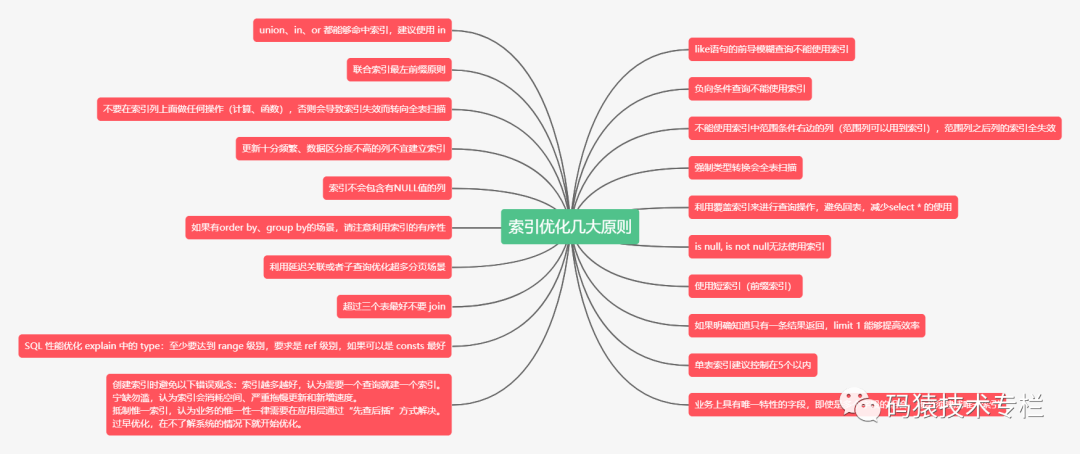
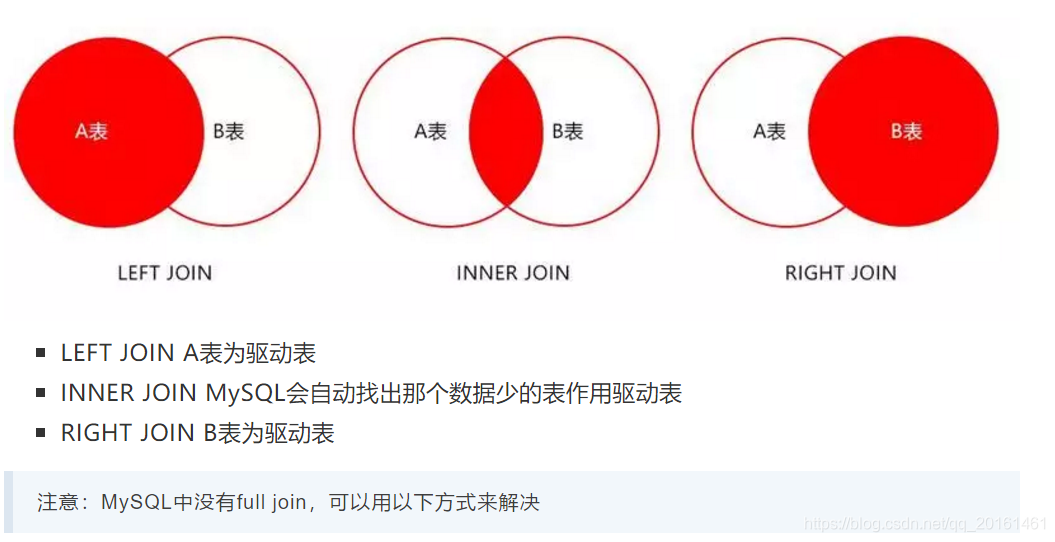
目录
Lecture I: Introduction of Deep Learning
1. 深度学习的步骤
2. 全连接前馈神经网络(Fully Connect Feedforward Network)
2.1 神经元
2.2. 激励函数
2.3 Softmax layer
2.4 网络结构
2.5 应用举例(数字识别)
3. 对函数进行优化(goodness of function)
3.1 学习目标(Learning Target)
3.2 损失(Loss)
4. 选择最好的函数(How to pick the best function)
4.1 梯度下降(Gradient Descent)
5. Keras
Example: Handwriting Digit Recognition
Lecture II: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network
1. 选择合适的loss function
2. Mini-batch
3. 新的激活函数(activation function)
3.1 ReLU
3.2 Maxout
3.3 合适的学习率(Adagrad)
3.4 冲量(Momentum)
4. Early Stopping
5. Weight Decay
