Comparable
Comparable可以认为是一个内比较器,实现了Comparable接口的类有一个特点,就是这些类是可以和自己比较的,至于具体和另一个实现了Comparable接口的类如何比较,则依赖compareTo方法的实现,compareTo方法也被称为自然比较方法。如果开发者add进入一个Collection的对象想要Collections的sort方法帮你自动进行排序的话,那么这个对象必须实现Comparable接口。compareTo方法的返回值是int,有三种情况:
1、比较者大于被比较者(也就是compareTo方法里面的对象),那么返回正整数
2、比较者等于被比较者,那么返回0
3、比较者小于被比较者,那么返回负整数
为什么需要实现Comparable接口
写个很简单的例子:
public class test {public static void main(String[] args){ArrayList list=new ArrayList();list.add("Java");list.add("rose");list.add("lucy");System.out.println(list);Collections.sort(list);System.out.println(list);}
}
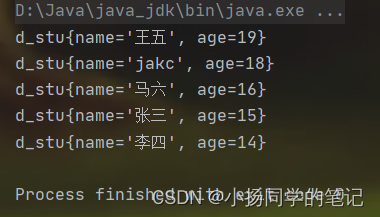
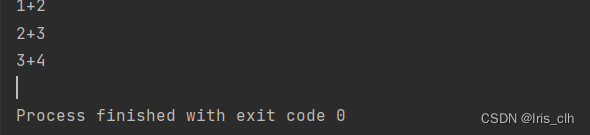
我们来排序输出一下结果
[Java, rose, lucy]
[Java, lucy, rose]
好像并没有什么问题。但是当List容器添加的元素对象是属于自己写的类时, 就可能出问题了.
例子:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;class Student{private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;} public String toString(){return this.name + ":" + this.age;}
}public class CompareT{public static void add(){ArrayList list = new ArrayList();list.add(new Student("Jack",10));list.add(new Student("rose",11));list.add(new Student("lucy",27));System.out.println(list);}
上面定义了1个Student类, 它只有两个成员, 名字和年龄.
在add()方法内, 添加3个Student的对象到1个list容器中, 然后输出(必须重写String方法, 这里不解释了):
执行结果:
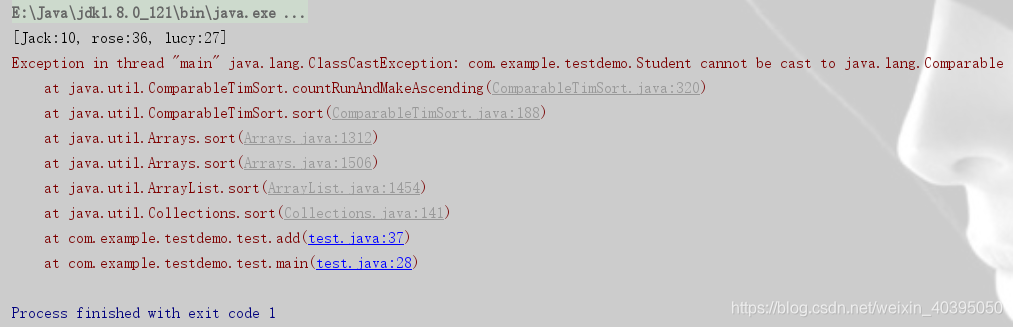
报错了 ClassCastException异常
提示这个类Student没有实现Comparable接口.
原因也很简单, 因为Java不知道应该怎样为Student对象排序, 是应该按名字排序? 还是按age来排序?
为什么本文第1个例子就排序成功? 是因为Java本身提供的类Integer已经实现了Comparable接口. 也表明Integer这个类的对象是可以比较的.
而Student类的对象默认是不可以比较的. 除非它实现了Comparable接口.
总而言之, 如果你想1个类的对象支持比较(排序), 就需要实现Comparable接口.
Comparable接口简介
Comparable 接口内部只有1个要重写的关键的方法.
