目录
- 1 Unet网络介绍
- 1.1 Unet论文
- 1.2 简介
- 1.3 6大特点
- 2 Unet网络3种不同的实现方式
- 2.1 Unet网络的class实现(mIou)
- 2.2 Unet网络的layer的实现(mIou)
- 2.3 第3种实现方法(存在问题,验证集准确率一直不变)
- 2.4 实现一个遥感影像二分类
- 2.5 在2.1训练模型的基础上增加了训练过程的可视化
1 Unet网络介绍
1.1 Unet论文
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/90418337
1.2 简介

网络结构
分为下采样和上采样两大部分

(1)Encoder:左半部分,由两个3x3的卷积层(ReLU)+2x2的max polling层(stride=2)反复组成,每经过一次下采样,通道数翻倍;
(2)Decoder:右半部分,由一个2x2的上采样卷积层(ReLU)+Concatenation(crop[3]对应的Encoder层的输出feature map然后与Decoder层的上采样结果相加)+2个3x3的卷积层(ReLU)反复构成;
(3)最后一层通过一个1x1卷积将通道数变成期望的类别数。
1.3 6大特点

2 Unet网络3种不同的实现方式
实现Unet网络时,可以把网络分成6大部分
(1)两次卷积
(2)4次下采样卷积卷积
(3)1次上采样
(4)3次拼接卷积卷积上采样
(5)1次拼接卷积卷积
(6)1次卷积,输出通道数就是语义分割的类别数,有8类那么通道数就为8,背景也属于1类
2.1 Unet网络的class实现(mIou)
参考网易云课堂日月光华老师的语义分割教程,感谢!
两个文件代码:
一个是网络训练
一个是网络的应用
# 1 网络训练import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import glob
import matplotlib as mpl
import os
import time
# 使用cpu
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
# 下面这行代码是为了绘图时显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ["SimHei"]# 开始计时
time_start=time.time()######################################### 1 获取图像和图像预处理imgs = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\images\train\*\*.png")
print("训练图像数量:", len(imgs))
print(imgs[20:25])labels = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\gtFine分割图\train\*\*gtFine_labelIds.png")
print("训练标签数量:", len(labels))
print(labels[20:25])### 这里注意一定要让图片和标签一一对应,本例中通过验证是对应的,但是一般都需要安名称进行重新排序,这样确保一致
# 这里进行一个乱序,为了让图像训练时,不至于每个批次的图像属于同一类,
# 当然语义分割中不需要进行乱序,因为本身每张图像就包括各种类型,本例中是因为有17个城市拍的照片,所以还是进行了排序
index= np.random.permutation(len(imgs))
imgs = np.array(imgs)[index]
labels = np.array(labels)[index]imgs_val = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\images\val\*\*.png")
print("验证图像数量:", len(imgs_val))
print(imgs_val[20:25])labels_val = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\gtFine分割图\val\*\*gtFine_labelIds.png")
print("验证标签数量:", len(labels_val))
print(labels_val[20:25])dataset_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs, labels))
dataset_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs_val, labels_val))# 通过上面获取的只是图像的路径,还没有获取图像,所以要进行读取图像的操作
def read_png_img(path):"读取原始3通道的图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=3)return imgdef read_png_label(path):"读取单通道的语义分割图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=1)return imgimg_1 = read_png_img(imgs[0])
label_1 = read_png_label(labels[0])print("图像大小")############## 1.2 图像预处理
# 1 图像翻转
# 2 图像裁剪,先将img图像和label图像进行拼接,拼接成4通道影像,然后裁剪
concat_img = tf.concat([img_1, label_1], axis=-1)
print("拼接后图像的形状:", concat_img.shape)# 剪切图像
def crop_img(img, mask):concat_img = tf.concat([img, mask], axis=-1)concat_img = tf.image.resize(concat_img, (280,280), method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)crop_img1 = tf.image.random_crop(concat_img, [256,256,4])# 如果直接用[:,:,3]那最后一个维度就没了,就是二维的了# return crop_img1[:,:,:3], crop_img1[:,:,3]# print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)# (256, 256, 3) (256, 256)return crop_img1[:,:,:3], crop_img1[:,:,3:]# print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)# (256, 256, 3) (256, 256, 1)# 这样才能保留最后一个维度img_crop, label_crop = crop_img(img_1, label_1)
print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)"""
### 绘制图像
fig,axes=plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(10,8))# axes[0,0].imshow(img_crop) 这样写反而会报错,只有一行第一个维度就不能写
axes[0].imshow(img_crop)
axes[0].set_title("原图1")
axes[1].imshow(label_crop)
axes[1].set_title("标签图像1")
plt.show()
"""
# 归一化
def normal(img, mask):"这里的两个输入分别代表图像和标签图像"# 归一化到-1到1之间,如果除以255就归一化到了0-1之间img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32)/127.5-1mask = tf.cast(mask, tf.int32)return img, maskdef load_image_train(img_path, mask_path):"对图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)mask = read_png_label(mask_path)# 2 再进行裁剪img, mask = crop_img(img, mask)# 3 再进行随即反转if tf.random.uniform(())>0.5:img = tf.image.flip_left_right(img)mask = tf.image.flip_left_right(mask)# 4 再进行归一化img, mask = normal(img, mask)return img, maskdef load_image_test(img_path, mask_path):"对测试图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)mask = read_png_label(mask_path)img = tf.image.resize(img, (256, 256))mask = tf.image.resize(mask, (256, 256))# 2 再进行归一化img, mask = normal(img, mask)return img, mask# 让计算机根据cpu自动读取线程数
auto = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
dataset_train = dataset_train.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls = auto)
dataset_val = dataset_val.map(load_image_test, num_parallel_calls = auto)"""
for i, m in dataset_train.take(1):fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8))# axes[0,0].imshow(img_crop) 这样写反而会报错,只有一行第一个维度就不能写axes[0].imshow((i.numpy()+1)/2)axes[0].set_title("原图2")axes[1].imshow(np.squeeze(m.numpy()))axes[1].set_title("标签图像2")plt.show()
"""
############## 1.2 图像预处理结束BATCH_SIZE = 2 # 32
BUFFER_SIZE = 300
Step_per_epoch = len(imgs)//BATCH_SIZE
Val_step = len(imgs_val)//BATCH_SIZEdataset_train = dataset_train.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
dataset_val = dataset_val.batch(BATCH_SIZE)######################################### 1 图像预处理结束######################################### 2 前向传播
class Downsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行下采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Downsample,self).__init__()# 使用了same填充,原论文使用valid填充self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3,padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")# tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()和tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D()区别是什么?self.pool = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()def call(self, x, is_pool = True):if is_pool:x = self.pool(x)x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Upsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行上采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Upsample, self).__init__()self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.deconv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(units//2,kernel_size=3,strides=2,padding="same")def call(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.deconv(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Unet_model(tf.keras.Model):def __init__(self):"只进行初始化,定义层,还没有进行前向传播"super(Unet_model, self).__init__()# 这步只是进行卷积self.down1 = Downsample(64)# 4次下采样self.down2 = Downsample(128)self.down3 = Downsample(256)self.down4 = Downsample(512)self.down5 = Downsample(1024)# 4次上采样,定义一个上采样层# 第一个上采样只进行上采样,不进行卷积self.up1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(512, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same")# 上采样加卷积self.up2 = Upsample(512)self.up3 = Upsample(256)self.up4 = Upsample(128)# 进行两次卷积self.conv_last = Downsample(64)# 进行最后的1*1卷积分类,进行城市街景共34个类别的分类,所以输出层为34self.last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(34, kernel_size=1, padding="same")def call(self, x):"进行前向传播模型的构建"# 第一次先进行两次卷积x1 = self.down1(x, is_pool = False)# 进行4次下采样加两次卷积x2 = self.down2(x1)x3 = self.down3(x2)x4 = self.down4(x3)x5 = self.down5(x4)# 进行一次上采样x5 = self.up1(x5)# 进行合并,然后卷积卷积上采样x6 = tf.concat([x4, x5], axis=-1)x6 = self.up2(x6)x7 = tf.concat([x3, x6], axis=-1)x7 = self.up3(x7)x8 = tf.concat([x2, x7], axis=-1)x8 = self.up4(x8)# 合并,然后两层卷积x9 = tf.concat([x1, x8], axis=-1)x9 = self.conv_last(x9, is_pool = False)# 输出为34层,共34个类别out = self.last(x9)return outmodel = Unet_model()