6. Dropout
Lecture III: Variants of Neural Network
Connected Neural Network(CNN)
1. 一个神经元只需要检测一个pattern
2. Subsampling
3. Max Pooling
4. Flatten
5. CNN整体过程
Recurrent Neural Network(RNN)
1. 基本概念
2. 双向RNN(Bidirectional RNN)
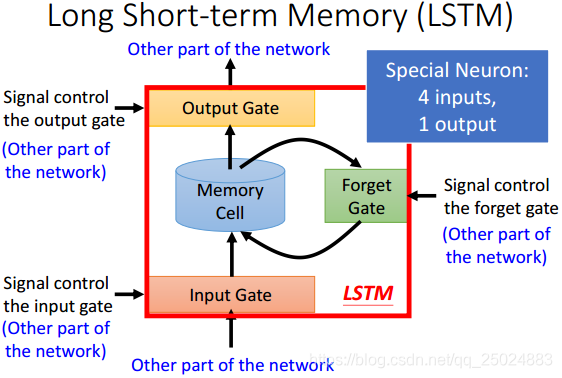
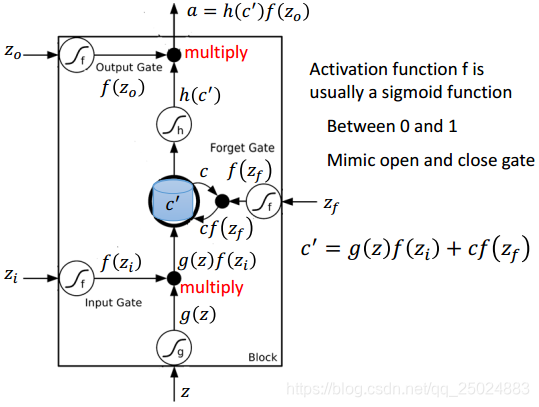
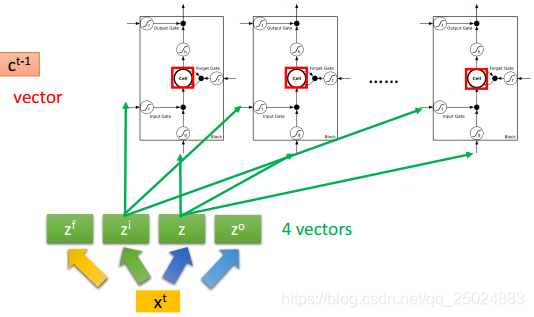
3. 长短期记忆网络(Long Short-term Memory, LSTM)
Lecture IV: Next Wave
1. Supervised Learning
2. Reinforcement Learning
3. Unsupervised Learning
Lecture I: Introduction of Deep Learning
1. 深度学习的步骤
机器学习的步骤:
Step 1: 定义一个函数集合(define a set of function)
Step 2: 对函数进行优化(goodness of function)
Step 3: 选择最好的函数(pick the best function)

