一、DBSCAN算法
简介
DBSCAN(Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise)是一个基于密度的聚类算法。算法把簇看作数据空间中由低密度区域分割开的高密度对象区域;将足够高密度的区域划为簇,可以在有噪音的数据集中发现任意形状的聚类。
基本概念
在DBSCAN 算法中有两个重要的参数:Eps 和 MinPtS。Eps 是定义密度时的邻域半径,MinPts 为定义核心点时的阈值。
基于中心定义密度的方法可将点分为三类:
(1)核心点:给定用户指定阈值MinPts,如果一个点的给定邻域内的点的数目超过给定阈值MinPts, 那么该点称为核心点。
(2)边界点:边界点不是核心点,但它落在某个核心点的Eps邻域内。
(3)噪声点:噪声点既不是核心点,也不是边界点。
基于密度的簇定义如下:
(1)密度直达:给定一个对象集合D,如果p是在q的邻域内,且q是一个核心对象,则称p从对象q出发是直接密度直达的。
(2)密度可达:如果存在一个对象链 , 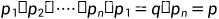 ,对于
,对于
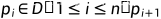 是从
是从 关于Eps和MinPts直接密度可达的,则对象p是从对象q关于Eps和MinPts密度可达的。
关于Eps和MinPts直接密度可达的,则对象p是从对象q关于Eps和MinPts密度可达的。
(3)密度连接:如果对象集D中存在一个对象o,使得对象p和q是从o关于Eps和MinPts密度可达的,那么对象p和q是关于Eps和MinPts密度连接的。
(4)密度可达是密度直达的传递闭包,这种关系非对称的,只有核心对象之间是相互密度直达的。
算法过程

通俗的来讲,算法流程如下:
(1)将所有数据对象标记为核心对象、边界对象或噪声对象。
(2)删除噪声对象。
(3)为距离在Eps之内的所有核心对象之间赋予一条边。
(4)每组联通的核心对象形成一个簇。
(5)将每个边界对象指派到一个与之关联的核心对象的簇中。
二、DBSCAN算法举例
案例说明和数据
给定一组二维数据(x,y)作为点,可以自己定义也可以利用下面的数据,将数据存入文本文档中,放入相应目录下即可。Eps设为2,MinPts为3。使用DBSCAN算法进行分类操作。
0,0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
12,1
12,2
12,3
12,4
12,5
12,6
0,6
0,7
12,7
0,8
0,9
1,1
6,8
8,7
6,7
3,5
代码
//定义点类
public class Point {private int x;private int y;private boolean isKey;private boolean isClassed;public boolean isKey() {return isKey;}public void setKey(boolean isKey) {this.isKey = isKey;this.isClassed = true;}public boolean isClassed() {return isClassed;}public void setClassed(boolean isClassed) {this.isClassed = isClassed;}public int getX() {return x;}public void setX(int x) {this.x = x;}public int getY() {return y;}public void setY(int y) {this.y = y;}public Point() {x = 0;y = 0;}public Point(int x, int y) {this.x = x;this.y = y;}public Point(String str) {String[] p = str.split(",");this.x = Integer.parseInt(p[0]);this.y = Integer.parseInt(p[1]);}public String print() {return "(" + this.x + "," + this.y + ")";}
}//对点进行操作
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class Utility {/*** 测试两个点之间的距离* @param p 点* @param q 点* @return 返回两个点之间的距离*/public static double getDistance(Point p,Point q){int dx=p.getX()-q.getX();int dy=p.getY()-q.getY();double distance=Math.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);return distance;}/*** 检查给定点是不是核心点* @param lst 存放点的链表* @param p 待测试的点* @param e e半径* @param minp 密度阈值* @return*/public static List<Point> isKeyPoint(List<Point> lst,Point p,int e,int minp){int count=0;List<Point> tmpLst=new ArrayList<Point>();for (Point q : lst) {if (getDistance(p, q) <= e) {++count;if (!tmpLst.contains(q)) {tmpLst.add(q);}}}if(count>=minp){p.setKey(true);return tmpLst;}return null;}/*** 设置已经分类点的标志* @param lst*/public static void setListClassed(List<Point> lst){for (Point p : lst) {if (!p.isClassed()) {p.setClassed(true);}}}/*** 如果b中含有a中包含的元素,则把两个集合合并* @param a* @param b* @return a*/public static boolean mergeList(List<Point> a,List<Point> b){boolean merge=false;for (Point value : b) {if (a.contains(value)) {merge = true;break;}}if(merge){for (Point point : b) {if (!a.contains(point)) {a.add(point);}}}return merge;}/*** 读取数据* @return 返回文本中点的集合*/public static List<Point> getPointsList() throws IOException{List<Point> lst=new ArrayList<Point>();//String txtPath="D:"+File.separatorChar+"Points.txt";String txtPath="E:\\myfile\\Points.txt";BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(txtPath));String str="";while((str = br.readLine()) != null && !str.equals("")){lst.add(new Point(str));}br.close();return lst;}
}//主要算法import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class DBScan {private static List<Point> pointsList = new ArrayList<Point>();// 初始点列表private static List<List<Point>> resultList = new ArrayList<List<Point>>();// 分类结果集private static int e = 2;// e半径//private static int e = 2;// e半径private static int minp = 3;// 密度阈值//private static int minp = 4;// 密度阈值/*** 打印结果**/private static void display() {int index = 1;for (List<Point> lst : resultList) {if (lst.isEmpty()) {continue;}System.out.println("*****第" + index + "个分类*****");for (Point p : lst) {System.out.print(p.print());}System.out.print("\n");index++;}}/*** 调用算法*/private static void applyDbscan() {try {pointsList = Utility.getPointsList();for (Point p : pointsList) {if (!p.isClassed()) {List<Point> tmpLst = new ArrayList<Point>();if ((tmpLst = Utility.isKeyPoint(pointsList, p, e, minp)) != null) {// 为所有聚类完毕的点做标示Utility.setListClassed(tmpLst);resultList.add(tmpLst);}}}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 合并结果集* @return*/private static List<List<Point>> getResult() {applyDbscan();// 找到所有直达的聚类int length = resultList.size();for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {for (int j = i + 1; j < length; ++j) {if (Utility.mergeList(resultList.get(i), resultList.get(j))) {resultList.get(j).clear();}}}return resultList;}/*** 程序主函数* @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) {getResult();display();}
}3.运行结果

三、总结
DBSCAN算法可以对任意形状的稠密数据集进行聚类,相对于K-Means、Mean Shift之类的聚类算法一般只适用于凸数据集。除此之外该算法在聚类的同时发现异常点,对数据集中的异常点不敏感。
DBSCAN算法也存着缺点,如果样本集的密度不均匀、聚类间距差相差很大时,聚类质量比较差;样本集较大时,聚类收敛时间较长;以及对Eps和MinPts的联合调参是比较困难的。
在日常生活中,我们可以根据数据的类型进行合理选择该算法进行聚类分类。
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42735631/article/details/120983729
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/139926467




![c++ char[]与int之间的类型转换](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0e7a8b1a276e484f8c49405e478d3f70.png#pic_center)