######################################### 2 前向传播结束######################################### 3 反向传播
# 1 优化器
# 2 损失函数
# 3 评价指标class MeanIOU(tf.keras.metrics.MeanIoU):"重写MeanIIOU指标"def __call__(self, y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None):# 把34维的张量变成一维的分类y_pred = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)# 因为内置的求MIOU是需要在一维上求return super().__call__(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=sample_weight)optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0001)
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')
train_iou = MeanIOU(34, name='train_iou')test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
test_iou = MeanIOU(34, name='test_iou')######################################### 3 反向传播结束######################################### 4 模型训练
@tf.function
def train_step(images, labels):with tf.GradientTape() as tape:predictions = model(images)loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))train_loss(loss)train_accuracy(labels, predictions)train_iou(labels, predictions)@tf.function
def test_step(images, labels):predictions = model(images)t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)test_loss(t_loss)test_accuracy(labels, predictions)test_iou(labels, predictions)EPOCHS = 2# jishu用来查看下面的进度
jishu = 0for epoch in range(EPOCHS):# 在下一个epoch开始时,重置评估指标print("开始训练了:")train_loss.reset_states()train_accuracy.reset_states()train_iou.reset_states()test_loss.reset_states()test_accuracy.reset_states()test_iou.reset_states()for images, labels in dataset_train:jishu +=1print("第%d次"%jishu)## print(images.shape)## (2, 256, 256, 3)train_step(images, labels)for test_images, test_labels in dataset_val:test_step(test_images, test_labels)template = 'Epoch {:.3f}, Loss: {:.3f}, Accuracy: {:.3f}, \IOU: {:.3f}, Test Loss: {:.3f}, \Test Accuracy: {:.3f}, Test IOU: {:.3f}'print(template.format(epoch+1,train_loss.result(),train_accuracy.result()*100,train_iou.result(),test_loss.result(),test_accuracy.result()*100,test_iou.result()))######################################### 4 模型训练结束######################################### 5 模型保存"""
model.save('unet_v7.h5') 这种保存会出错,class定义的不能这样保存NotImplementedError: Saving the model to HDF5 format requires the model to be a Functional model or a Sequential model.
It does not work for subclassed models, because such models are defined via the body of a Python method,
which isn't safely serializable.
Consider saving to the Tensorflow SavedModel format (by setting save_format="tf") or using `save_weights`.
"""
"""
问题解决
# 创建模型
model = create_model()
# 保存权重
model.save_weights('model_weight')
# 创建新模型读取权重
newModel = create_model()
# 读取权重到新模型
newModel.load_weights('model_weight')
"""
model.save_weights('model_weight')# 时间截止
time_end=time.time()
print('totally cost',time_end-time_start)
# 2 实现模型的预测应用
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import glob
import matplotlib as mpl
# 下面这行代码是为了绘图时显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ["SimHei"]"""
下面2行代码是解决这个问题的Failed to get convolution algorithm. This is probably because cuDNN failed to initialize, so try looking to see if a warning log message was printed above.
[[node model_1/model/block1_conv1/Conv2D (defined at G:/XiaoMa/Bursxylophilus/310FCN/app.py:44) ]] [Op:__inference_predict_function_1613]
"""physical_device = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_device[0], True)def read_png_img(path):"读取原始3通道的图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=3)return img# 归一化
def normal(img):"这里的两个输入分别代表图像和标签图像"# 归一化到-1到1之间,如果除以255就归一化到了0-1之间img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32)/127.5-1return imgdef load_image_train(img_path):"对图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)# 2 进行resizeimg = tf.image.resize(img, (256, 256))# 3 再进行归一化img = normal(img)return imgclass Downsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行下采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Downsample,self).__init__()# 使用了same填充,原论文使用valid填充self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3,padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")# tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()和tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D()区别是什么?self.pool = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()def call(self, x, is_pool = True):if is_pool:x = self.pool(x)x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Upsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行上采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Upsample, self).__init__()self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.deconv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(units//2,kernel_size=3,strides=2,padding="same")def call(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.deconv(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Unet_model(tf.keras.Model):def __init__(self):"只进行初始化,定义层,还没有进行前向传播"super(Unet_model, self).__init__()# 这步只是进行卷积self.down1 = Downsample(64)# 4次下采样self.down2 = Downsample(128)self.down3 = Downsample(256)self.down4 = Downsample(512)self.down5 = Downsample(1024)# 4次上采样,定义一个上采样层# 第一个上采样只进行上采样,不进行卷积self.up1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(512, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same")# 上采样加卷积self.up2 = Upsample(512)self.up3 = Upsample(256)self.up4 = Upsample(128)# 进行两次卷积self.conv_last = Downsample(64)# 进行最后的1*1卷积分类,进行城市街景共34个类别的分类,所以输出层为34self.last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(34, kernel_size=1, padding="same")def call(self, x):"进行前向传播模型的构建"# 第一次先进行两次卷积x1 = self.down1(x, is_pool = False)# 进行4次下采样加两次卷积x2 = self.down2(x1)x3 = self.down3(x2)x4 = self.down4(x3)x5 = self.down5(x4)# 进行一次上采样x5 = self.up1(x5)# 进行合并,然后卷积卷积上采样x6 = tf.concat([x4, x5], axis=-1)x6 = self.up2(x6)x7 = tf.concat([x3, x6], axis=-1)x7 = self.up3(x7)x8 = tf.concat([x2, x7], axis=-1)x8 = self.up4(x8)# 合并,然后两层卷积x9 = tf.concat([x1, x8], axis=-1)x9 = self.conv_last(x9, is_pool = False)# 输出为34层,共34个类别out = self.last(x9)return outmodel = Unet_model()
model.load_weights('model_weight')while 1:### 1 获取图像和图像预处理input_images_path = input("请输入文件路径:")print('文件路径:',input_images_path)test_img = load_image_train(input_images_path)print("输入图像形状:",test_img.shape)# 给图像增加维度test_img = tf.expand_dims(test_img, 0)print("增加维度后的图像形状:",test_img.shape)### 2 预测pred_img = model.predict(test_img) # 预测print("输出图像形状:", pred_img.shape)# 输出图像形状: (1, 256, 256, 34)### 3 压缩图像维度并显示图像test_img = tf.squeeze(test_img)pred_img = tf.squeeze(pred_img)#### 4 将34个通道变成单通道pred_img = np.argmax(pred_img, axis=-1)print("经过压缩和取最大值后的图像形状变化:", pred_img.shape)plt.figure()plt.subplot(1,2,1)plt.imshow(test_img)plt.subplot(1,2,2)plt.imshow(pred_img)plt.show()# H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\images\train\bochum\bochum_000000_000885_leftImg8bit.png
2.2 Unet网络的layer的实现(mIou)
参考日月光华老师的课程的原始Unet方法,但是一直有问题,
Shapes of all inputs must match: values[0].shape = [65536] != values[1].shape = [2228224]
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import glob
import time
import matplotlib as mpl# 下面这行代码是为了绘图时显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ["SimHei"]"""
下面2行代码是解决这个问题的Failed to get convolution algorithm. This is probably because cuDNN failed to initialize, so try looking to see if a warning log message was printed above.