将图像识别抽象为一个函数,以下举例说明:

深度学习的步骤:
Step 1: 定义神经网络(Neural Network)
Step 2: 对函数进行优化(goodness of function)
Step 3: 选择最好的函数(pick the best function)
2. 全连接前馈神经网络(Fully Connect Feedforward Network)
2.1 神经元

2.2. 激励函数
对于激励函数的理解:https://blog.csdn.net/hyman_yx/article/details/51789186

2.3 Softmax layer
传统输出层:

softmax layer作为输出层(重点)

2.4 网络结构

备注:激励函数设定见3图。
2.5 应用举例(数字识别)
将图片划分为16*16,每一个像素作为一个输入的x,X的维度为256*1。

建立模型后,

3. 对函数进行优化(goodness of function)
3.1 学习目标(Learning Target)

3.2 损失(Loss)

4. 选择最好的函数(How to pick the best function)
4.1 梯度下降(Gradient Descent)

5. Keras
Example: Handwriting Digit Recognition





Lecture II: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network
1. 选择合适的loss function
例如:
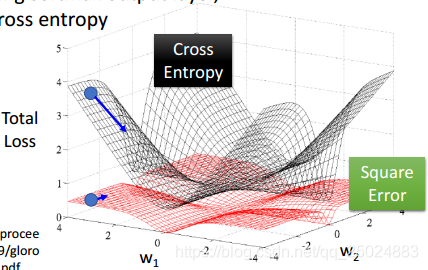
平方误差(loss='mse'),交叉熵(loss='categorical_crossentropy')
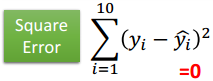
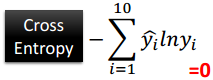
当使用softmax作为输出层时,选择交叉熵作为loss。见下图。
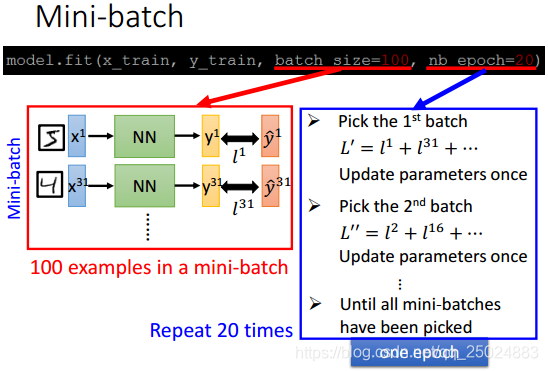
2. Mini-batch
下图中为mini-batch的代码解释。
3. 新的激活函数(activation function)
由于存在梯度消失问题,所以需要选择新的activation function.
3.1 ReLU
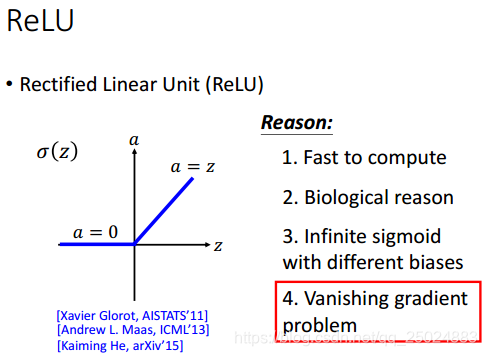
ReLU会将复杂的网络部分置0,简化网络。
model.add(Activation('sigmoid'))
// 改变为
model.add(Activation('relu'))
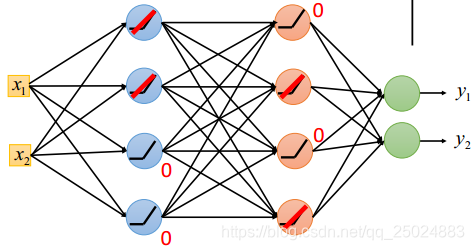
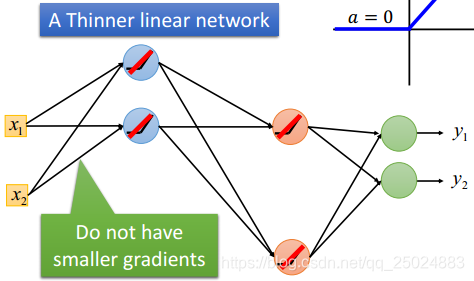
3.2 Maxout
ReLU是一种特殊的Maxout函数。
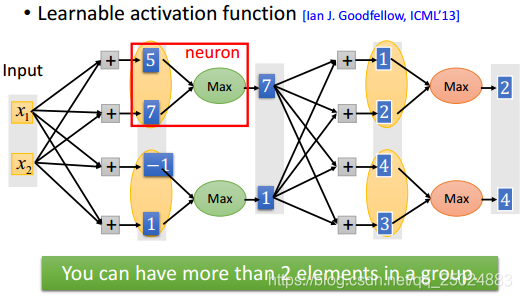
3.3 合适的学习率(Adagrad)
