文章目录
- 一、数据库定义语言(DDL)
- 1.1 库操作
- 1.2 表操作
- 二、数据库操纵语言(DML)
- 2.1 插入 insert
- 2.2 修改 update
- 2.3 删除 delete
- 三、数据库查询语言(DQL)
- 3.1 单表查询
- ①查询:select
- ②条件:where
- ③去重:distinct
- ④排序:order by
- ⑤分页:limit
- 3.2 聚合查询
- ①聚合函数
- ②group by 分组
- ③having 过滤
- 3.3 联表查询
- ①内连接
- ②外连接
- ③自连接
- ④子查询
- ⑤合并查询
- 四、数据库控制语言(DCL)
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,MySQL 系列学习将会持续更新
一、数据库定义语言(DDL)
1.1 库操作
-- 建库
create database test1;
create database test2 default charset utf8mb4;-- 展示所有库
show databases;-- 设置默认库,表示之后的操作都是对该库进行的
use test1;-- 删库
drop datebase test2;
1.2 表操作
列级约束:主键 Primary key、外键 foreign key 、唯一 unique、默认值 default 、非空/空值 not null/ null、自增 auto_increment
①创建表:
create table 表名(列名 数据类型 [列级约束条件],列名 数据类型 [列级约束条件],...列名 数据类型 [列级约束条件]);create table user (uid int primary key not null auto_increment,name varchar(10) not null,sex enum('男','女') not null default '男'
);
②修改表:
alter table 表名 [add column 新列名 数据类型[列级约束条件]],[drop column 列名[restrict|cascade]],[change column 原列名 新列名 数据类型[列级约束条件]];alter table `test`.`user` add column `age` INT NOT NULL after `sex`,change column `name` `name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL ;
我们可以通过 ADD 来添加一个新的列,通过 DROP 来删除一个列,不过我们可以添加 restrict 或 cascade,默认是 restrict,表示如果此列作为其他表的约束或视图引用到此列时,将无法删除,而 cascade 会强制连带引用此列的约束、视图一起删除。还可以通过 ALTER 来修改此列的属性。
③删除表:
-- 展示默认库的所有表名称
show tables;-- 删表
DROP TABLE 表名 [restrict|cascade];-- 清空表数据(截断)
truncate table student;
回到目录…
二、数据库操纵语言(DML)
2.1 插入 insert
①单行+全列插入
insert into student values (100, 10000, ‘唐三藏’, NULL);
insert into student values (101, 10001, ‘孙悟空’, 12345);
②多行+指定列插入
insert into student (id, sn, name) values(102, 20001, ‘刘大耳’),(103, 20002, ‘曹阿瞒’),(104, 20003, ‘孙仲谋’);
2.2 修改 update
UPDATE 表名 SET 列名=值,... WHERE 条件;
示例:
-- 修改曹孟德的数学成绩为80分,语文成绩为90分
update student set math = 80, chinese = 90 where name = ‘曹孟德’;-- 将总分倒数三名同学的数学成绩加上20分 (支持limit,不支持offset)
update student set math = math + 80 order by Chinese + math + english limit 3;-- 将所有同学的语文成绩更新为2倍
update student set chinese = chinese * 2;
2.3 删除 delete
DELETE FROM 表名 WHERE 条件;
示例:
-- 删除孙悟空的信息
delete from student where name = ‘孙悟空’;-- 仅删除表的全部数据 for-each
delete from student;
回到目录…
三、数据库查询语言(DQL)
3.1 单表查询
单表查询是最简单的一种查询,我们只需要在一张表中去查找数据即可,通过使用 select 语句来进行。
①查询:select
-- 全表查询,不建议使用
select * from student;
-- 指定列查询
select id, name, english from student;-- 结果集为表达式
select id, name, (chinese + math + english) / 3 from student;
-- 自定义结果集的列名
select id, name, chinese + math + english 总分 from student;
②条件:where
-- 查询english成绩高于60分的学生
select * from student where english > 60;-- and与or