[[node model_1/model/block1_conv1/Conv2D (defined at G:/XiaoMa/Bursxylophilus/310FCN/app.py:44) ]] [Op:__inference_predict_function_1613]
"""
physical_device = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_device[0], True)# 开始计时
time_start=time.time()######################################### 1 获取图像和图像预处理
## 1.1 获取图像
imgs = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\images\train\*\*.png")
print("训练图像数量:", len(imgs))
print(imgs[20:25])labels = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\gtFine分割图\train\*\*gtFine_labelIds.png")
print("训练标签数量:", len(labels))
print(labels[20:25])imgs_val = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\images\val\*\*.png")
print("验证图像数量:", len(imgs_val))
print(imgs_val[20:25])labels_val = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集的一小部分\gtFine分割图\val\*\*gtFine_labelIds.png")
print("验证标签数量:", len(labels_val))
print(labels_val[20:25])## 1.2 安名称排序
### 这里注意一定要让图片和标签一一对应,本例中通过验证是对应的,但是一般都需要安名称进行重新排序,这样确保一致imgs.sort(key=lambda x:x.split('train/')[-1].split('_leftImg8bit.png')[0])
labels.sort(key=lambda x:x.split('train/')[-1].split('_gtFine_labelIds.png')[0])print("排序以后:")
print(imgs[20:25])
print(labels[20:25])## 1.3 乱序,注意必须要有一个统一的乱序规则,否则会导致图像和标签不是一一对应
# 这里进行一个乱序,为了让图像训练时,不至于每个批次的图像属于同一类,
# 当然语义分割中不需要进行乱序,因为本身每张图像就包括各种类型,本例中是因为有17个城市拍的照片,所以还是进行了排序np.random.seed(2019)
index = np.random.permutation(len(imgs))
images = np.array(imgs)[index]
anno = np.array(labels)[index]print("乱序以后:")
print(images[20:25])
print(anno[20:25])# 1.4 查看唯一值
img = tf.io.read_file(labels[36])
img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=1)
print(np.unique(img))# 1.5 组合成训练和验证数据集
dataset_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images, anno))
dataset_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs_val, labels_val))# 1.6 读取图像
def read_png(path):"读取图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=3)return imgdef read_png_label(path):"读取标签"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=1)return img# 1.7 归一化
def normalize(input_image, input_mask):"进行归一化为-1到1"input_image = tf.cast(input_image, tf.float32)/127.5 - 1input_mask = tf.cast(input_mask, tf.int32)return input_image, input_maskIMG_HEIGHT = 256
IMG_WIDTH = 256# 1.8 图像裁剪
def random_crop(img, mask):concat_img = tf.concat([img, mask], axis=-1)concat_img = tf.image.resize(concat_img, (280, 280),method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)crop_img = tf.image.random_crop(concat_img, [256, 256, 4])return crop_img[ :, :, :3], crop_img[ :, :, 3:]# 1.9 随机翻转
def load_image_train(input_image_path, input_mask_path):"对训练数据的处理"input_image = read_png(input_image_path)input_mask = read_png_label(input_mask_path)input_image, input_mask = random_crop(input_image, input_mask)# input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image, [256, 256])# input_mask = tf.image.resize(input_mask, [256, 256])if tf.random.uniform(()) > 0.5:input_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(input_image)input_mask = tf.image.flip_left_right(input_mask)input_image, input_mask = normalize(input_image, input_mask)return input_image, input_maskdef load_image_val(input_image_path, input_mask_path):"对验证数据的处理"input_image = read_png(input_image_path)input_mask = read_png_label(input_mask_path)input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image, (IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH))input_mask = tf.image.resize(input_mask, (IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH))input_image, input_mask = normalize(input_image, input_mask)return input_image, input_mask#BATCH_SIZE = 8 * tpu_strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
BATCH_SIZE = 1
BUFFER_SIZE = 300
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = len(imgs) // BATCH_SIZE
VALIDATION_STEPS = len(imgs_val) // BATCH_SIZE# 对每张图像都进行预处理
AUTO = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
dataset_train = dataset_train.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls=AUTO)
dataset_val = dataset_val.map(load_image_val, num_parallel_calls=AUTO)# 1.10 划分批次
dataset_train = dataset_train.cache().repeat().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE).prefetch(AUTO)
dataset_val = dataset_val.cache().batch(BATCH_SIZE)print("数据集:")
print(dataset_train)
print(dataset_val)######################################### 2 构建模型
# 下面这个变量没有用到,如果想用可以当作模型方法的参数输进去
# OUTPUT_CHANNELS = 34def create_model():"创建Unet模型"inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(256, 256, 3))x = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(inputs)x = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)x = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x)x = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x) # 256*256*64x1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(padding='same')(x) # 128*128*64x1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x1)x1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x1)x1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x1)x1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x1) # 128*128*128x2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(padding='same')(x1) # 64*64*128x2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x2)x2 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x2)x2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x2)x2 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x2) # 64*64*256x3 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(padding='same')(x2) # 32*32*256x3 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x3)x3 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x3)x3 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x3)x3 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x3) # 32*32*512x4 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(padding='same')(x3) # 16*16*512x4 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1024, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x4)x4 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x4)x4 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1024, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x4)x4 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x4) # 16*16*1024# 上采样部分x5 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(512, 2, strides=2,padding='same', activation='relu')(x4)x5 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x5) # 32*32*512x6 = tf.concat([x3, x5], axis=-1) # 32*32*1024x6 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x6)x6 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x6)x6 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x6)x6 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x6) # 32*32*512x7 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(256, 2, strides=2,padding='same', activation='relu')(x6)x7 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x7) # 64*64*256x8 = tf.concat([x2, x7], axis=-1) # 64*64*512x8 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x8)x8 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x8)x8 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x8)x8 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x8) # 64*64*256x9 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, 