开始的学习率设置的较大,每一个epoch都将学习率降低。
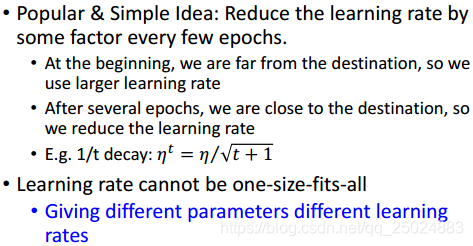
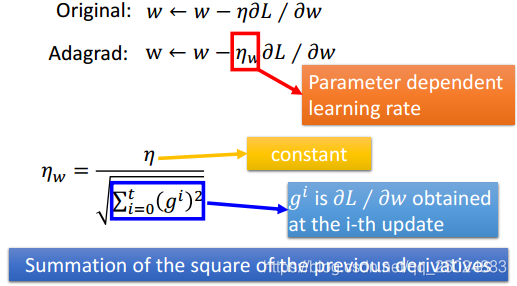
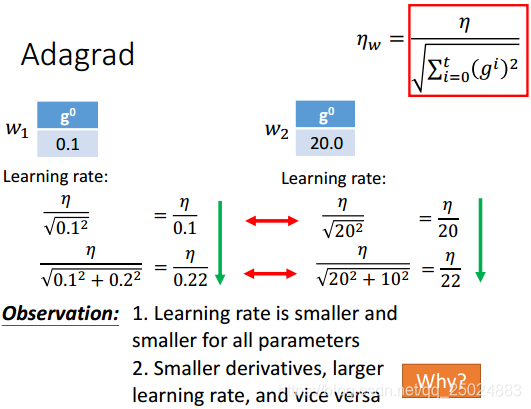
其他:
- Adagrad
- RMSprop
- Adadelta
- "No more pesky learning rates"
- AdaSecant
- Adam
- Nadam
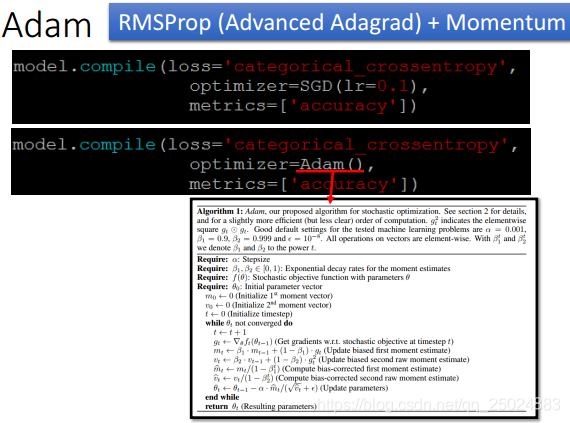
3.4 冲量(Momentum)
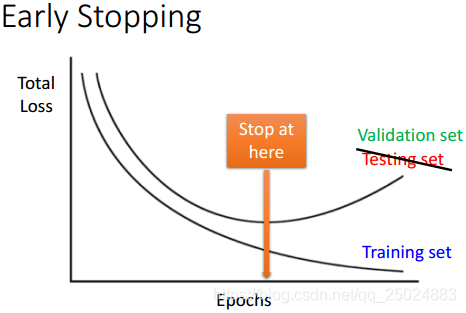
4. Early Stopping
Early Stopping可以防止过拟合。详细见下图。
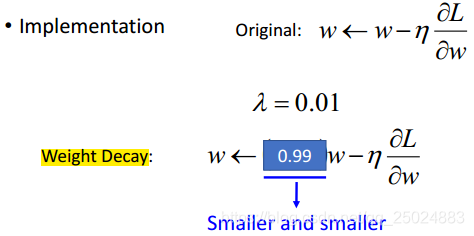
5. Weight Decay
6. Dropout
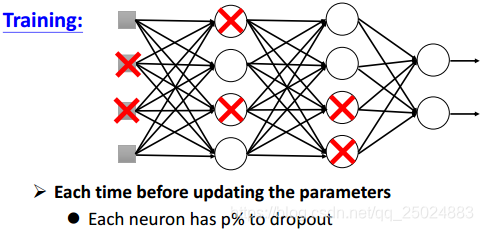
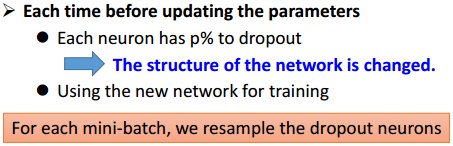
Dropout可以是一种模型融合。
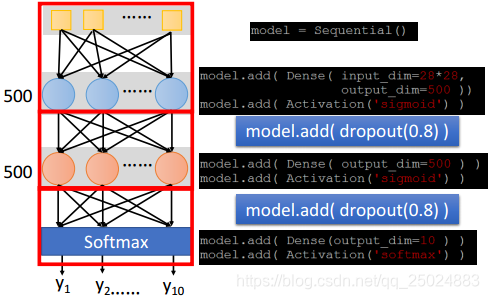
Lecture III: Variants of Neural Network
Connected Neural Network(CNN)