就是
int compareTo(T o)
这个方法返回1个Int数值,
例如 i = x.compareTo(y)
如果i=0, 也表明对象x与y排位上是相等的(并非意味x.equals(y) = true, 但是jdk api上强烈建议这样处理)
如果返回数值i>0 则意味者, x > y啦,
反之若i<0则 意味x < y
什么是compareTo函数
compareTo() 方法用于将对象与方法的参数进行比较。
public interface Comparable<T> {/*** Compares this object with the specified object for order. Returns a* negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as this object is less* than, equal to, or greater than the specified object.** <p>The implementor must ensure <tt>sgn(x.compareTo(y)) ==* -sgn(y.compareTo(x))</tt> for all <tt>x</tt> and <tt>y</tt>. (This* implies that <tt>x.compareTo(y)</tt> must throw an exception iff* <tt>y.compareTo(x)</tt> throws an exception.)** <p>The implementor must also ensure that the relation is transitive:* <tt>(x.compareTo(y)>0 && y.compareTo(z)>0)</tt> implies* <tt>x.compareTo(z)>0</tt>.** <p>Finally, the implementor must ensure that <tt>x.compareTo(y)==0</tt>* implies that <tt>sgn(x.compareTo(z)) == sgn(y.compareTo(z))</tt>, for* all <tt>z</tt>.** <p>It is strongly recommended, but <i>not</i> strictly required that* <tt>(x.compareTo(y)==0) == (x.equals(y))</tt>. Generally speaking, any* class that implements the <tt>Comparable</tt> interface and violates* this condition should clearly indicate this fact. The recommended* language is "Note: this class has a natural ordering that is* inconsistent with equals."** <p>In the foregoing description, the notation* <tt>sgn(</tt><i>expression</i><tt>)</tt> designates the mathematical* <i>signum</i> function, which is defined to return one of <tt>-1</tt>,* <tt>0</tt>, or <tt>1</tt> according to whether the value of* <i>expression</i> is negative, zero or positive.** @param o the object to be compared.* @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as this object* is less than, equal to, or greater than the specified object.** @throws NullPointerException if the specified object is null* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object's type prevents it* from being compared to this object.*/public int compareTo(T o);
官方给出的解释是
-
将此对象与指定的order对象进行比较。返回一个负整数,零,或正整数,因为这个对象比较小于、等于或大于指定的对象。
-
实现者必须确保所有和x和y的比较如果出现异常必须确保抛出一个异常
-
最后,实现者必须确保 x.compareTo(y)==0,(x.compareTo(y)>0 && y.compareTo(z)>0)相当于x.compareTo(z)>0
-
强烈建议(x.compareTo(y)==0) == (x.equals(y)),但不是严格要求必须这么写,任何实现comparable接口并违反此条件的类都应该清楚地指出这一事实。该类的自然顺序与equals不一致
参数
- @param o要比较的对象。
- @return 一个负整数、零或正整数作为该对象小于、等于或大于指定的对象。
- @throws NullPointerException 指定对象为空抛出NullPointerException 异常
- @throws ClassCastException 如果指定对象的类型组织将其与此对象进行比较,抛出ClassCastException异常
位置
package java.lang;import java.util.*;
位于lang包下
是Compareable下的一个方法,参数是一个泛型
实现
compareTo具体实现在Number类和String类中
Number类中的实现–https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/number_compareto.htm
String类中的实现–https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_string_compareto.htm
Number类中的实现
1.描述
该方法将调用方法的Number对象与参数进行比较。可以比较Byte,Long,Integer等。
但是,无法比较两种不同的类型,参数和调用方法的Number对象应该是相同的类型。
2.语法
public int compareTo( NumberSubClass referenceName )
3.参数
这是参数的细节 -
- referenceName-可以是Byte,Double,Integer,Float,Long或Short。
4.返回值
- 如果Integer等于参数,则返回0。
- 如果Integer小于参数,则返回-1。
- 如果Integer大于参数,则返回1。
5.例子
public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) {Integer x = 5;System.out.println(x.compareTo(3));System.out.println(x.compareTo(5));System.out.println(x.compareTo(8)); }
}
6.结果
1
0
-1
String类中的实现
官方的文档可以看到compareTo()在String类中有两种实现
1.第一种传入的参数可以是一个Object的对象
注意:compareTo()的接口传入的是一个泛型而不是一个Object对象这里注意一下
2.第二种传入的参数可以是一个任意的字符串

传入对象的情况
1.描述
此方法将String与另一个Object进行比较。
2.语法
一下是此方法的语法
int compareTo(Object o)
3.参数
- O —要比较的对象
4.返回值
如果参数是一个按字典顺序排列等于该字符串的字符串,则值为0; 如果参数是按字典顺序大于此字符串的字符串,则小于0的值; 如果参数是按字典顺序小于此字符串的字符串,则值大于0。
5.例子
public class Test {public static void main(String args[]) {String str1 = "Strings are immutable";String str2 = new String("Strings are immutable");String str3 = new String("Integers are not immutable");int result = str1.compareTo( str2 );System.out.println(result);result = str2.compareTo( str3 );System.out.println(result);}
}
6.结果
0
10
传入字符串的情况
1.描述
此方法按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
2.语法
int compareTo(String anotherString)
3.参数
- anotherString - 要比较的String。
4.返回值
如果参数是一个按字典顺序排列等于该字符串的字符串,则值为0; 如果参数是按字典顺序大于此字符串的字符串,则小于0的值; 如果参数是按字典顺序小于此字符串的字符串,则值大于0。
5.例子
public class Test {public static void main(String args[]) {String str1 = "Strings are immutable";String str2 = "Strings are immutable";String str3 = "Integers are not immutable";int result = str1.compareTo( str2 );System.out.println(result);result = str2.compareTo( str3 );System.out.println(result);result = str3.compareTo( str1 );System.out.println(result);}
}
6.结果
0
10
-10
下一篇继续介绍Comparator 外部比较器
--作者:额滴神