2, strides=2,padding='same', activation='relu')(x8)x9 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x9) # 128*128*128x10 = tf.concat([x1, x9], axis=-1) # 128*128*256x10 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x10)x10 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x10)x10 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x10)x10 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x10) # 128*128*128x11 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, 2, strides=2,padding='same', activation='relu')(x10)x11 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x11) # 256*256*64x12 = tf.concat([x, x11], axis=-1) # 256*256*128x12 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x12)x12 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x12)x12 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu')(x12)x12 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x12) # 256*256*64output = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(34, 1, padding='same', activation='softmax')(x12)# 256*256*34return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=output)model = create_model()
model.summary()######################################### 3 模型训练
class MeanIoU(tf.keras.metrics.MeanIoU):def __call__(self, y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None):y_pred = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)return super().__call__(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=sample_weight)model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001),loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),metrics=['acc', MeanIoU(num_classes=34)])EPOCHS = 60history = model.fit(dataset_train,epochs=EPOCHS,steps_per_epoch=STEPS_PER_EPOCH,validation_steps=VALIDATION_STEPS,validation_data=dataset_val)
# callbacks=[lr_callback],)####################################### 4 模型保存model.save('unet_v1.h5')# 加载模型
# Unet_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('001_model.h5')######### 模型的训练效果展示
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']epochs = range(EPOCHS)plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'r', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'bo', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss Value')
#plt.ylim([0, 1])
plt.legend()plt.savefig('./Accuracy_loss.jpg')
plt.show()num = 3for image, mask in dataset_val.take(1):pred_mask = model.predict(image)pred_mask = tf.argmax(pred_mask, axis=-1)pred_mask = pred_mask[..., tf.newaxis]plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))for i in range(num):plt.subplot(num, 3, i * num + 1)plt.imshow(tf.keras.preprocessing.image.array_to_img(image[i]))plt.subplot(num, 3, i * num + 2)plt.imshow(tf.keras.preprocessing.image.array_to_img(mask[i]))plt.subplot(num, 3, i * num + 3)plt.imshow(tf.keras.preprocessing.image.array_to_img(pred_mask[i]))for image, mask in dataset_train.take(1):pred_mask = model.predict(image)pred_mask = tf.argmax(pred_mask, axis=-1)pred_mask = pred_mask[..., tf.newaxis]plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))for i in range(num):plt.subplot(num, 3, i * num + 1)plt.imshow(tf.keras.preprocessing.image.array_to_img(image[i]))plt.subplot(num, 3, i * num + 2)plt.imshow(tf.keras.preprocessing.image.array_to_img(mask[i]))plt.subplot(num, 3, i * num + 3)plt.imshow(tf.keras.preprocessing.image.array_to_img(pred_mask[i]))
2.3 第3种实现方法(存在问题,验证集准确率一直不变)
本网络实现参考下面网址,特别感谢:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1v7411Z7b9/?spm_id_from=333.788.videocard.5
三个文件:
(1)预处理文件datapro
(2)模型训练文件
(3)模型应用文件
# (1)预处理文件dataproimport glob
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np"""
下面2行代码是解决这个问题的Failed to get convolution algorithm. This is probably because cuDNN failed to initialize, so try looking to see if a warning log message was printed above.
[[node model_1/model/block1_conv1/Conv2D (defined at G:/XiaoMa/Bursxylophilus/310FCN/app.py:44) ]] [Op:__inference_predict_function_1613]
"""
#physical_device = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
#tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_device[0], True)def read_jpg(path):"""读取并解码jpg图像"""img_de = tf.io.read_file(path)img_de = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img_de,channels=3)return img_dedef read_png(path):"""读取并解码png图像"""img_de_png = tf.io.read_file(path)img_de_png = tf.image.decode_png(img_de_png,channels=1)return img_de_pngdef normal_img(input_images,input_anno):"""数据归一化"""input_images = tf.cast(input_images,tf.float32)input_images = input_images/127.5-1input_anno = tf.cast(input_anno, tf.float32)input_anno = input_anno/255.0return input_images,input_annodef load_images(input_images_path,input_anno_path):"""加载图片并改变图像大小"""input_image = read_jpg(input_images_path)input_anno = read_png(input_anno_path)input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image,(256,256)) # 这个resize()的原理input_anno = tf.image.resize(input_anno,(256,256))return normal_img(input_image,input_anno)def get_data():"""获取训练集和验证集(测试集)"""# 获取所有图像路径# images = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\语义分割数据\images\*.jpg')images = glob.glob(r"H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集\images\train\*\*.png")len(images)# anno = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\语义分割数据\单波段处理后的png\*.png')anno = glob.glob(r'H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\语义分割课程资料\UNET语义分割\城市街景数据集\gtFine分割图\train\*\*gtFine_labelIds.png')print(anno[-5:])print(images[-5:])# 进行乱序,inages和anno必须保持一致np.random.seed(2019) # 随机数种子index = np.random.permutation(len(images)) # 随机数的索引,随机排列序列,https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44188264/article/details/93752505images = np.array(images)[index]anno = np.array(anno)[index]print(anno[-5:])print(images[-5:]) # 查看标签和影像是否是一一对应# 将读取的图片转换为数据集dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images, anno))test_count = int(len(images) * 0.2) # 一部分为测试集train_count = len(images) - test_count # 一部分为训练集print("测试和训练数据集数量:")print(test_count, train_count)data_train = dataset.skip(test_count) # 跳过多少个进行选取data_test = dataset.take(test_count) # 选取多少个# 对图像进行预处理data_train = data_train.map(load_images) # map()函数是,对所有数据用某个函数进行处理data_test = data_test.map(load_images)BATCH_SIZE = 8# repeat()函数就是对数据集进行重复,防止将数据读取完 https://blog.csdn.net/seuzhouchenglong/article/details/104047784# shuffle()函数就是将数据打乱data_train = data_train.repeat().shuffle(30).batch(BATCH_SIZE)data_test = data_test.batch(BATCH_SIZE)return data_train,data_test,train_count,test_count,BATCH_SIZE
# 2 模型训练文件
# 这个网络绝对有问题# 参考下面的网址实现
#https://blog.csdn.net/cst95295299/article/details/106181568?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-
#blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-4.control&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-4.controlimport os
#os.environ["CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER"] = "PCI_BUS_ID"
#os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
import datapro
import time
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1""""
下面2行代码是解决这个问题的Failed to get convolution algorithm. This is probably because cuDNN failed to initialize, so try looking to see if a warning log message was printed above.