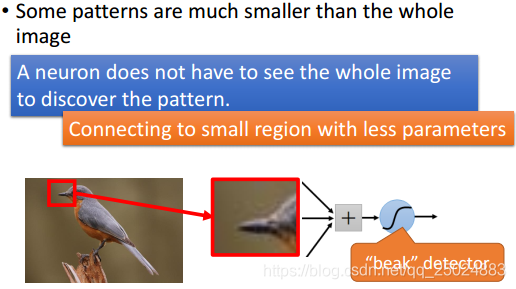
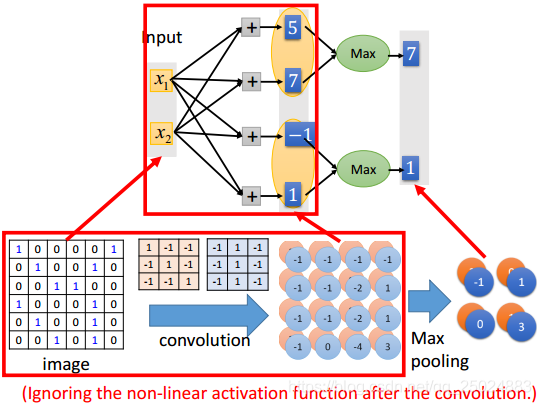
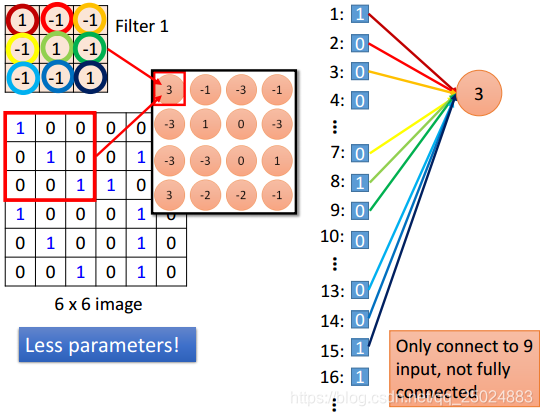
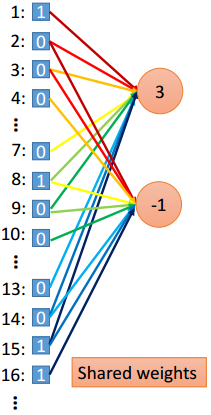
1. 一个神经元只需要检测一个pattern
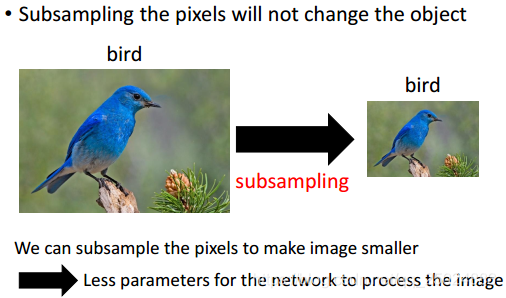
2. Subsampling
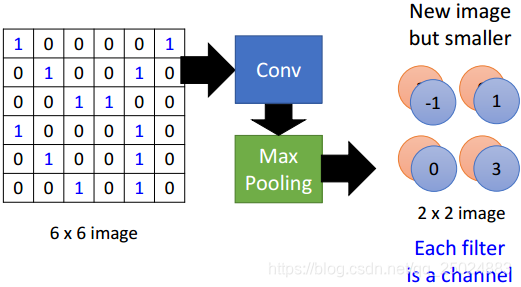
3. Max Pooling
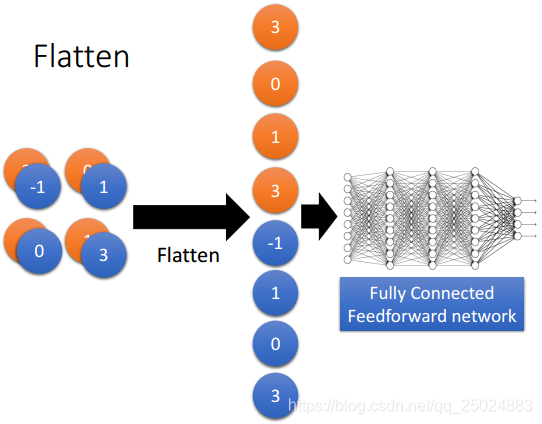
4. Flatten
5. CNN整体过程
Recurrent Neural Network(RNN)
1. 基本概念
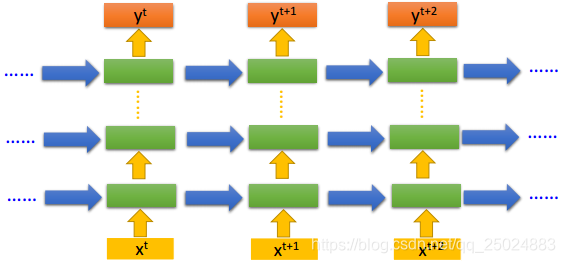
在RNN中,隐层神经元的输出值都被保存到记忆单元中,下一次再计算输出时,隐层神经元会将记忆单元中的值认为是输入的一部分来考虑。
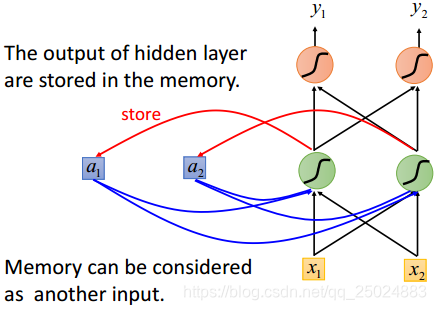
举例:
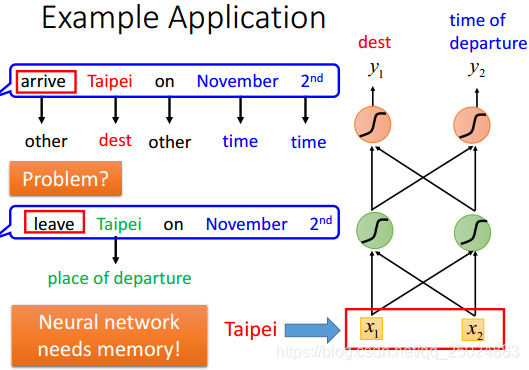
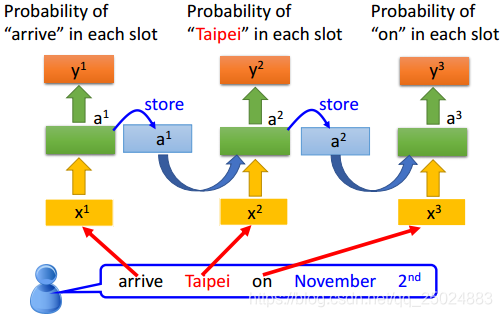
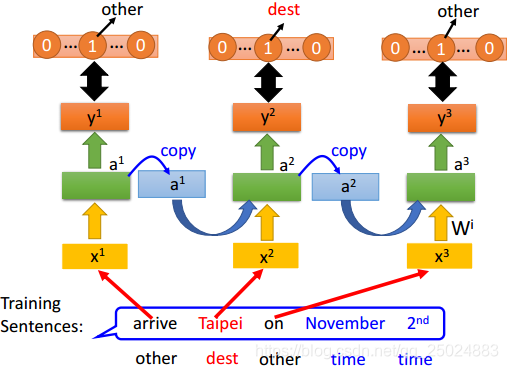
2. 双向RNN(Bidirectional RNN)