select * from student where english > 60 and math > 60;
select * from student where english > 90 or math > 90;-- 范围查询
select * from student where english between 80 and 100;-- in查询
select * from student where math in (80, 85, 90, 95, 100);-- 模糊查询
-- %匹配任意多个(包括0个)字符
select name from student where name like ‘孙%’;
select name from student where name like ‘%孙’;
select name from student where name like ‘%孙%’;
-- _严格匹配一个任意字符
select name from student where name like ‘孙_’;-- NULL查询
select * from student where qq_mail is not null;
select * from student where qq_mail is null;
| 比较运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| >,<,>=,<=,=,!= | 和 Java 中一样 |
| between a and b | 范围匹配 [a,b],返回TRUE |
| in (option, …) | 如果是 option 中的任意一个,返回 TRUE |
| is null,is not null | 是否为 NULL |
| like | 模糊匹配,如 like ‘孙%’ 或 like ‘孙_’ |
| 逻辑运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| and | 条件都满足,取true |
| or | 满足其中一个条件,取true |
回到目录…
③去重:distinct
-- 可以列出所有不重复的math成绩集合
select distinct math from student;-- 此时就没有去重功能了,因为没有id和math同时重复的学生
select distinct id, math from student;
④排序:order by
asc:升序,默认值;desc:降序- NULL 视为比任何数据都小
-- 先优先 math 升序;若 math 相等,则按 Chinese 降序;若都相等,按 id 升序
select * from student order by math asc, chinese desc, id;
-- 使用表达式 + 别名排序
select name, math + chinese + english 总分 from student order by 总分;
⑤分页:limit
-- 从下标0开始,筛选5条结果
select * from student limit 5;
-- 从下标2开始,筛选5条结果
select * from student limit 2, 5;
-- 筛选5条结果,从下标2开始。这种写法意思更明确
select * from student limit 5 offset 2;-- 综合运用
-- 查询数学成绩高于80分,且排名前三的学生
select name, math from student where math > 80 order by math desc limit 3;
回到目录…
3.2 聚合查询
①聚合函数
count(*):统计所有的行数count(列名):统计某列的值总和sum(列名):求一列的和avg(列名):求一列的平均值max(列名):求一列的最大值min(列名):求一列的最小值
-- 统计数据的数量
select count(*) from student;
-- 统计邮箱的个数,qq_mail为null不计入结果
select count(qq_mail) from student;-- 统计所有学生的数学总分
select sum(math) from student;-- 统计班级数学平均分
select avg(math) from student;-- 统计班级数学最高分
select max(math) from student;-- 统计班级数学最低分
select min(math) from student;
②group by 分组
通过使用 group by 来对查询结果进行分组,它需要结合聚合函数一起使用:
SELECT sum(*) FROM 表名 WHERE 条件 GROUP BY 列名;
示例:
-- 查询每种角色的最高工资、最低工资、平均工资
select role, max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary) from emp group by role;-- 统计每种角色薪资高于500的人数
select role, count(*) from emp where salary > 500 group by role;-- 多聚合,在不同列的组合下进行聚合查询
select company, role, count(*) from emp2 group by company, role;
③having 过滤
我们还可以添加 having 来限制分组条件:
-- having关键字用于聚合之后进行过滤操作
select role, avg(salary) from emp group by role having avg(salary) > 300;
注意顺序:where > group by > having
emp 表:

回到目录…
3.3 联表查询
实际开发中往往数据来自不同的表,所以需要多表联合查询。多表查询是对多张表的数据取笛卡尔积。
两张表:
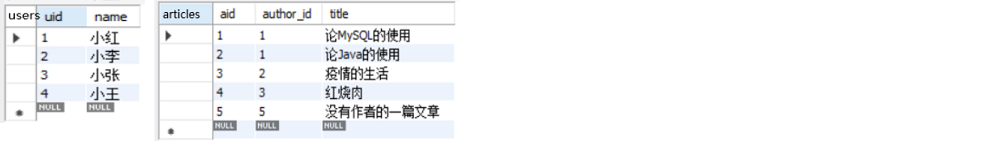
①内连接

select 字段 from 表1 inner join 表2 on 连接条件 where 其他条件;
示例:
-- inner 可以省略
select * from users join articles on uid = author_id where users.name = '小红';-- 查询作者对应的书籍
select name, title from users inner join articles on users.uid = articles.author_id;
内连查询结果:

回到目录…
②外连接
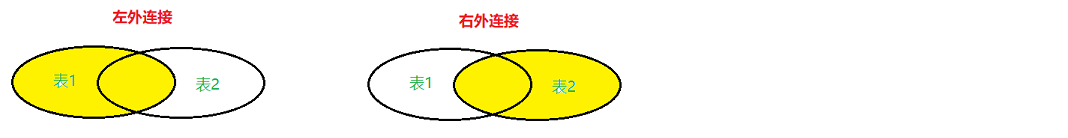
-- 左外连接
select 字段名 from 表名1 left join 表名2 on 连接条件;-- 右外连接
select 字段名 from 表名1 right join 表名2 on 连接条件;
左外连查询结果:

右外连查询结果:

回到目录…
③自连接
自连接是指在同一张表连接自身进行查询。
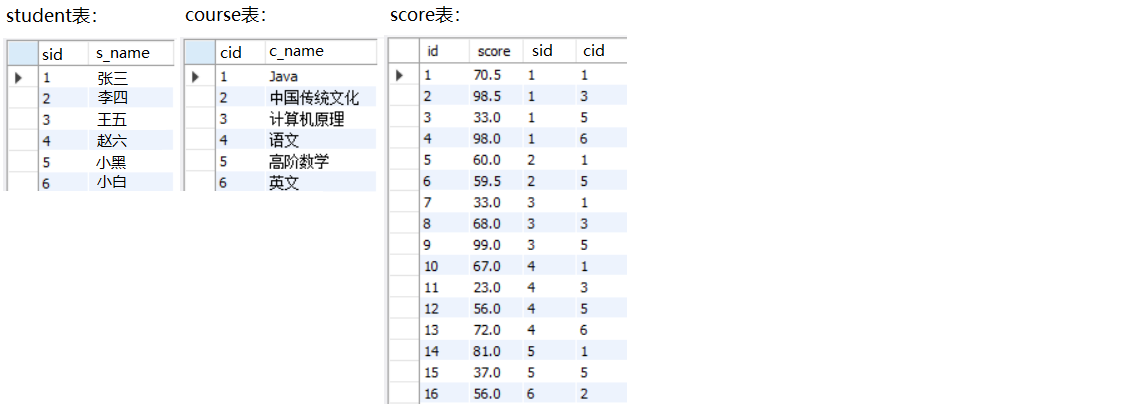
查询所有 “Java” 成绩比 “计算机原理” 成绩低的信息:
SELECT s1.sid, s1.score, s2.score
FROM score s1 JOIN score s2
ON s1.sid = s2.sid -- 指向同一个学生
AND s1.cid = 1 -- 表1指向Java成绩
AND s2.cid = 3 -- 表2指向计算机原理成绩
AND s1.score < s2.score; -- Java < 计算机原理
查询结果:

回到目录…
④子查询

案例:查询所有同学的 ‘计算机原理’ 成绩
-- 使用IN
select sid, score from score where cid in (select cid from course where c_name='计算机原理');-- select * from 表名 where exists(子查询);
-- 如果子查询没有返回结果,则不执行外层的 sql
select sid, score from score where exists (select cid from course where c_name='计算机原理' and score.cid=course.cid);
查询结果:

回到目录…
⑤合并查询
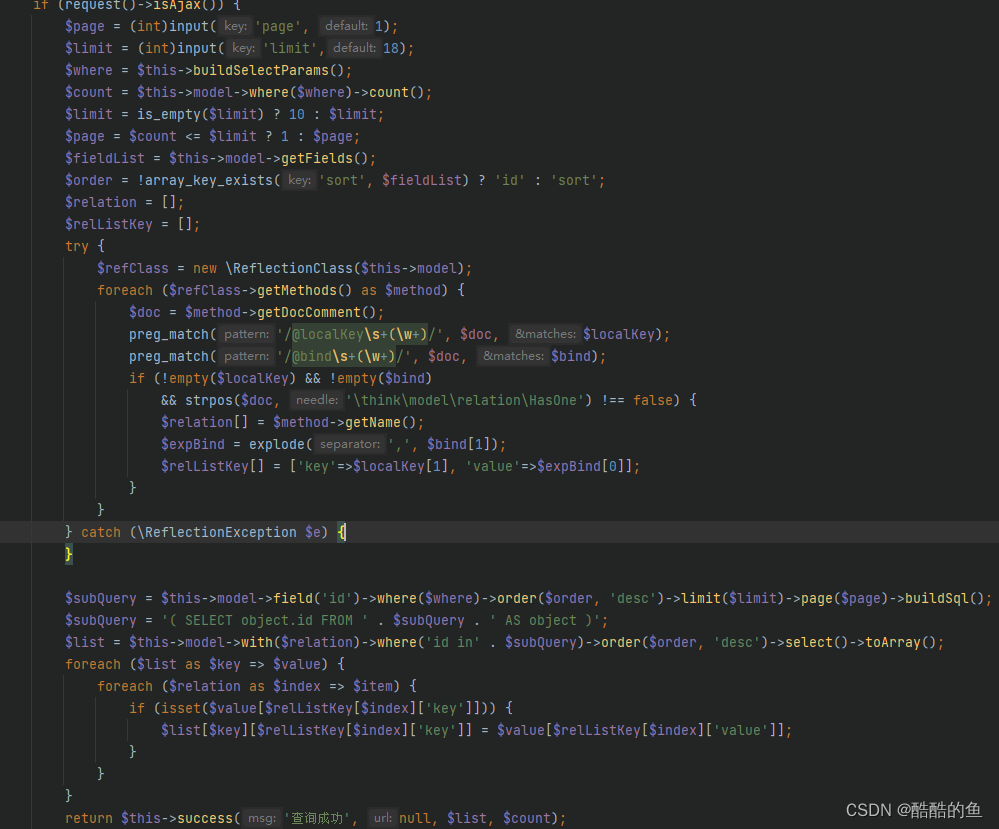
在实际应用中,为了合并多个select的执行结果,可以使用 union 和 union all 时,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要一致。
案例:查询 sid < 5 或者 age > 18 的同学。
其实直接用 or 就可以实现:
select * from student where sid<5 or age>18;
-- union: 该操作符用于取得两个结果集的并集。当使用该操作符时,会自动去掉结果集中的重复行。
select * from student where sid<5
union
select * from student where age>18;-- union all: 和 union 几乎一样。但当使用该操作符时,不会去掉结果集中的重复行。
select * from student where sid<5
union all
select * from student where age>18;
回到目录…
四、数据库控制语言(DCL)
庞大的数据库不可能由一个人来管理,我们需要更多的用户来一起管理整个数据库。可参考文章:MySQL之用户及权限操作
①创建用户
-- 用户名: test, 密码: 123456, 可访问主机: %任意主机
create user 'test'@'%' identified by '123456';
②授权
-- 给该用户赋予对所有库表的所有操作权限
grant all on *.* to 'test'@'%';-- 撤销所有权限
revoke all on *.* from 'test'@'%';-- 刷新系统权限表
flush privileges;
回到目录…
总结:
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
以上就是今天的学习内容,本文是MySQL的学习,我们学习整理了MySQL常用语句:基础的CURD操作和高阶的聚合查询和联表查询。之后的学习内容将持续更新!!!