[[node model_1/model/block1_conv1/Conv2D (defined at G:/XiaoMa/Bursxylophilus/310FCN/app.py:44) ]] [Op:__inference_predict_function_1613]
"""
#physical_device = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
#tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_device[0], True)time_start=time.time()def Unet(num_class,image_size):"""构建unet模型"""inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[image_size, image_size, 3])# 本来在unet网络中的padding应该不是same,应该是valid吧# 第一层下采样conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(inputs)conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv1)pool1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(conv1)conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(pool1)conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv2)pool2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(conv2)conv3 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(pool2)conv3 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv3)pool3 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(conv3)conv4 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(pool3)conv4 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv4)drop4 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(conv4)pool4 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(drop4)conv5 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1024, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(pool4)conv5 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1024, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv5)drop5 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(conv5)up6 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 2, activation='relu', padding='same')(tf.keras.layers.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2))(drop5))merge6 = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([drop4, up6], axis=3)conv6 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(merge6)conv6 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv6)up7 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 2, activation='relu', padding='same')(tf.keras.layers.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2))(conv6))merge7 = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([conv3, up7], axis=3)conv7 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(merge7)conv7 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(256, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv7)up8 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 2, activation='relu', padding='same')(tf.keras.layers.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2))(conv7))merge8 = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([conv2, up8], axis=3)conv8 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(merge8)conv8 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv8)up9 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 2, activation='relu', padding='same')(tf.keras.layers.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2))(conv8))merge9 = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([conv1, up9], axis=3)conv9 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(merge9)conv9 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')(conv9)# 通道数是numclassconv10 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(num_class, 1, activation='sigmoid')(conv9)# sigmoidmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=conv10)model.summary()return model# 获取训练集和验证集
data_train,data_test,train_count,test_count,BATCH_SIZE= datapro.get_data()#输入必须是16的倍数
# model = Unet(2,592)
model = Unet(34,256)# 模型编译,放到外面也可以
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-3),loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['acc']
)train_history = model.fit(data_train,epochs=500,steps_per_epoch=train_count // BATCH_SIZE,validation_data=data_test,validation_freq=1,
)# 时间截止
time_end=time.time()print('totally cost',time_end-time_start)# 保存模型结构和权重
model.save('001_model.h5')# 模型训练损失和准确率可视化# 得到参数
acc = train_history.history['acc']
val_acc = train_history.history['val_acc']
loss = train_history.history['loss']
val_loss = train_history.history['val_loss']# 画图,一行两列
plt.subplot(1,1,1) # 一行两列第一列
plt.plot(acc,label="Training Accuracy")
plt.plot(val_acc,label="Validation Accuracy")
plt.plot(loss,label="Training Loss")
plt.plot(val_loss,label="Validation Loss")
plt.title("Accuracy and Loss")
plt.legend()# 保存和显示
plt.savefig('./Accuracy_loss.jpg')
plt.show()
# 模型应用文件# 这个模块实现模型的加载和应用import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datapro"""
下面2行代码是解决这个问题的Failed to get convolution algorithm. This is probably because cuDNN failed to initialize, so try looking to see if a warning log message was printed above.
[[node model_1/model/block1_conv1/Conv2D (defined at G:/XiaoMa/Bursxylophilus/310FCN/app.py:44) ]] [Op:__inference_predict_function_1613]
"""physical_device = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_device[0], True)def read_jpg(path):"""读取并解码jpg图像"""img_de = tf.io.read_file(path)img_de = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img_de,channels=3)return img_dedef normal_img(input_images):"""数据归一化"""input_images = tf.cast(input_images,tf.float32)input_images = input_images/127.5-1return input_imagesdef load_images(input_images_path):"""加载并resize模型"""input_image = read_jpg(input_images_path)input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image,(224,224))return normal_img(input_image)while 1:input_images_path = input("请输入文件路径:")print('文件路径:',input_images_path)test_img = load_images(input_images_path)print("输入图像形状:",test_img.shape)# 给图像增加维度test_img = tf.expand_dims(test_img, 0)print("增加维度后的图像形状:",test_img.shape)# 加载模型FCN_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('001_model.h5')pred_img =FCN_model.predict(test_img) # 预测print("输出图像形状:",pred_img.shape)# 压缩图像维度并显示图像test_img = tf.squeeze(test_img)pred_img = tf.squeeze(pred_img)plt.figure()plt.subplot(1,2,1)plt.imshow(test_img)plt.subplot(1,2,2)plt.imshow(pred_img)plt.show()# G:\XiaoMa\Bursxylophilus\dataset\SemSegdataset\images\1_1zx53.jpg
# 1_40zx30.jpg# G:\XiaoMa\07AllDataset\004VOCdevkit\VOC2007\JPEGImages\000032.jpg# G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\语义分割数据\images\z1.jpg
# H:\05学习资料\14,软件开发\深度学习\日月光华2.0课程\00.配套资料(代码、讲义、数据)\数据集\数据集\图片定位与分割数据集\images\images\Abyssinian_1.jpg2.4 实现一个遥感影像二分类
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import glob
import matplotlib as mpl
import os
import time
# 使用cpu
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
# 下面这行代码是为了绘图时显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ["SimHei"]# 开始计时
time_start=time.time()######################################### 1 获取图像和图像预处理imgs = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\images\*.jpg')
print("训练图像数量:", len(imgs))
print(imgs[2:5])labels = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\单波段处理后的png\*.png')
print("训练标签数量:", len(labels))
print(labels[2:5])### 这里注意一定要让图片和标签一一对应,本例中通过验证是对应的,但是一般都需要安名称进行重新排序,这样确保一致
# 这里进行一个乱序,为了让图像训练时,不至于每个批次的图像属于同一类,
# 当然语义分割中不需要进行乱序,因为本身每张图像就包括各种类型,本例中是因为有17个城市拍的照片,所以还是进行了排序
index= np.random.permutation(len(imgs))
imgs = np.array(imgs)[index]
labels = np.array(labels)[index]imgs_val = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\val图片\*.jpg')
print("验证图像数量:", len(imgs_val))
print(imgs_val[2:5])labels_val = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\val分割\*.png')
print("验证标签数量:", len(labels_val))
print(labels_val[2:5])dataset_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs, labels))
dataset_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs_val, labels_val))# 通过上面获取的只是图像的路径,还没有获取图像,所以要进行读取图像的操作