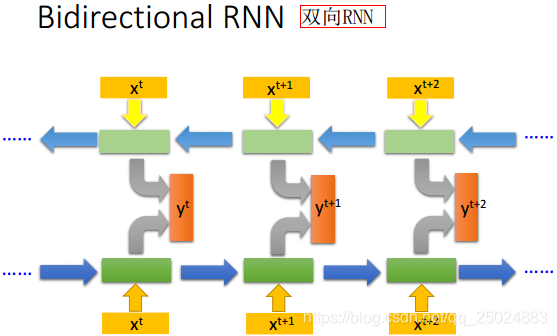
3. 长短期记忆网络(Long Short-term Memory, LSTM)
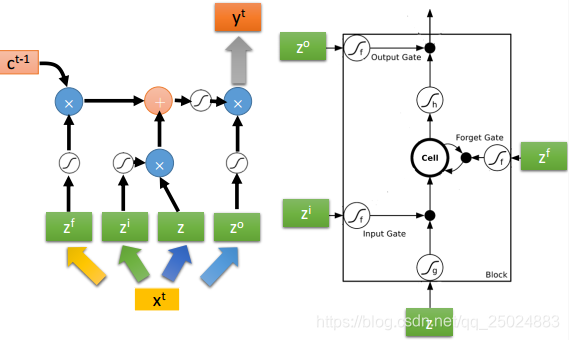
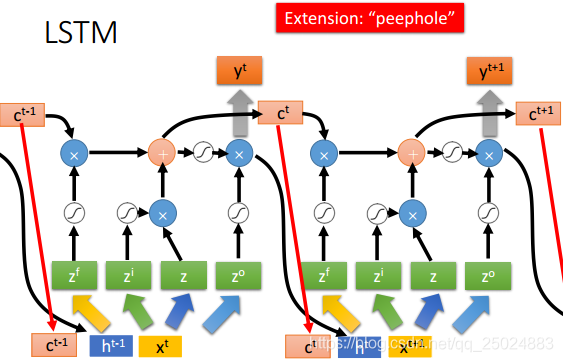
Lecture IV: Next Wave
1. Supervised Learning
- Ultra Deep Network
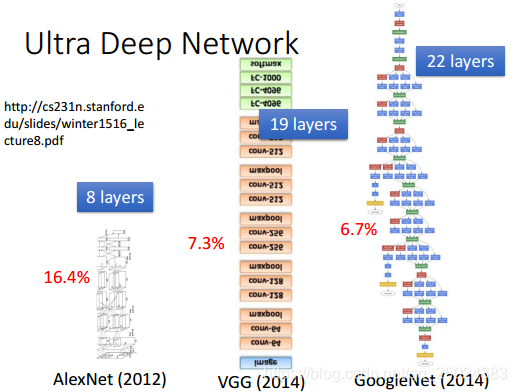
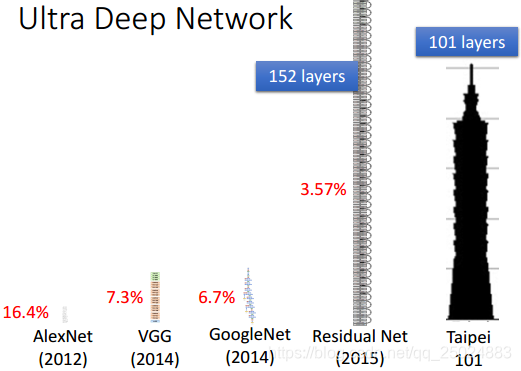
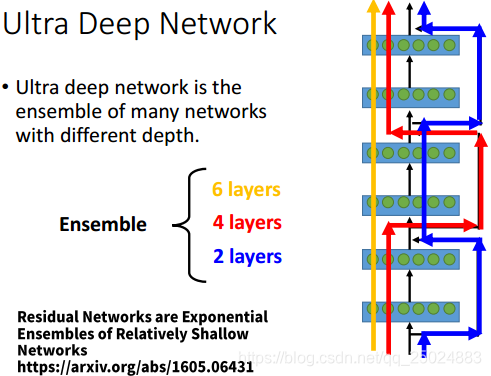
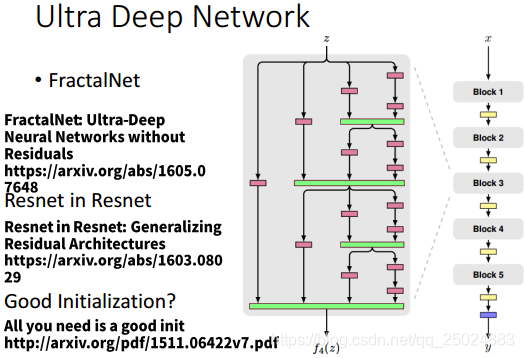
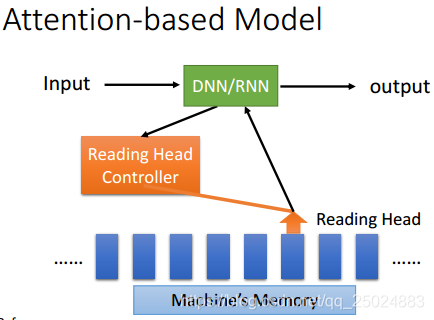
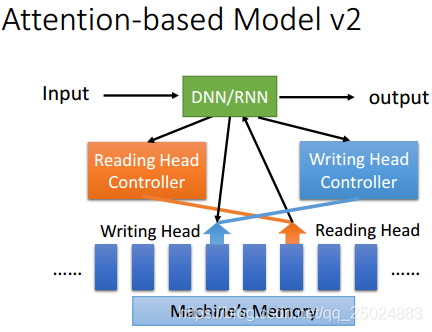
- Attention Model
2. Reinforcement Learning
3. Unsupervised Learning
- Image: Realizing what the World Looks Like
- Text: Understanding the Meaning of Words
- Audio: Learning human language without supervision