def read_png_img(path):"读取原始3通道的图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img, channels=3)return imgdef read_png_label(path):"读取单通道的语义分割图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=1)return imgimg_1 = read_png_img(imgs[0])
label_1 = read_png_label(labels[0])print("图像大小")############## 1.2 图像预处理
# 1 图像翻转
# 2 图像裁剪,先将img图像和label图像进行拼接,拼接成4通道影像,然后裁剪
concat_img = tf.concat([img_1, label_1], axis=-1)
print("拼接后图像的形状:", concat_img.shape)# 剪切图像
def crop_img(img, mask):concat_img = tf.concat([img, mask], axis=-1)concat_img = tf.image.resize(concat_img, (280,280), method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)crop_img1 = tf.image.random_crop(concat_img, [256,256,4])# 如果直接用[:,:,3]那最后一个维度就没了,就是二维的了# return crop_img1[:,:,:3], crop_img1[:,:,3]# print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)# (256, 256, 3) (256, 256)return crop_img1[:,:,:3], crop_img1[:,:,3:]# print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)# (256, 256, 3) (256, 256, 1)# 这样才能保留最后一个维度img_crop, label_crop = crop_img(img_1, label_1)
print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)"""
### 绘制图像
fig,axes=plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(10,8))# axes[0,0].imshow(img_crop) 这样写反而会报错,只有一行第一个维度就不能写
axes[0].imshow(img_crop)
axes[0].set_title("原图1")
axes[1].imshow(label_crop)
axes[1].set_title("标签图像1")
plt.show()
"""
# 归一化
def normal(img, mask):"这里的两个输入分别代表图像和标签图像"# 归一化到-1到1之间,如果除以255就归一化到了0-1之间img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32)/127.5-1# 这里不除以会超出34或者2类的限制mask = mask/255mask = tf.cast(mask, tf.int32)return img, maskdef load_image_train(img_path, mask_path):"对图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)mask = read_png_label(mask_path)# 2 再进行裁剪img, mask = crop_img(img, mask)# 3 再进行随即反转if tf.random.uniform(())>0.5:img = tf.image.flip_left_right(img)mask = tf.image.flip_left_right(mask)# 4 再进行归一化img, mask = normal(img, mask)return img, maskdef load_image_test(img_path, mask_path):"对测试图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)mask = read_png_label(mask_path)img = tf.image.resize(img, (256, 256))mask = tf.image.resize(mask, (256, 256))# 2 再进行归一化img, mask = normal(img, mask)return img, mask# 让计算机根据cpu自动读取线程数
auto = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
dataset_train = dataset_train.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls = auto)
dataset_val = dataset_val.map(load_image_test, num_parallel_calls = auto)"""
for i, m in dataset_train.take(1):fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8))# axes[0,0].imshow(img_crop) 这样写反而会报错,只有一行第一个维度就不能写axes[0].imshow((i.numpy()+1)/2)axes[0].set_title("原图2")axes[1].imshow(np.squeeze(m.numpy()))axes[1].set_title("标签图像2")plt.show()
"""
############## 1.2 图像预处理结束BATCH_SIZE = 2 # 32
BUFFER_SIZE = 300
Step_per_epoch = len(imgs)//BATCH_SIZE
Val_step = len(imgs_val)//BATCH_SIZEdataset_train = dataset_train.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
dataset_val = dataset_val.batch(BATCH_SIZE)######################################### 1 图像预处理结束######################################### 2 前向传播
class Downsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行下采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Downsample,self).__init__()# 使用了same填充,原论文使用valid填充self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3,padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")# tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()和tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D()区别是什么?self.pool = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()def call(self, x, is_pool = True):if is_pool:x = self.pool(x)x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Upsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行上采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Upsample, self).__init__()self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.deconv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(units//2,kernel_size=3,strides=2,padding="same")def call(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.deconv(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Unet_model(tf.keras.Model):def __init__(self):"只进行初始化,定义层,还没有进行前向传播"super(Unet_model, self).__init__()# 这步只是进行卷积self.down1 = Downsample(64)# 4次下采样self.down2 = Downsample(128)self.down3 = Downsample(256)self.down4 = Downsample(512)self.down5 = Downsample(1024)# 4次上采样,定义一个上采样层# 第一个上采样只进行上采样,不进行卷积self.up1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(512, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same")# 上采样加卷积self.up2 = Upsample(512)self.up3 = Upsample(256)self.up4 = Upsample(128)# 进行两次卷积self.conv_last = Downsample(64)# 进行最后的1*1卷积分类,进行城市街景共34个类别的分类,所以输出层为34self.last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(2, kernel_size=1, padding="same")def call(self, x):"进行前向传播模型的构建"# 第一次先进行两次卷积x1 = self.down1(x, is_pool = False)# 进行4次下采样加两次卷积x2 = self.down2(x1)x3 = self.down3(x2)x4 = self.down4(x3)x5 = self.down5(x4)# 进行一次上采样x5 = self.up1(x5)# 进行合并,然后卷积卷积上采样x6 = tf.concat([x4, x5], axis=-1)x6 = self.up2(x6)x7 = tf.concat([x3, x6], axis=-1)x7 = self.up3(x7)x8 = tf.concat([x2, x7], axis=-1)x8 = self.up4(x8)# 合并,然后两层卷积x9 = tf.concat([x1, x8], axis=-1)x9 = self.conv_last(x9, is_pool = False)# 输出为34层,共34个类别out = self.last(x9)return outmodel = Unet_model()
######################################### 2 前向传播结束######################################### 3 反向传播
# 1 优化器
# 2 损失函数
# 3 评价指标class MeanIOU(tf.keras.metrics.MeanIoU):"重写MeanIIOU指标"def __call__(self, y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None):# 把34维的张量变成一维的分类y_pred = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)# 因为内置的求MIOU是需要在一维上求return super().__call__(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=sample_weight)optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0001)
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')
train_iou = MeanIOU(2, name='train_iou')test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
test_iou = MeanIOU(2, name='test_iou')######################################### 3 反向传播结束######################################### 4 模型训练
@tf.function
def train_step(images, labels):with tf.GradientTape() as tape:predictions = model(images)loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))train_loss(loss)train_accuracy(labels, predictions)train_iou(labels, predictions)@tf.function
def test_step(images, labels):predictions = model(images)t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)test_loss(t_loss)test_accuracy(labels, predictions)test_iou(labels, predictions)EPOCHS = 2000# jishu用来查看下面的进度
jishu = 0for epoch in range(EPOCHS):# 在下一个epoch开始时,重置评估指标print("开始训练了:")train_loss.reset_states()train_accuracy.reset_states()train_iou.reset_states()test_loss.reset_states()test_accuracy.reset_states()test_iou.reset_states()for images, labels in dataset_train:jishu +=1print("第%d次"%jishu)## print(images.shape)## (2, 256, 256, 3)train_step(images, labels)for test_images, test_labels in dataset_val:test_step(test_images, test_labels)template = 'Epoch {:.3f}, Loss: {:.3f}, Accuracy: {:.3f}, \IOU: {:.3f}, Test Loss: {:.3f}, \Test Accuracy: {:.3f}, Test IOU: {:.3f}'print(template.format(epoch+1,train_loss.result(),train_accuracy.result()*100,train_iou.result(),test_loss.result(),test_accuracy.result()*100,test_iou.result()))######################################### 4 模型训练结束######################################### 5 模型保存"""
model.save('unet_v7.h5') 这种保存会出错,class定义的不能这样保存NotImplementedError: Saving the model to HDF5 format requires the model to be a Functional model or a Sequential model.
It does not work for subclassed models, because such models are defined via the body of a Python method,
which isn't safely serializable.
Consider saving to the Tensorflow SavedModel format (by setting save_format="tf") or using `save_weights`.
"""
"""
问题解决
# 创建模型
model = create_model()
# 保存权重
model.save_weights('model_weight')
# 创建新模型读取权重
newModel = create_model()
# 读取权重到新模型
newModel.load_weights('model_weight')
"""
model.save_weights('./参数/model_weight')# 时间截止
time_end=time.time()
print('totally cost',time_end-time_start)
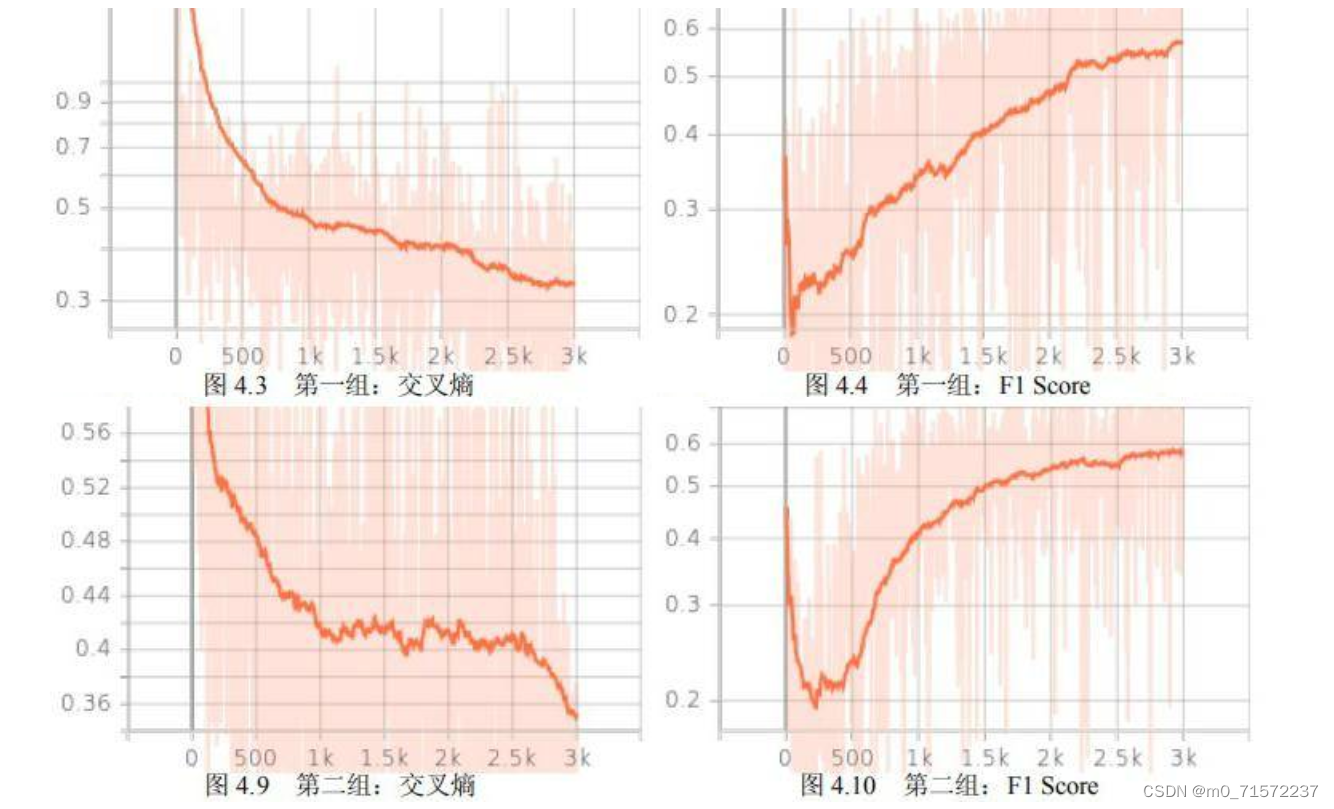
2.5 在2.1训练模型的基础上增加了训练过程的可视化
也就是增加了训练过程的记录,然后以折线图形式显示出来
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import glob
import matplotlib as mpl
import os
import time
# 使用cpu
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
# 下面这行代码是为了绘图时显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ["SimHei"]# 开始计时
time_start=time.time()######################################### 1 获取图像和图像预处理imgs = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\images\*.jpg')
print("训练图像数量:", len(imgs))
print(imgs[2:5])labels = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\单波段处理后的png\*.png')
print("训练标签数量:", len(labels))
print(labels[2:5])### 这里注意一定要让图片和标签一一对应,本例中通过验证是对应的,但是一般都需要安名称进行重新排序,这样确保一致
# 这里进行一个乱序,为了让图像训练时,不至于每个批次的图像属于同一类,
# 当然语义分割中不需要进行乱序,因为本身每张图像就包括各种类型,本例中是因为有17个城市拍的照片,所以还是进行了排序
index= np.random.permutation(len(imgs))
imgs = np.array(imgs)[index]
labels = np.array(labels)[index]imgs_val = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\val图片\*.jpg')
print("验证图像数量:", len(imgs_val))
print(imgs_val[2:5])labels_val = glob.glob(r'G:\XiaoMa\08OwnWork\zhongxian\unet\语义分割数据\val分割\*.png')
print("验证标签数量:", len(labels_val))
print(labels_val[2:5])dataset_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs, labels))
dataset_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((imgs_val, labels_val))# 通过上面获取的只是图像的路径,还没有获取图像,所以要进行读取图像的操作
def read_png_img(path):"读取原始3通道的图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img, channels=3)return imgdef read_png_label(path):"读取单通道的语义分割图像"img = tf.io.read_file(path)img = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=1)return imgimg_1 = read_png_img(imgs[0])
label_1 = read_png_label(labels[0])print("图像大小")############## 1.2 图像预处理
# 1 图像翻转
# 2 图像裁剪,先将img图像和label图像进行拼接,拼接成4通道影像,然后裁剪
concat_img = tf.concat([img_1, label_1], axis=-1)
print("拼接后图像的形状:", concat_img.shape)# 剪切图像
def crop_img(img, mask):concat_img = tf.concat([img, mask], axis=-1)concat_img = tf.image.resize(concat_img, (280,280), method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)crop_img1 = tf.image.random_crop(concat_img, [256,256,4])# 如果直接用[:,:,3]那最后一个维度就没了,就是二维的了# return crop_img1[:,:,:3], crop_img1[:,:,3]# print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)# (256, 256, 3) (256, 256)return crop_img1[:,:,:3], crop_img1[:,:,3:]# print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)# (256, 256, 3) (256, 256, 1)# 这样才能保留最后一个维度img_crop, label_crop = crop_img(img_1, label_1)
print(img_crop.shape, label_crop.shape)"""
### 绘制图像
fig,axes=plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(10,8))# axes[0,0].imshow(img_crop) 这样写反而会报错,只有一行第一个维度就不能写
axes[0].imshow(img_crop)
axes[0].set_title("原图1")
axes[1].imshow(label_crop)
axes[1].set_title("标签图像1")
plt.show()
"""
# 归一化
def normal(img, mask):"这里的两个输入分别代表图像和标签图像"# 归一化到-1到1之间,如果除以255就归一化到了0-1之间img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32)/127.5-1# 这里不除以会超出34或者2类的限制mask = mask/255mask = tf.cast(mask, tf.int32)return img, maskdef load_image_train(img_path, mask_path):"对图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)mask = read_png_label(mask_path)# 2 再进行裁剪img, mask = crop_img(img, mask)# 3 再进行随即反转if tf.random.uniform(())>0.5:img = tf.image.flip_left_right(img)mask = tf.image.flip_left_right(mask)# 4 再进行归一化img, mask = normal(img, mask)return img, maskdef load_image_test(img_path, mask_path):"对测试图像进行处理"# 1 先进行读取img = read_png_img(img_path)mask = read_png_label(mask_path)img = tf.image.resize(img, (256, 256))mask = tf.image.resize(mask, (256, 256))# 2 再进行归一化img, mask = normal(img, mask)return img, mask# 让计算机根据cpu自动读取线程数
auto = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
dataset_train = dataset_train.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls = auto)
dataset_val = dataset_val.map(load_image_test, num_parallel_calls = auto)"""
for i, m in dataset_train.take(1):fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8))# axes[0,0].imshow(img_crop) 这样写反而会报错,只有一行第一个维度就不能写axes[0].imshow((i.numpy()+1)/2)axes[0].set_title("原图2")axes[1].imshow(np.squeeze(m.numpy()))axes[1].set_title("标签图像2")plt.show()
"""
############## 1.2 图像预处理结束BATCH_SIZE = 16 # 32
BUFFER_SIZE = 300
Step_per_epoch = len(imgs)//BATCH_SIZE
Val_step = len(imgs_val)//BATCH_SIZEdataset_train = dataset_train.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
dataset_val = dataset_val.batch(BATCH_SIZE)######################################### 1 图像预处理结束######################################### 2 前向传播
class Downsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行下采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Downsample,self).__init__()# 使用了same填充,原论文使用valid填充self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3,padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")# tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()和tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D()区别是什么?self.pool = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D()def call(self, x, is_pool = True):if is_pool:x = self.pool(x)x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Upsample(tf.keras.layers.Layer):"先定义,再调用,进行上采样"def __init__(self, units):"units是卷积核的数量"super(Upsample, self).__init__()self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(units, kernel_size=3, padding="same")self.deconv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(units//2,kernel_size=3,strides=2,padding="same")def call(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)x = self.deconv(x)x = tf.nn.relu(x)return xclass Unet_model(tf.keras.Model):def __init__(self):"只进行初始化,定义层,还没有进行前向传播"super(Unet_model, self).__init__()# 这步只是进行卷积self.down1 = Downsample(64)# 4次下采样self.down2 = Downsample(128)self.down3 = Downsample(256)self.down4 = Downsample(512)self.down5 = Downsample(1024)# 4次上采样,定义一个上采样层# 第一个上采样只进行上采样,不进行卷积self.up1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(512, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same")# 上采样加卷积self.up2 = Upsample(512)self.up3 = Upsample(256)self.up4 = Upsample(128)# 进行两次卷积self.conv_last = Downsample(64)# 进行最后的1*1卷积分类,进行城市街景共34个类别的分类,所以输出层为34,,# 如果进行别的任务,是几类就写几,因为需要喝MeanIou一样,否则会报错self.last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(2, kernel_size=1, padding="same")def call(self, x):"进行前向传播模型的构建"# 第一次先进行两次卷积x1 = self.down1(x, is_pool = False)# 进行4次下采样加两次卷积x2 = self.down2(x1)x3 = self.down3(x2)x4 = self.down4(x3)x5 = self.down5(x4)# 进行一次上采样x5 = self.up1(x5)# 进行合并,然后卷积卷积上采样x6 = tf.concat([x4, x5], axis=-1)x6 = self.up2(x6)x7 = tf.concat([x3, x6], axis=-1)x7 = self.up3(x7)x8 = tf.concat([x2, x7], axis=-1)x8 = self.up4(x8)# 合并,然后两层卷积x9 = tf.concat([x1, x8], axis=-1)x9 = self.conv_last(x9, is_pool = False)# 输出为34层,共34个类别out = self.last(x9)return outmodel = Unet_model()
######################################### 2 前向传播结束######################################### 3 反向传播
# 1 优化器
# 2 损失函数
# 3 评价指标class MeanIOU(tf.keras.metrics.MeanIoU):"重写MeanIIOU指标"def __call__(self, y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None):# 把34维的张量变成一维的分类y_pred = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)# 因为内置的求MIOU是需要在一维上求return super().__call__(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=sample_weight)LEARNING_RATE = 0.0001optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE)
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')#################################### 这里是两类,MeanIOU(2, name='train_iou')为2
train_iou = MeanIOU(2, name='train_iou')test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
test_iou = MeanIOU(2, name='test_iou')######################################### 3 反向传播结束######################################### 4 模型训练
@tf.function
def train_step(images, labels):with tf.GradientTape() as tape:predictions = model(images)loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))train_loss(loss)train_accuracy(labels, predictions)train_iou(labels, predictions)@tf.function
def test_step(images, labels):predictions = model(images)t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)test_loss(t_loss)test_accuracy(labels, predictions)test_iou(labels, predictions)EPOCHS = 4# jishu用来查看下面的进度
jishu = 0history_train_loss = []
history_train_accuracy = []
history_train_iou = []
history_test_loss = []
history_test_accuracy = []
history_test_iou = []for epoch in range(EPOCHS):# 在下一个epoch开始时,重置评估指标print("开始训练了:")train_loss.reset_states()train_accuracy.reset_states()train_iou.reset_states()test_loss.reset_states()test_accuracy.reset_states()test_iou.reset_states()for images, labels in dataset_train:jishu +=1print("第%d次"%jishu)## print(images.shape)## (2, 256, 256, 3)train_step(images, labels)for test_images, test_labels in dataset_val:test_step(test_images, test_labels)template = 'Epoch {:.3f}, Loss: {:.3f}, Accuracy: {:.3f}, \IOU: {:.3f}, Valid Loss: {:.3f}, \Valid Accuracy: {:.3f}, Valid IOU: {:.3f}'print(template.format(epoch+1,train_loss.result(),train_accuracy.result()*100,train_iou.result(),test_loss.result(),test_accuracy.result()*100,test_iou.result()))history_train_loss.append(train_loss.result())history_train_accuracy.append(train_accuracy.result())history_train_iou.append(train_iou.result())history_test_loss.append(test_loss.result())history_test_accuracy.append(test_accuracy.result())history_test_iou.append(test_iou.result())######### 进行绘图和保存plt.subplot(1,1,1) # 一行两列第一列
plt.plot(history_train_accuracy,label="Training Accuracy")
plt.plot(history_test_accuracy,label="Validation Accuracy")
plt.plot(history_train_loss,label="Training Loss")
plt.plot(history_test_loss,label="Validation Loss")
plt.plot(history_train_iou,label="Training Iou")
plt.plot(history_test_iou,label="Validation Iou")plt.title("Accuracy Loss and Iou")
plt.legend()# 保存和显示
plt.savefig('./图片'+str(BATCH_SIZE)+'.jpg')
plt.show()####### 将列表清空
history_train_loss.clear()
history_train_accuracy.clear()
history_train_iou.clear()
history_test_loss.clear()
history_test_accuracy.clear()
history_test_iou.clear()######################################### 4 模型训练结束######################################### 5 模型保存"""
model.save('unet_v7.h5') 这种保存会出错,class定义的不能这样保存NotImplementedError: Saving the model to HDF5 format requires the model to be a Functional model or a Sequential model.
It does not work for subclassed models, because such models are defined via the body of a Python method,
which isn't safely serializable.
Consider saving to the Tensorflow SavedModel format (by setting save_format="tf") or using `save_weights`.
"""
"""
问题解决
# 创建模型
model = create_model()
# 保存权重
model.save_weights('model_weight')
# 创建新模型读取权重
newModel = create_model()
# 读取权重到新模型
newModel.load_weights('model_weight')
"""
model.save_weights('./参数/model_weightshishi')# 时间截止
time_end=time.time()
print('totally cost',time_end-time_start)